首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
1.Java SDK源码分析系列笔记-Integer
2025-06-28 12:30:02基础资料围观2002次
本篇文章分享1.Java SDK源码分析系列笔记-Integer,对你有帮助的话记得收藏一下,看Java资料网收获更多编程知识
目录
1. 使用
public class IntegerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Integer val = new Integer(1);
Integer val2 = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(val == val2);//false
Integer val3 = 1;
Integer val4 = 1;
System.out.println(val3 == val4);//true
Integer val5 = Integer.valueOf(1);
Integer val6 = Integer.valueOf(1);
System.out.println(val5 == val6);//true
System.out.println(val3 == val5);//true
}
}
2. 原理分析
2.1. 构造方法
//final表示Integer不能被继承。Comparable表示可以比较
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>
private final int value;//底层使用int类型,且使用final
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;//普通的对属性赋值
}
}
Integer是不可变的,所谓的不可变是指:
- 类使用final修饰
- 内部属性value使用final修饰
- 没有对外提供修改内部属性value的方法
2.2. valueOf方法
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
}
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
//-128-127直接返回缓存中的数字
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
//计算数组下标
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
//否则创建对象
return new Integer(i);
}
2.2.1. 范围正在-128-127的从缓存中取
- IntegerCache类
private static class IntegerCache {
//缓存的最小数字-128
static final int low = -128;
//缓存的最大数字需要计算
static final int high;
//最常用的数字缓存在Integer数组中
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
//最大数字默认127
int h = 127;
//从环境变量中读取java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
//取两者中的最大者作为最大数字
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
//创建缓存数组
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
//把low-high之间的数字全部放入缓存数组中
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
2.2.2. 解释Integer.valueOf(1)==Integer.valueOf(1)
如下面使用所输出的:
Integer val5 = Integer.valueOf(1);
Integer val6 = Integer.valueOf(1);
System.out.println(val5 == val6);//true
Integer.valueOf(1) == Integer.valueOf(1)是true,原因很简单,因为加载Integer类的时候会把-128-127丢进IntegerCache中缓存,当调用Integer.valueOf的实现中会判断-128-127的时候会从这个缓存中取,没有在创建。
因此Integer.valueOf(1)返回的是同一个对象
2.2.3. 解释(Integer val1 = 1) == (Integer val2 = 1)
如下面的这段代码:
Integer val3 = 1;
Integer val4 = 1;
System.out.println(val3 == val4);//true
使用Idea运行后,使用Show ByteCode插件查看字节码
结果如下:
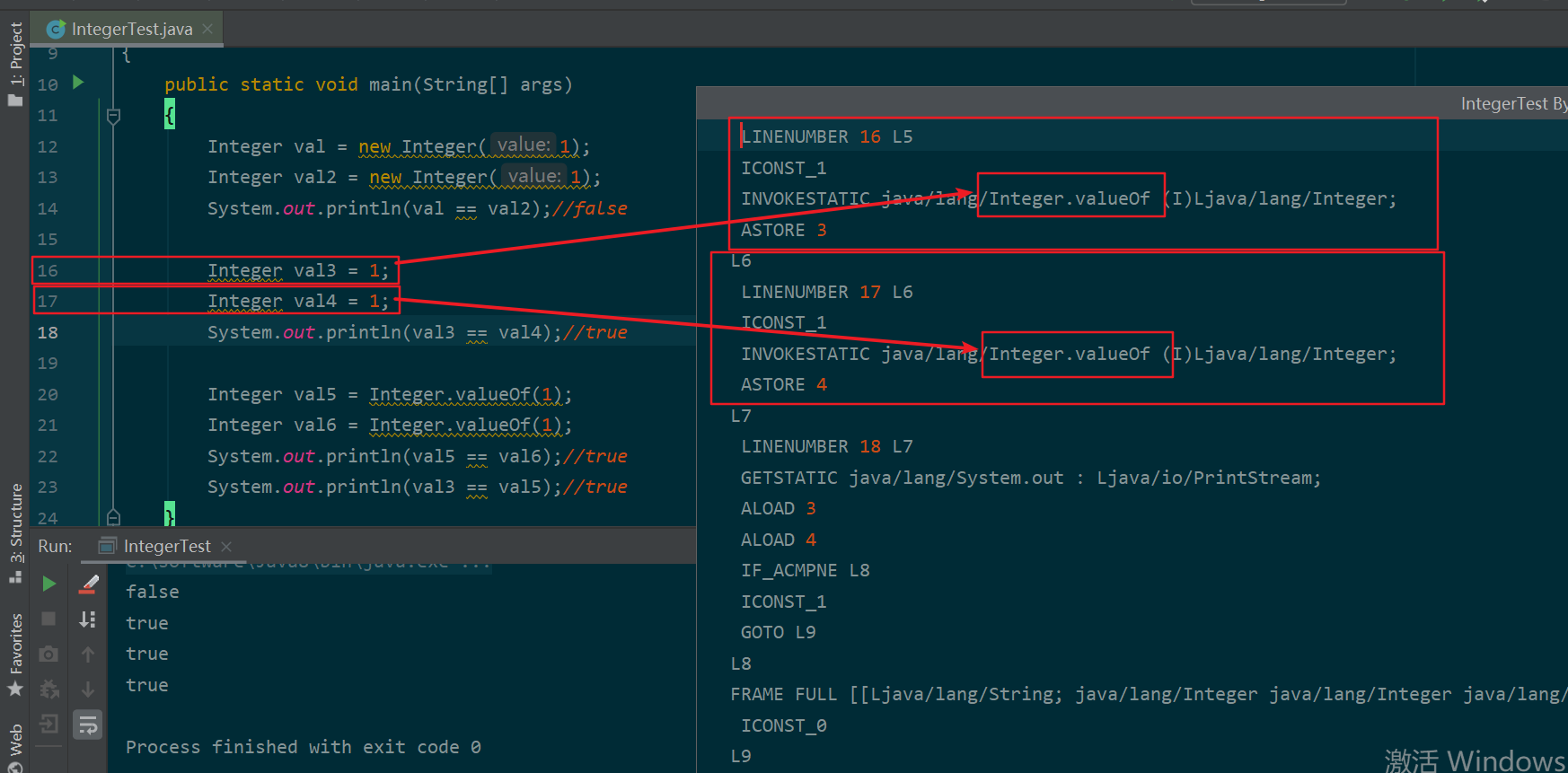
可以看出字节码调用的仍然是Integer.valueOf方法
2.2.4. 解释(Integer val1 = 128) != (Integer val2 = 128)
如下面的这段代码:
Integer val3 = 128;
Integer val4 = 128;
System.out.println(val3 == val4);//false
IntegerCache只缓存了-128-127的Integer,这里的val3和val4虽然都是128,但是他们是不同的对象,所以引用不等。
文章来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/ThinkerQAQ/p/18953465
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:

