首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
设计模式篇(Java):单例模式
2023-07-24 09:55:05基础资料围观689次
四、单例模式
所谓类的单例设计模式,就是采取一定的方法保证在整个的软件系统中,对某个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法(静态方法)。
4.1 饿汉式
- 构造器私有化 (防止 new )
- 类的内部创建对象
- 向外暴露一个静态的公共方法。getInstance
- 代码实现
静态变量
class Singleton_01 {
// 私有化构造器
private Singleton_01() {
}
// 类内部构建对象
private final static Singleton_01 instance = new Singleton_01();
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton_01 getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
- 优点:在类装载的时候就完成实例化。避免了线程同步问题
- 缺点:在类装载的时候就完成实例化,没有达到Lazy Loading的效果。如果从始至终从未使用过这个实例,则会造成内存的浪费
这种单例模式不可用,可能造成内存浪费
静态代码块
class Singleton_02 {
private static Singleton_02 instance;
static {
instance = new Singleton_02();
}
private Singleton_02() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton_02 getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
这种单例模式优缺点和静态变量的一样。也是在类加载的时候进行实例化,可能会造成内存浪费的问题,也没有达到懒加载的效果。
4.2 懒汉式
线程不安全
// 线程不安全,只能单线程
class Singleton02_01 {
private static Singleton02_01 instance;
private Singleton02_01() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton02_01 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton02_01();
}
return instance;
}
}
- 起到了Lazy Loading的效果,但是只能在单线程下使用。
- 如果有多个线程进入到if中,就会产生多个示例。
- 不推荐使用
同步方法线程安全
// 同步方法线程安全
class Singleton02_02 {
private static Singleton02_02 instance;
private Singleton02_02() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static synchronized Singleton02_02 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton02_02();
}
return instance;
}
}
- 解决了线程安全的问题
- 效率低,每个线程在想获得类的实例时候,执行getInstance()方法都要进行同步。而其实这个方法只执行一次实例化代码就够了,后面的想获得该类实例, 直接return就行了。方法进行同步效率太低。
同步代码块线程安全
// 同步代码块线程安全
class Singleton02_03 {
private static Singleton02_03 instance;
private Singleton02_03() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton02_03 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton02.class) {
instance = new Singleton02_03();
}
}
return instance;
}
}
- 此方法的单例看上去虽然是对同步方法线程安全的改进,但是改完之后多线程下就有可能破坏单例。
- 如果两个线程同时进入到if内被阻塞住,那么最后会有两个或者多个实例。
双重检测
// 双重检测
class Singleton02_04 {
private static Singleton02_04 instance;
private Singleton02_04() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton02_04 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton02.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton02_04();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
- 解决了效率低、线程安全等问题
- 也达到了懒加载的效果
- 推荐使用
其实双重检测也不是绝对安全的,因为instance = new Singleton02_04()不是一个原子性操作。
分析:instance = new Singleton02_04()不是一个原子性操作
instance = new Singleton02_04()的执行步骤
1、分配内存空间
2、执行构造方法,初始化对象
3、把这个对象指向这个空间
可能由于指令重排 把执行顺序变成 1-3-2
造成的结果:线程A还没有初始化对象,线程B获取对象是instance !=null就返回对象,此时instance 还没有完成构造
最终的DCL单例模式
// 双重检测
class Singleton02_04 {
// + volatile 防止指令重排
private volatile static Singleton02_04 instance;
private Singleton02_04() {
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton02_04 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton02.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton02_04();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
看后面的4.5能发现DCL也不是绝对安全的
4.3 静态内部类
/**
* 静态内部类
* @author cVzhanshi
* @create 2023-03-27 10:24
*/
public class Singleton03 {
// 私有化构造器
private Singleton03() {
}
private static class SingletonInstance {
private static final Singleton03 INSTANCE = new Singleton03();
}
// 向外暴露一个对外的静态方法获取到示例
public static Singleton03 getInstance() {
return SingletonInstance.INSTANCE;
}
}
- 这种方式采用了类装载的机制来保证初始化实例时只有一个线程。
- 静态内部类方式在Singleton类被装载时并不会立即实例化,而是在需要实例化时,调用getInstance方法,才会装载SingletonInstance类,从而完成Singleton的实例化。
- 类的静态属性只会在第一次加载类的时候初始化,所以在这里,JVM帮助我们保证了线程的安全性,在类进行初始化时,别的线程是无法进入的。
- 避免了线程不安全,利用静态内部类特点实现延迟加载,效率高
- 推荐使用
4.4 枚举
enum Singleton04_01 {
INSTANCE;
public void isOk() {
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
- 能避免多线程同步问题,而且还能防止反序列化(反射)重新创建新的对象。
- 推荐使用。
4.5 反射让单例不安全
单例不安全(因为反射)
-
情况1:第一个对象通过类去得到,第二个对象通过反射通过构造器造对象,破坏单例
- 代码示例:
public class LazyMan { // 私有化构造器 private LazyMan(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok"); } // + volatile 防止指令重排 private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan; // 双重检测锁模式的懒汉式单例 --> DCL懒汉式 public static LazyMan getInstance(){ if(lazyMan == null){ synchronized (LazyMan.class){ if(lazyMan == null){ lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是一个原子性操作 } } } return lazyMan; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { // 单线程下绝对正确且安全,但是在多线程下不安全 LazyMan lazyMan = LazyMan.getInstance(); Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMan lazyMan1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazyMan); System.out.println(lazyMan1); } }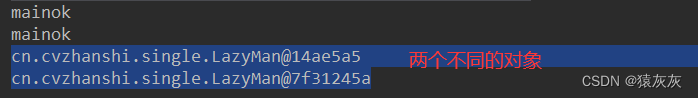
- 解决办法:可以在构造器中添加判断
... private LazyMan(){ if(lazyMan != null){ throw new RuntimeException("不要试图通过反射破坏单例"); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok"); } ...//省略的代码和上面一样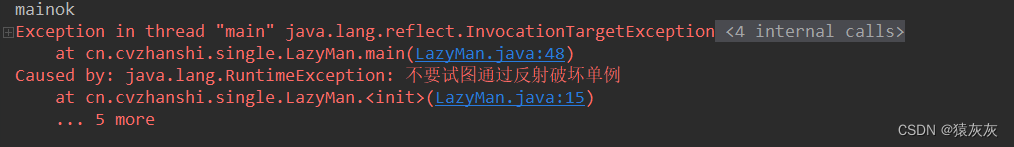
-
情况二:两个对象都通过反射得到
/** * @author cVzhanshi * @create 2021-09-26 10:22 */ public class LazyMan { // 私有化构造器 private LazyMan(){ if(lazyMan != null){ throw new RuntimeException("不要试图通过反射破坏单例"); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok"); } // + volatile 防止指令重排 private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan; // 双重检测锁模式的懒汉式单例 --> DCL懒汉式 public static LazyMan getInstance(){ if(lazyMan == null){ synchronized (LazyMan.class){ if(lazyMan == null){ lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是一个原子性操作 } } } return lazyMan; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { // 单线程下绝对正确且安全,但是在多线程下不安全 Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMan lazyMan = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); LazyMan lazyMan1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazyMan); System.out.println(lazyMan1); } }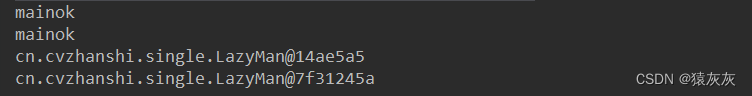
原因:对象都通过反射得到,导致原类中的LazyMan没有被构造且一直为null,所以都能通过构造器里面的判断
解决方案:设置一个红绿灯(一个标志,非当前对象)来判断
/** * @author cVzhanshi * @create 2021-09-26 10:22 */ public class LazyMan { private static boolean cvzhanshi = false; // 私有化构造器 private LazyMan(){ synchronized (LazyMan.class){ if(cvzhanshi == false){ cvzhanshi = true; }else{ throw new RuntimeException("不要试图通过反射破坏单例"); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok"); } // + volatile 防止指令重排 private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan; // 双重检测锁模式的懒汉式单例 --> DCL懒汉式 public static LazyMan getInstance(){ if(lazyMan == null){ synchronized (LazyMan.class){ if(lazyMan == null){ lazyMan = new LazyMan(); // 不是一个原子性操作 /** * lazyMan = new LazyMan();的执行步骤 * 1、分配内存空间 * 2、执行构造方法,初始化对象 * 3、把这个对象指向这个空间 * 可能由于指令重排 把执行顺序变成 1-3-2 * 造成的结果:线程A还没有初始化对象,线程B获取对象是lazyMan!=null就返回对象,此时lazyMan还没有完成构造 */ } } } return lazyMan; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { // 单线程下绝对正确且安全,但是在多线程下不安全 Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMan lazyMan = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); LazyMan lazyMan1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazyMan); System.out.println(lazyMan1); } }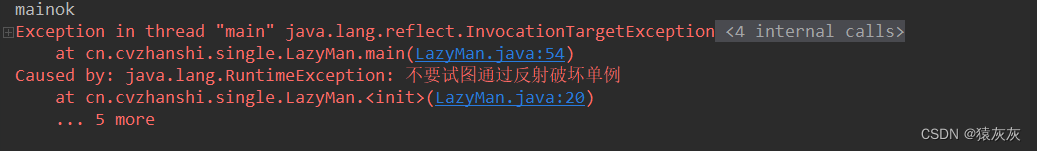
-
情况三:在二的基础上那个“红绿灯”被破解了,也通过反射进行修改,进而破坏单例
... public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException { // 单线程下绝对正确且安全,但是在多线程下不安全 Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); // 获取cvzhanshi属性 Field cvzhanshi = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredField("cvzhanshi"); cvzhanshi.setAccessible(false); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMan lazyMan = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); cvzhanshi.set(lazyMan,false); LazyMan lazyMan1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazyMan); System.out.println(lazyMan1); } ...//省略的代码和上面一样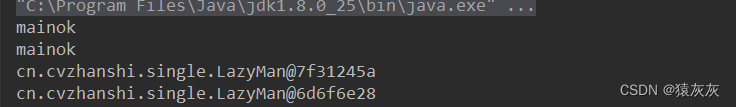
查看newInstance方法,发现不能使用反射而破坏枚举的单例模式

尝试通过反射,破坏枚举类的单例模式
-
正常取枚举类中的对象,确实是单例模式
/** * @author cVzhanshi * @create 2021-09-26 15:10 */ public enum EnumSingle { INSTANCE; public EnumSingle getInstance(){ return INSTANCE; } } class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; EnumSingle instance2 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } }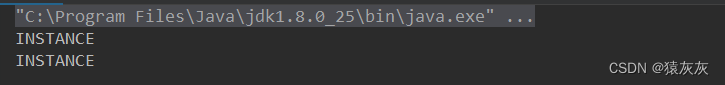
-
通过查看枚举类编译的class文件,可以看到一个无参构造器
package cn.cvzhanshi.single; public enum EnumSingle { INSTANCE; private EnumSingle() { } public EnumSingle getInstance() { return INSTANCE; } } -
通过反射调用构造器构造对象,破坏单例
/** * @author cVzhanshi * @create 2021-09-26 15:10 */ public enum EnumSingle { INSTANCE; public EnumSingle getInstance(){ return INSTANCE; } } class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); EnumSingle instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } }结果不尽人意,报错没有空参构造器
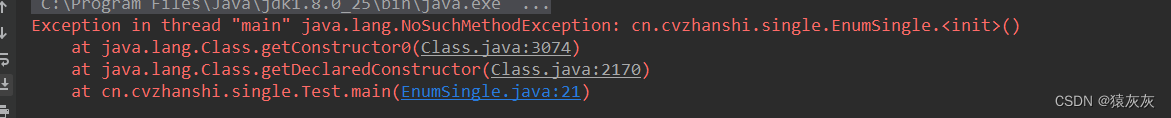
对class文件进行反编译查看代码,发现也有空参构造器
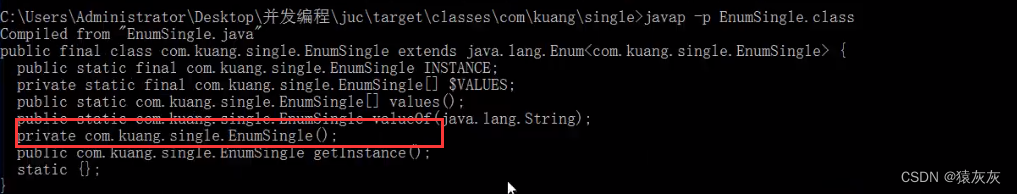
我们使用更专业的反编译工具jad.exe,查看源代码可知他是有参构造器
结论:idea骗了我们
public final class EnumSingle extends Enum { public static EnumSingle[] values() { return (EnumSingle[])$VALUES.clone(); } public static EnumSingle valueOf(String name) { return (EnumSingle)Enum.valueOf(com/ogj/single/EnumSingle, name); } private EnumSingle(String s, int i) { super(s, i); } public EnumSingle getInstance() { return INSTANCE; } public static final EnumSingle INSTANCE; private static final EnumSingle $VALUES[]; static { INSTANCE = new EnumSingle("INSTANCE", 0); $VALUES = (new EnumSingle[] { INSTANCE }); } } -
得知原因后继续通过反射通过构造器构造对象,破坏单例
.... class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); EnumSingle instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } } ...//省略的代码和上面一样通过结果,我们得知枚举确实不能通过反射去改变单例模式

4.6 jdk代码中的体现
JDK中的RunTime中使用了单例模式。
public class Runtime {
private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime();
/**
* Returns the runtime object associated with the current Java application.
* Most of the methods of class <code>Runtime</code> are instance
* methods and must be invoked with respect to the current runtime object.
*
* @return the <code>Runtime</code> object associated with the current
* Java application.
*/
public static Runtime getRuntime() {
return currentRuntime;
}
/** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */
private Runtime() {}
}
看的出使用了饿汉式的单例模式
4.7 注意事项和细节说明
- 单例模式保证了系统内存中该类只存在一个对象,节省了系统资源,对于一些需要频繁创建销毁的对象,使用单例模式可以提高系统性能
- 当想实例化一个单例类的时候,必须要记住使用相应的获取对象的方法,而不是使 用new
- 单例模式使用的场景:需要频繁的进行创建和销毁的对象、创建对象时耗时过多或 耗费资源过多(即:重量级对象),但又**经常用到的对象、工具类对象、频繁访问数据库或文件的对象(**比如数据源、session工厂等)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:

