首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
Spring MVC详解(学习总结)
2023-07-24 12:40:02基础资料围观753次
文章是看楠哥的视频做的总结,自己还查阅了一些资料,文章也加了自己的总结,这篇博客可以帮助大家入门,还有一些知识大家如果用到的话可以到时候再去学习一下,我写这篇主要是为了方便后面复习。
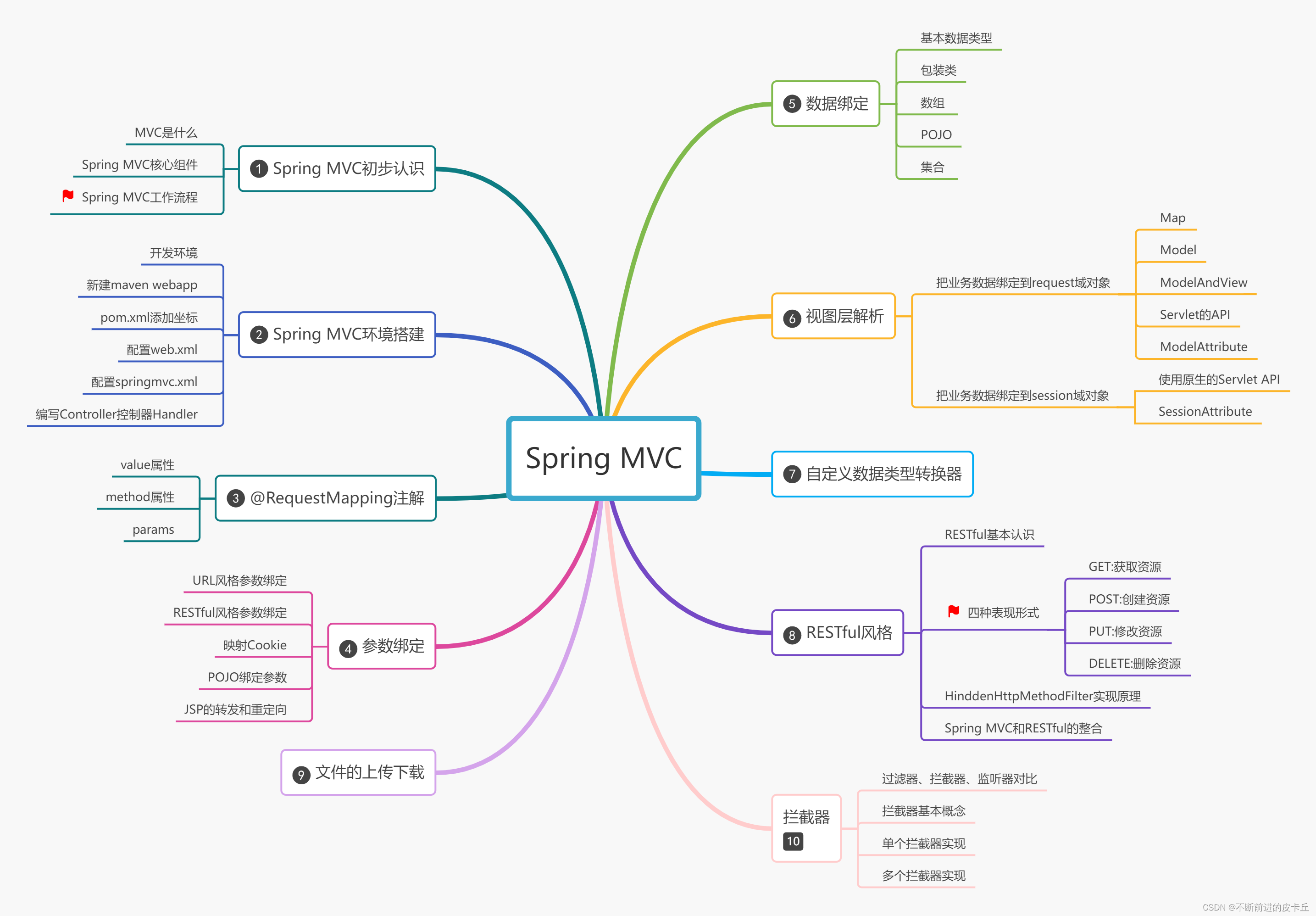
一、Sprig MVC简介
1.1介绍
Spring MVC是Spring Framework提供的Web组件,全称是Spring Web MVC,是目前主流的实现MVC设计模式的框架,提供前端路由映射、视图解析等功能
Java Web开发者必须要掌握的技术框架
1.2MVC是什么
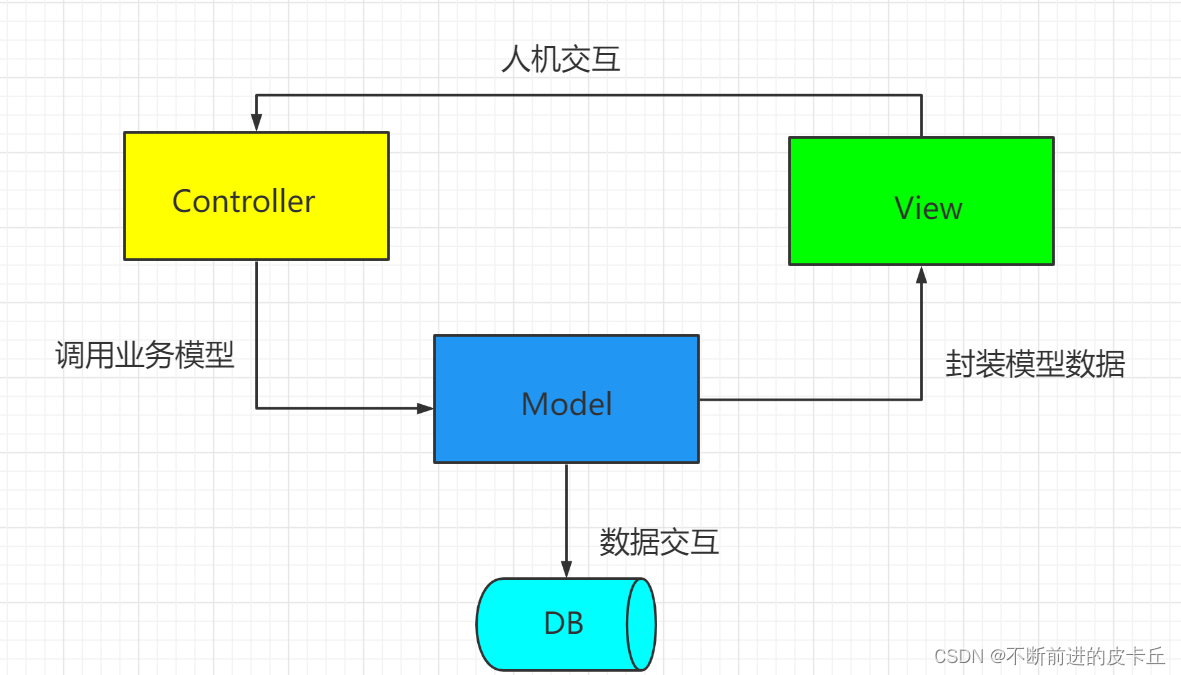
MVC是一种软件架构思想,把软件按照模型,视图,控制器来划分
Model:模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,用来处理数据
JavaBean分成两类:
- 一类称为实体类Bean:专门用来存储业务数据,比如Student,User
- 一类称为业务处理Bean:指Servlet或Dao对象,专门用来处理业务逻辑和数据访问
View:视图层,指工程中的html,jsp等页面,作用是和用户进行交互,展示数据
Controler:控制层,指工程中的Servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器 - 流程:
- 用户通过视图层发送请求到服务器,在服务器中请求被Controller接收
- Controller调用相应的Model层处理请求,处理完毕后结果返回到Controller
- Controller再根据请求处理的结果找到对应的View视图,渲染数据后最终响应给浏览器
Spring MVC对这套MVC流程进行封装,帮助开发者屏蔽底层细节,并且开放出相关接口供开发者调用,让MVC开发更简单方便
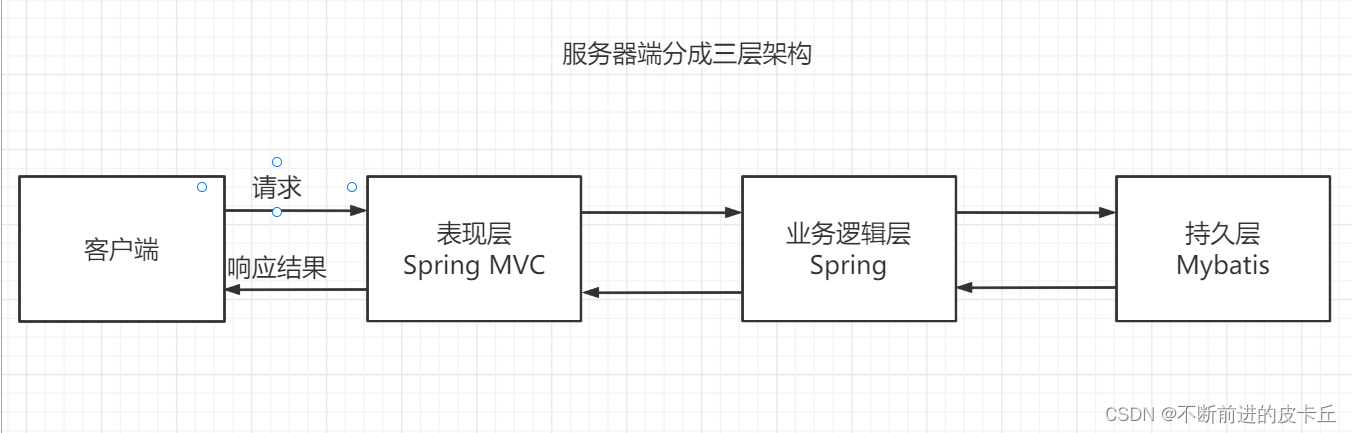
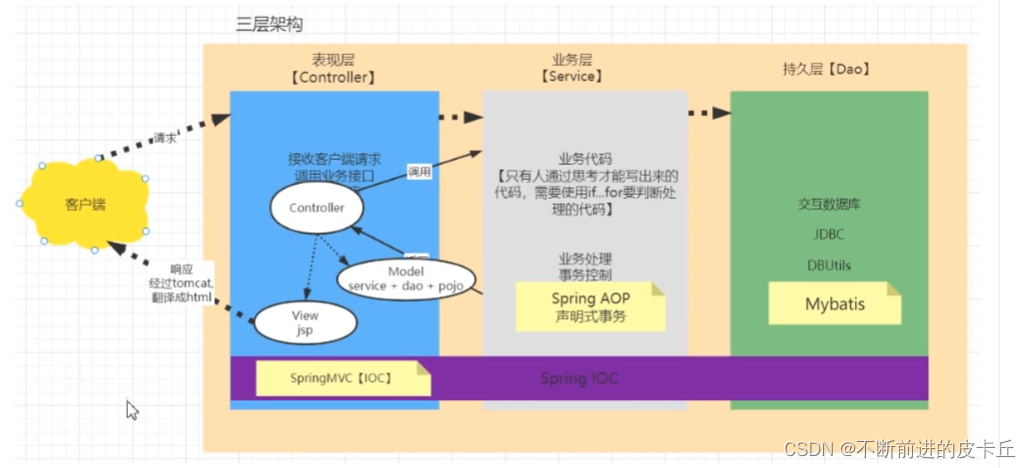
二、Spring MVC实现原理
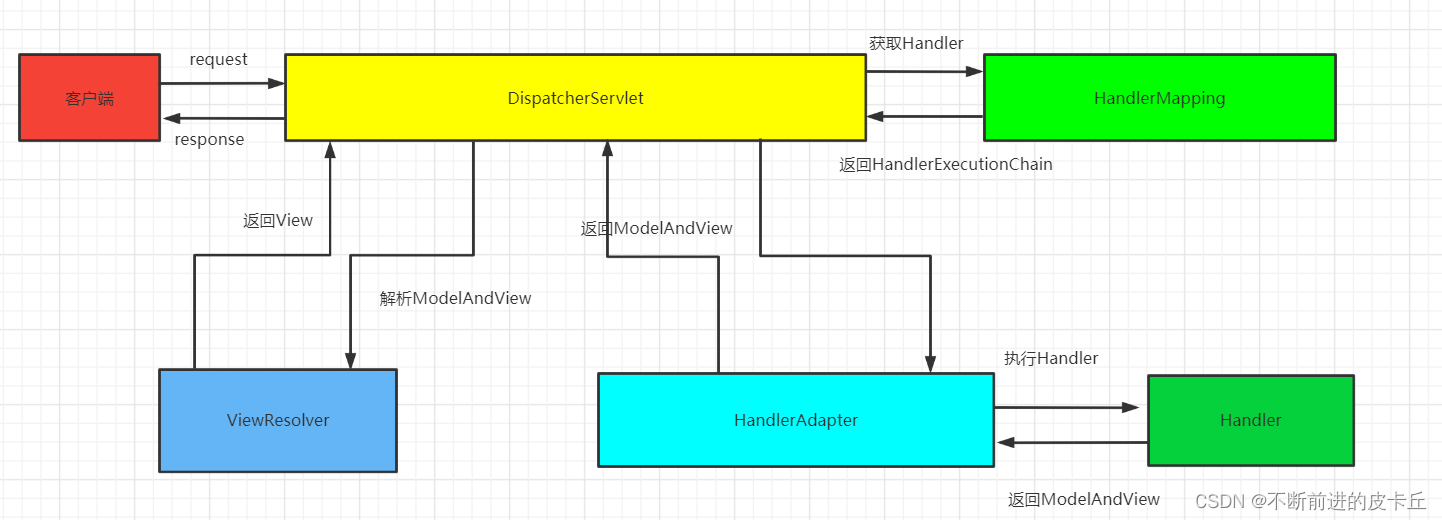
2.1核心组件
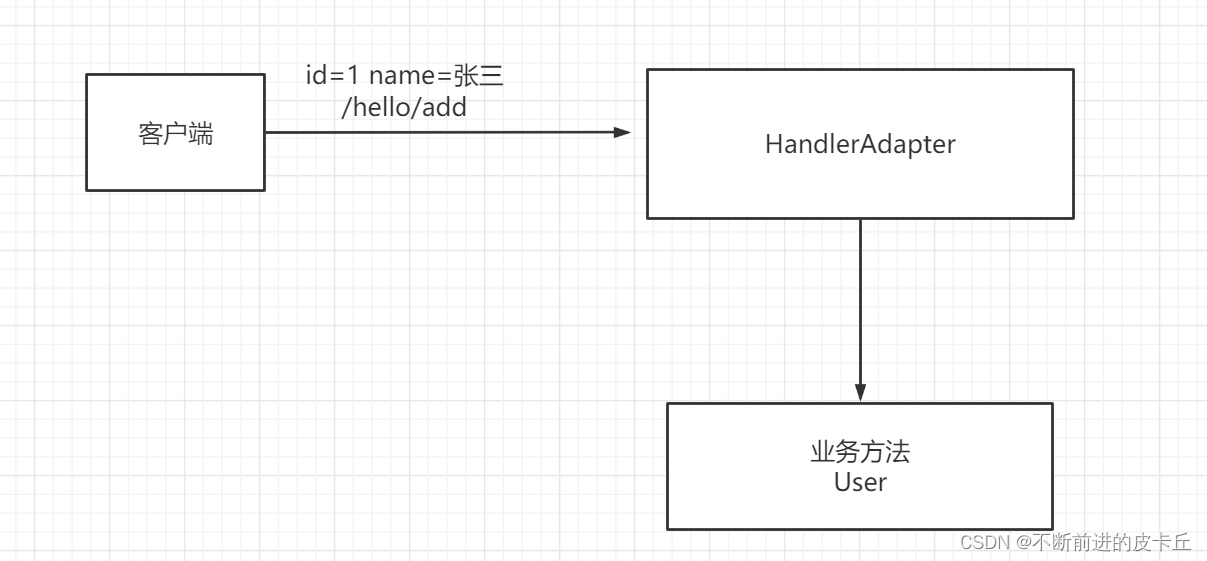
- DispatcherServlet:前置控制器,负责调度其他组件的执行,可以降低不同组件之间的耦合性,是整个Spring MVC的核心模块
- Handler:处理器,完成具体的业务逻辑,相当于Servlet
- HandlerMapping:DispatcherServlet是通过 HandlerMapping把请求映射到不同的Handler
- HandlerInterceptor:处理器拦截器,是一个接口,如果我们需要进行一些拦截处理,可以通过实现该接口完成
- HandlerExecutionChain:处理器执行链,包括两部分内容:Handler和HandlerInterceptor(系统会有一个默认的HandlerInterceptor,如果有额外拦截处理,可以添加拦截器进行设置)
- HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,Handler执行业务方法之前,需要进行一系列的操作包括表单的数据验证、数据类型转换、把表单数据封装到POJO等,这些一系列的操作都是由HandlerAdapter完成,DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter执行不同的Handler
- ModelAndView:封装了模型数据和视图信息,作为Handler的处理结果,返回给DispatcherServlet
- ViewResolver:视图解析器,DispatcherServlet通过它把逻辑视图解析为物理视图,最终把渲染的结果响应给客户端
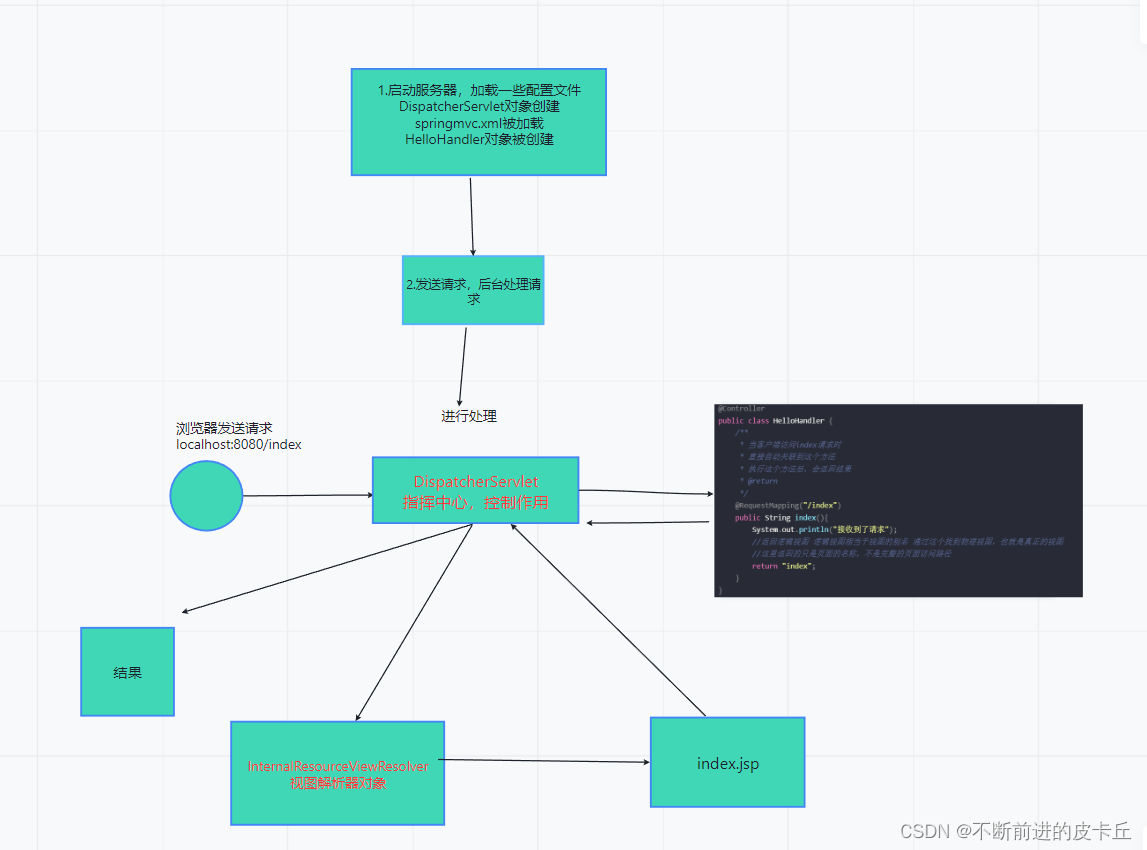
2.2工作流程
- 客户端请求被DispatcherServlet接收
- 根据HandlerMapping映射到Handler
- 生成Handler和HandlerInterceptor
- Handler和HandlerInterceptor以HandlerExecutionChain的形式一并返回给DispatcherServlet
- DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter调用Handler的方法完成业务逻辑处理
- 返回一个ModelAndView对象给DispatcherServlet
- DispatcherServlet把获取的ModelAndView对象传给ViewResolver视图解析器,把逻辑视图解析成物理视图
- ViewResolver返回一个View进行视图渲染(把模型填充到视图中)
- DispatcherServlet把渲染后的视图响应给客户端
三、第一个Spring MVC
- 创建maven改成工程,pom.xml加入Spring MVC的依赖

pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMVC</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>SpringMVC Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.19</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.19</version>
</dependency>
- 在web.xml中配置Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet
首先在项目中创建java和resources的目录
在resources目录中添加springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
然后在web.xml 配置Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!-- 配置核心控制器 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- springmvc配置文件加载路径
1)默认情况下,读取WEB-INF下面的文件
2)可以改为加载类路径下(resources目录),加上classpath:
-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--
DispatcherServlet对象创建时间问题
1)默认情况下,第一次访问该Servlet的创建对象,意味着在这个时间才去加载springMVC.xml
2)可以改变为在项目启动时候就创建该Servlet,提高用户访问体验。
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
数值越大,对象创建优先级越低! (数值越低,越先创建)
-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<!--/ 匹配所有的请求;(不包括.jsp)-->
<!--/* 匹配所有的请求;(包括.jsp)-->
<!--*.do拦截以do结尾的请求-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
拦截请求其实就是说,只要是符合这个URL的请求都会进入到Spring MVC中去看看有没有对应的Handler./不会拦截.jsp的路径,但是会拦截.html等静态资源

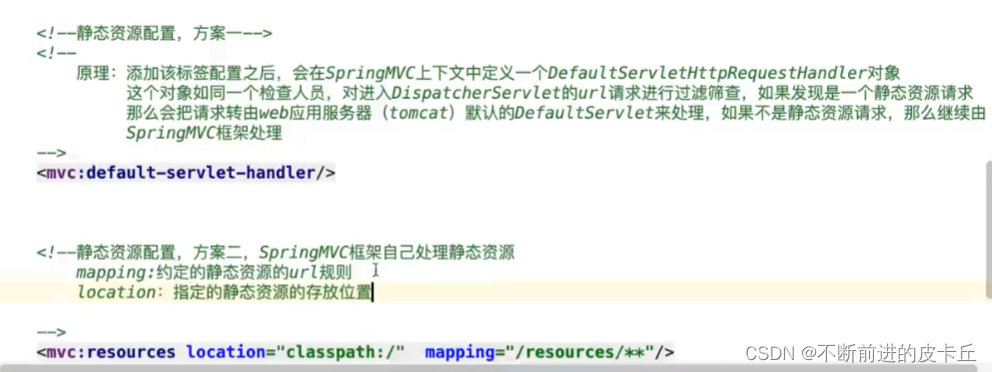
- DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC提供的核心控制器,这个一个Servlet程序,该Servlet程序会接收所有请求
- 核心控制器会读取一个springmvc.xml配置,加载Spring MVC的核心配置
- 配置/代表拦截所有请求
- 代表在项目启动时实例化DispathcerServlet,如果没有配置,则在第一次访问Servlet时进行实例化
3.springmvc.xml进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zyh.controller"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!--给逻辑视图加上前缀和后缀 -->
<!--前缀-->
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<!--后缀-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
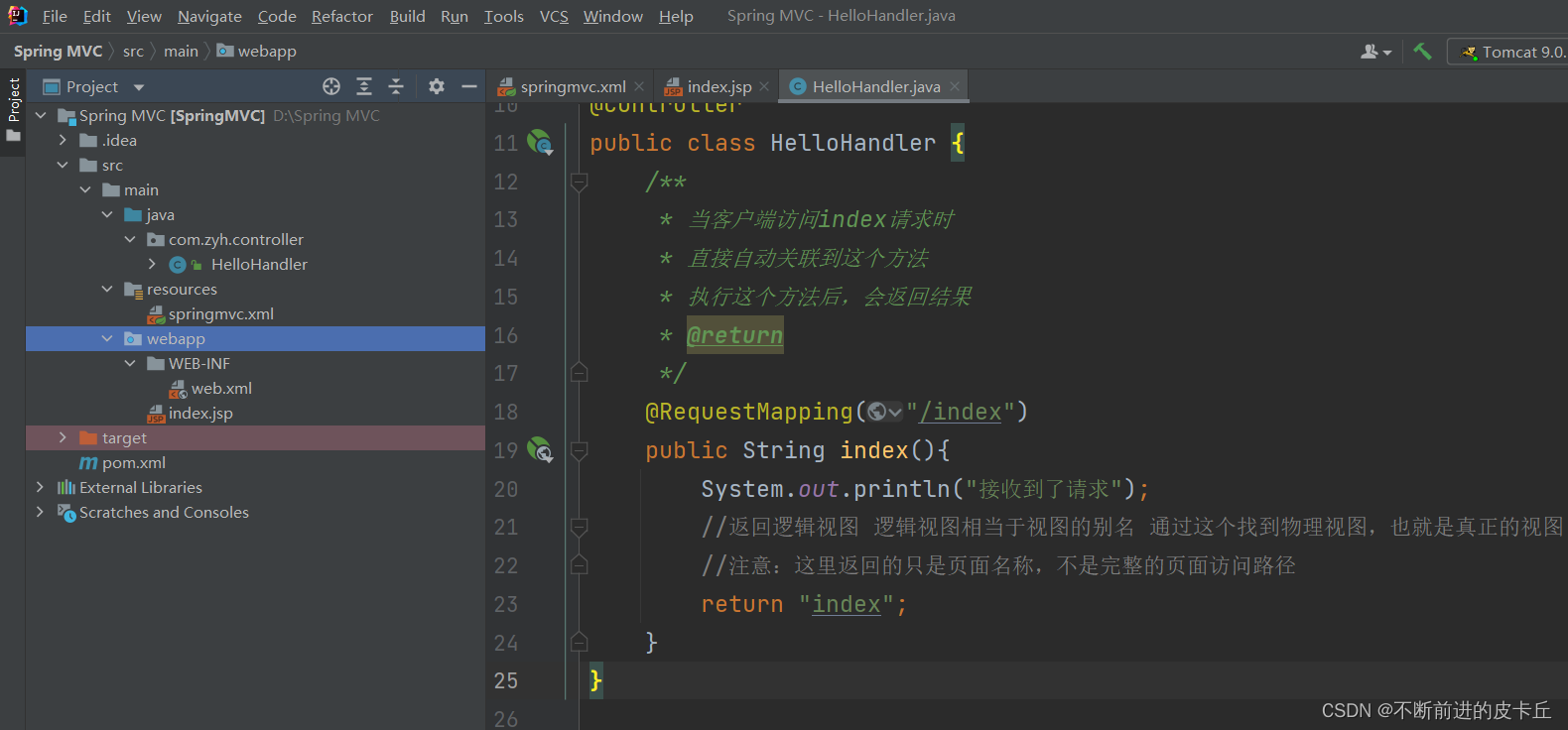
- 创建Controller控制器Handler,在里面编写接收参数,调用业务方法,返回视图页面等逻辑
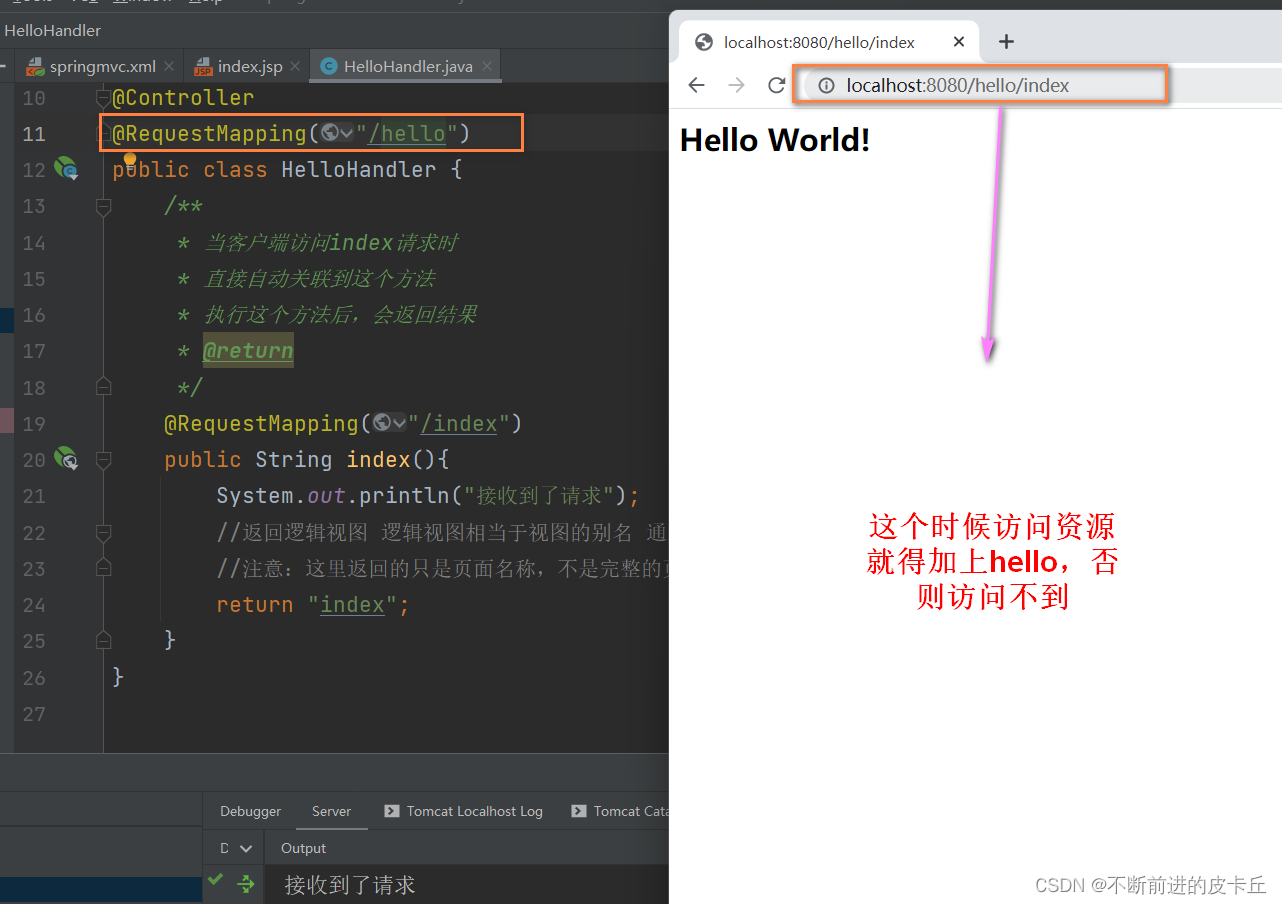
@Controller
public class HelloHandler {
/**
* 当客户端访问index请求时
* 直接自动关联到这个方法
* 执行这个方法后,会返回结果
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("接收到了请求");
//返回逻辑视图 逻辑视图相当于视图的别名 通过这个找到物理视图,也就是真正的视图
//这里返回的只是页面的名称,不是完整的页面访问路径
return "index";
}
}
@Controller注解是为了让Spring IOC容器初始化时自动扫描到该Controller类;@RequestMapping是为了映射请求路径,这里因为类与方法上都有映射所以访问时应该是/;方法返回的结果是视图的名称index,该名称不是完整页面路径,最终会经过视图解析器解析为完整页面路径并跳转。
配置Tomcat
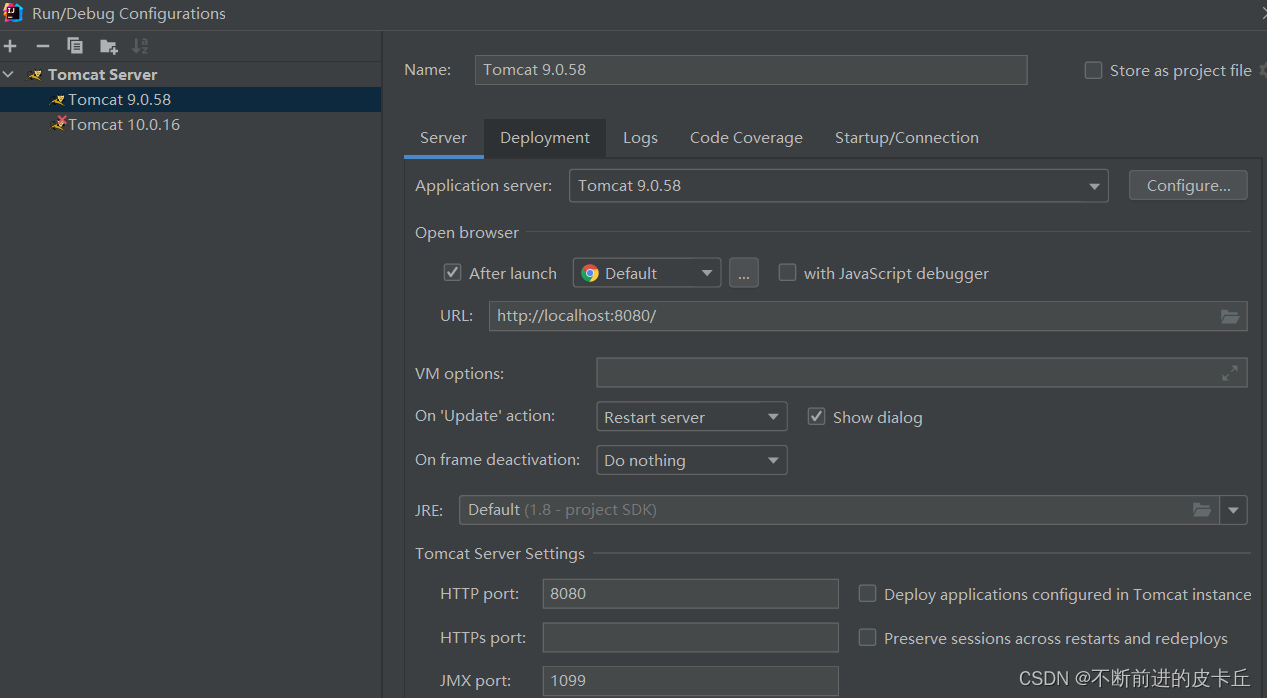
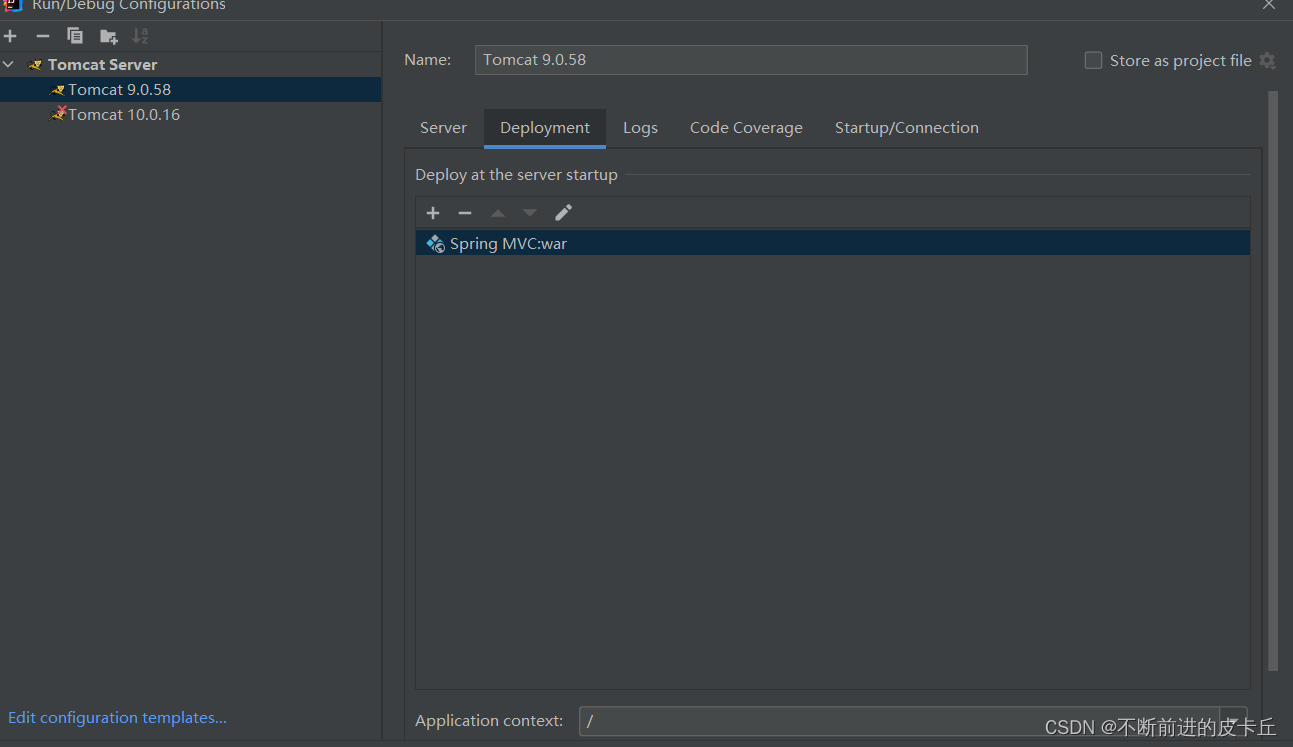
5. 测试
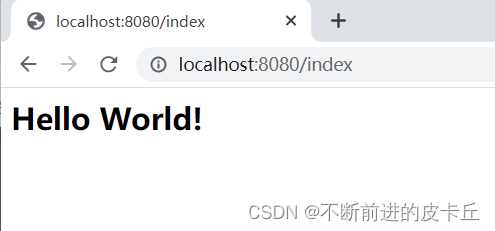
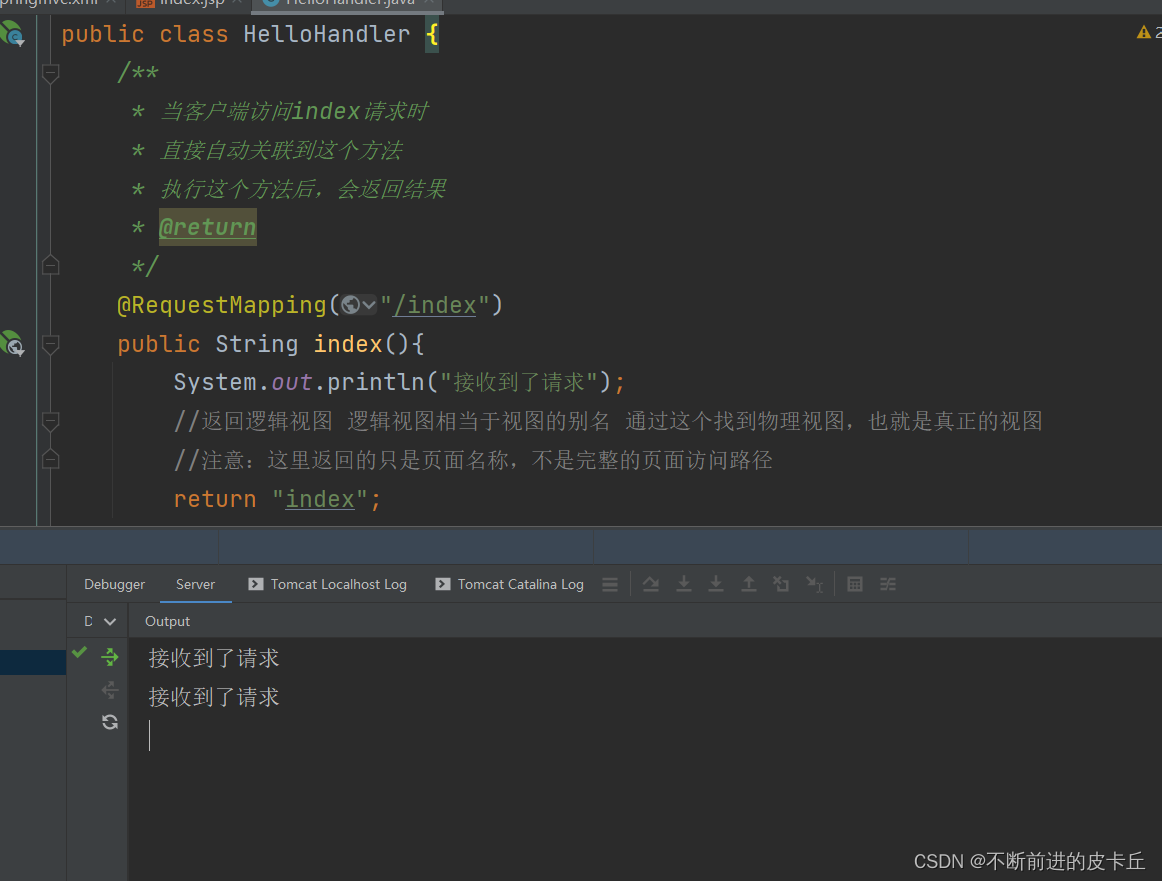
流程梳理
- DispatcherServlet接收到URL请求index,结合@RequestMapping(“/index”)注解把该请求交给index业务方法进行处理
- 执行index业务方法,控制台打印日志,并且返回"index"字符串(逻辑视图).
- 结合springmvc.xml中的视图解析器配置,找到目标资源:/index.jsp,即根目录下的index.jsp文件,把该JSP资源返回给客户端完成响应。
Spring MVC搭建成功
四、常用注解
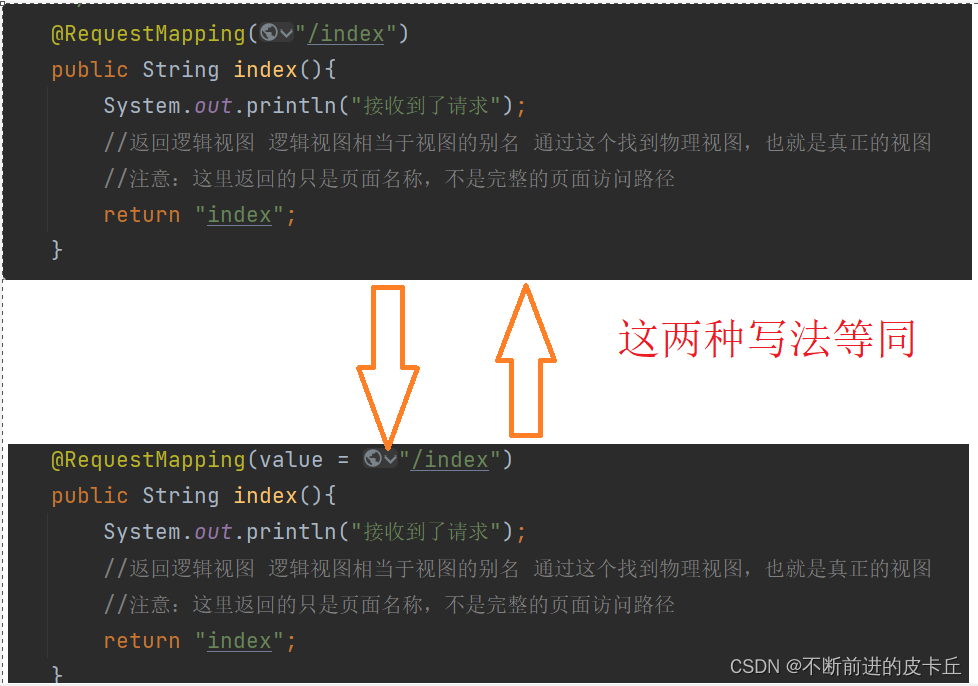
@RequestMapping
Spring MVC通过@RequestMapping注解把URL请求和业务方法进行映射,在控制器的类定义处以及方法定义处都可以添加@RequestMapping,在类定义处添加相当于多了一层访问路径
@RequestMapping常用参数
- value:指定URL请求的实际地址,是@RequestMapping的默认值
- method:指定请求的method类型,包括GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等
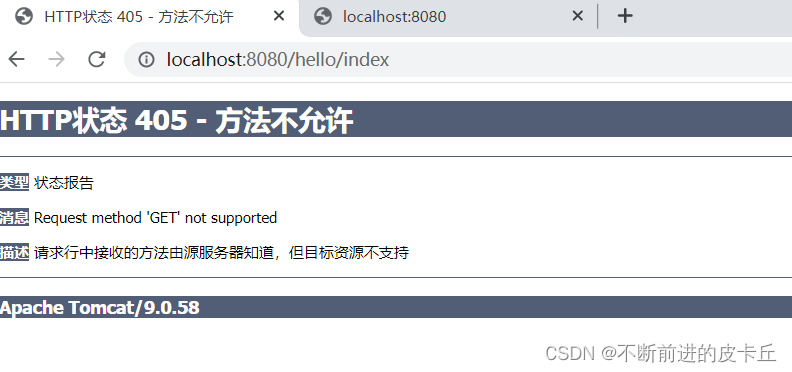
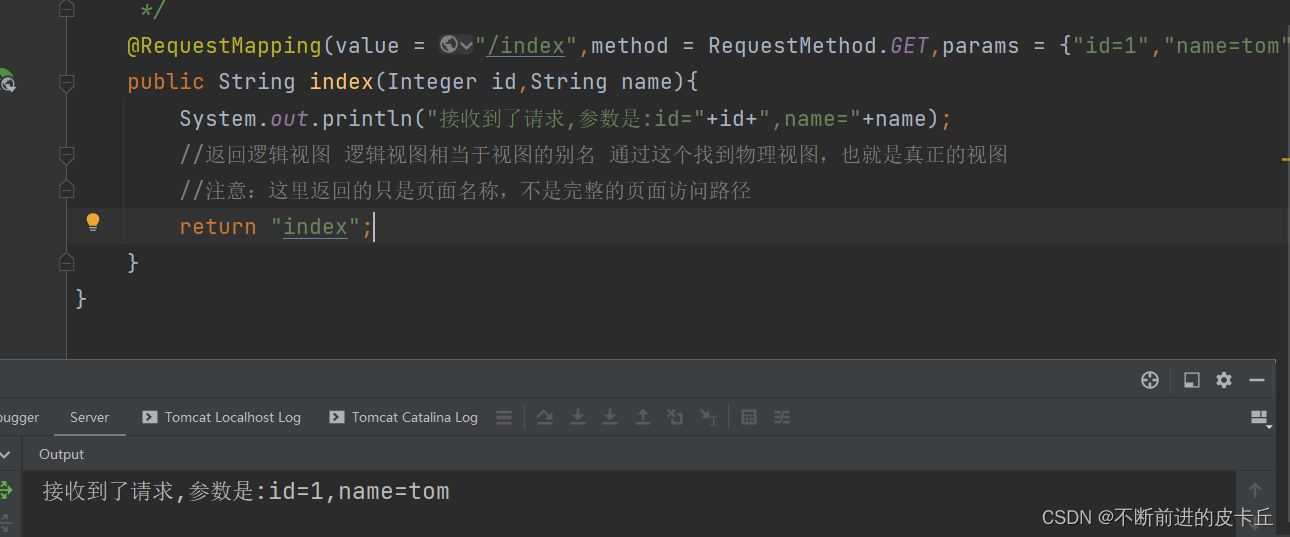
@RequestMapping(value = "/index",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String index(){
System.out.println("接收到了请求");
//返回逻辑视图 逻辑视图相当于视图的别名 通过这个找到物理视图,也就是真正的视图
//注意:这里返回的只是页面名称,不是完整的页面访问路径
return "index";
}
上述代码表示只有POST请求可以访问该方法,如果使用其他请求访问的话,直接抛出异常,比如GET请求
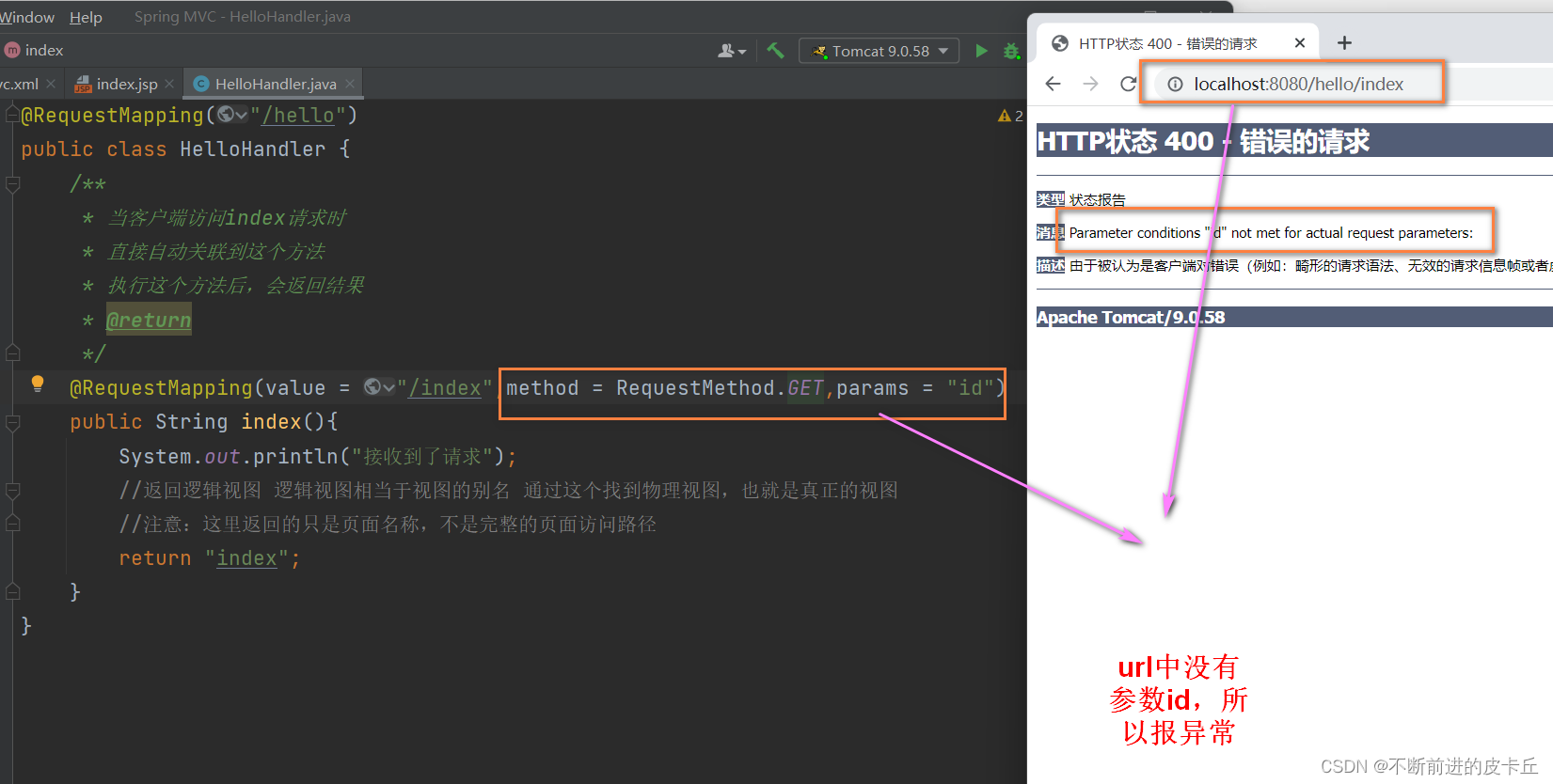
- params:指定request请求中必须包含的参数值,如果不包含的话,就无法调用该方法
五、参数绑定
5.1URL风格参数绑定
params是对URL请求参数进行限制,不满足条件的URL无法访问该方法,需要在业务方法中获取URL的参数值。
- 在业务方法定义时声明参数列表
- 给参数列表添加@RequestParam注解进行绑定
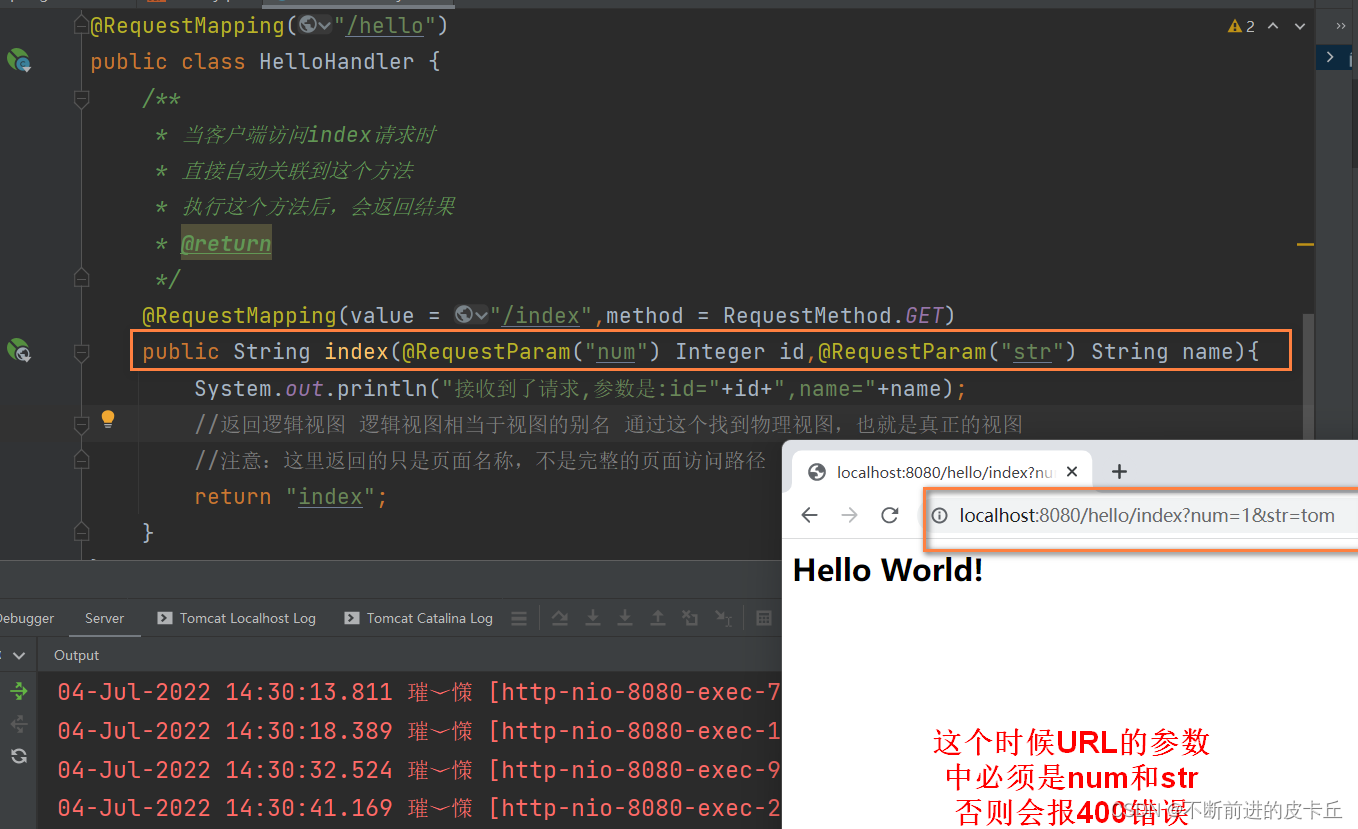
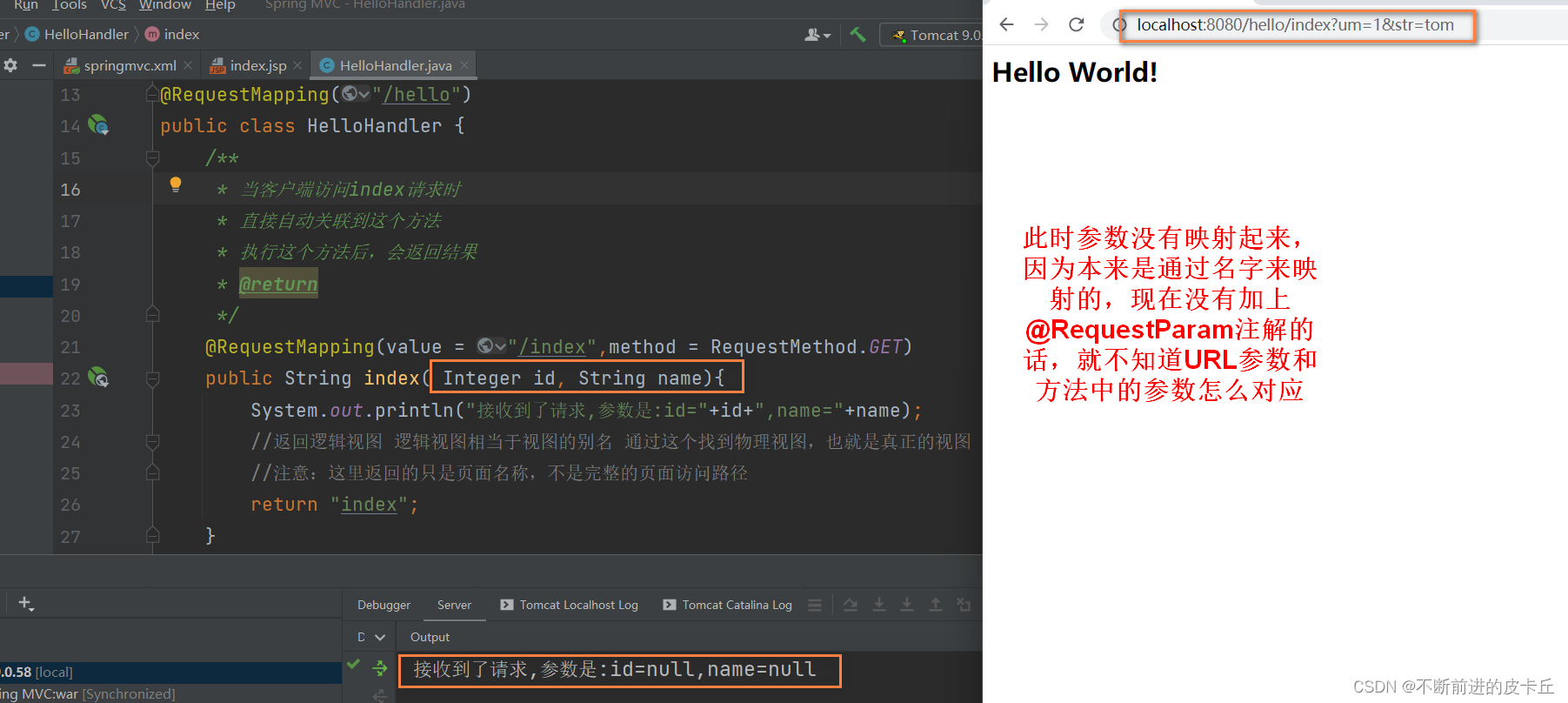
Spring MVC可以自动完成数据类型转换,该工作是由HandlerAdapter来完成的
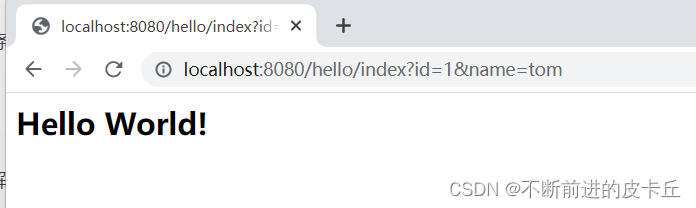
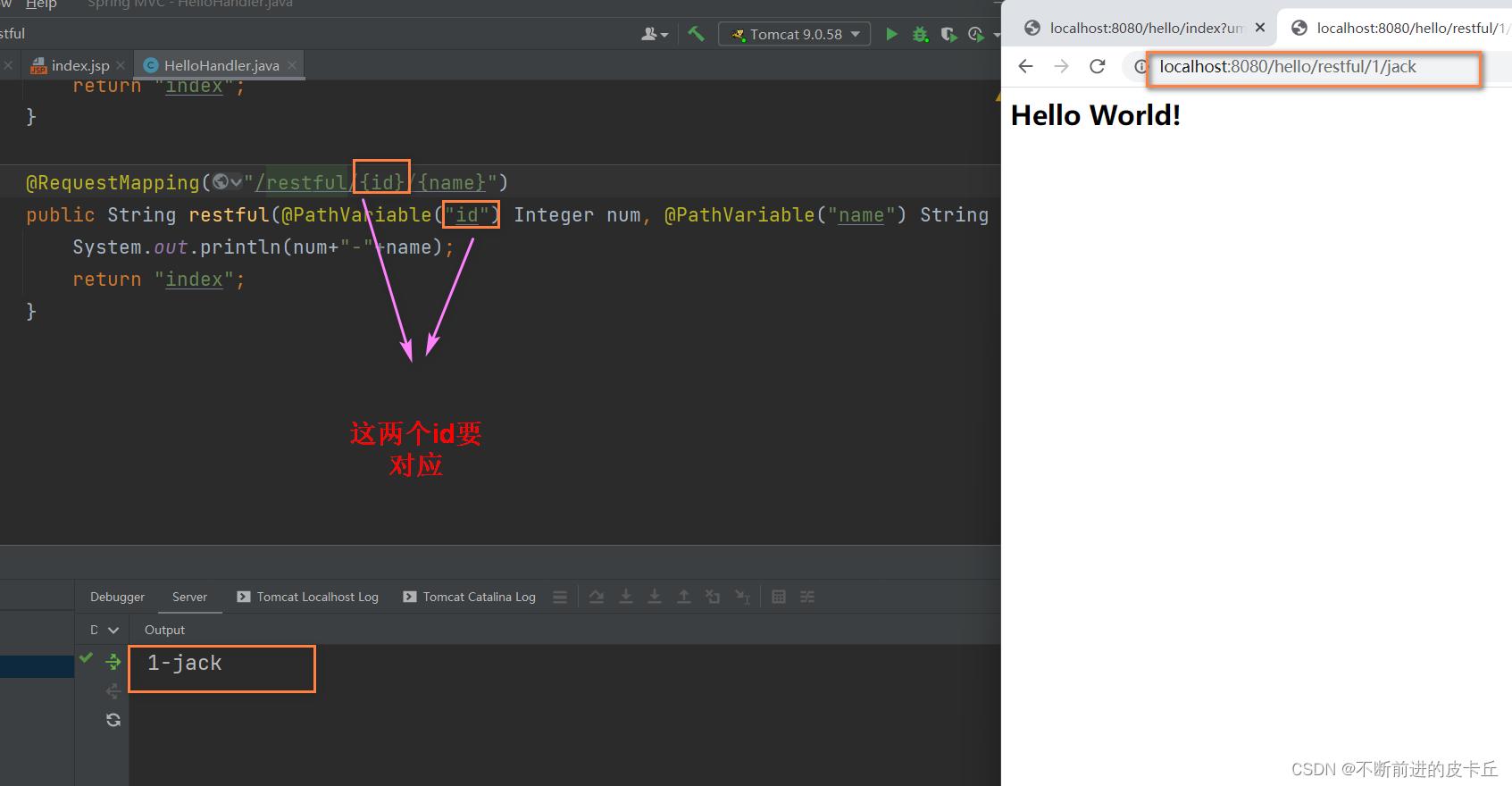
5.2RESTful风格的URL参数获取
- 传统的URL:localhost:8080/hello/index?id=1&name=tom
- RESTful URL:localhost:8080/hello/index/1/tom
@RequestMapping("/restful/{id}/{name}")
public String restful(@PathVariable("id") Integer num, @PathVariable("name") String name){
System.out.println(num+"-"+name);
return "index";
}
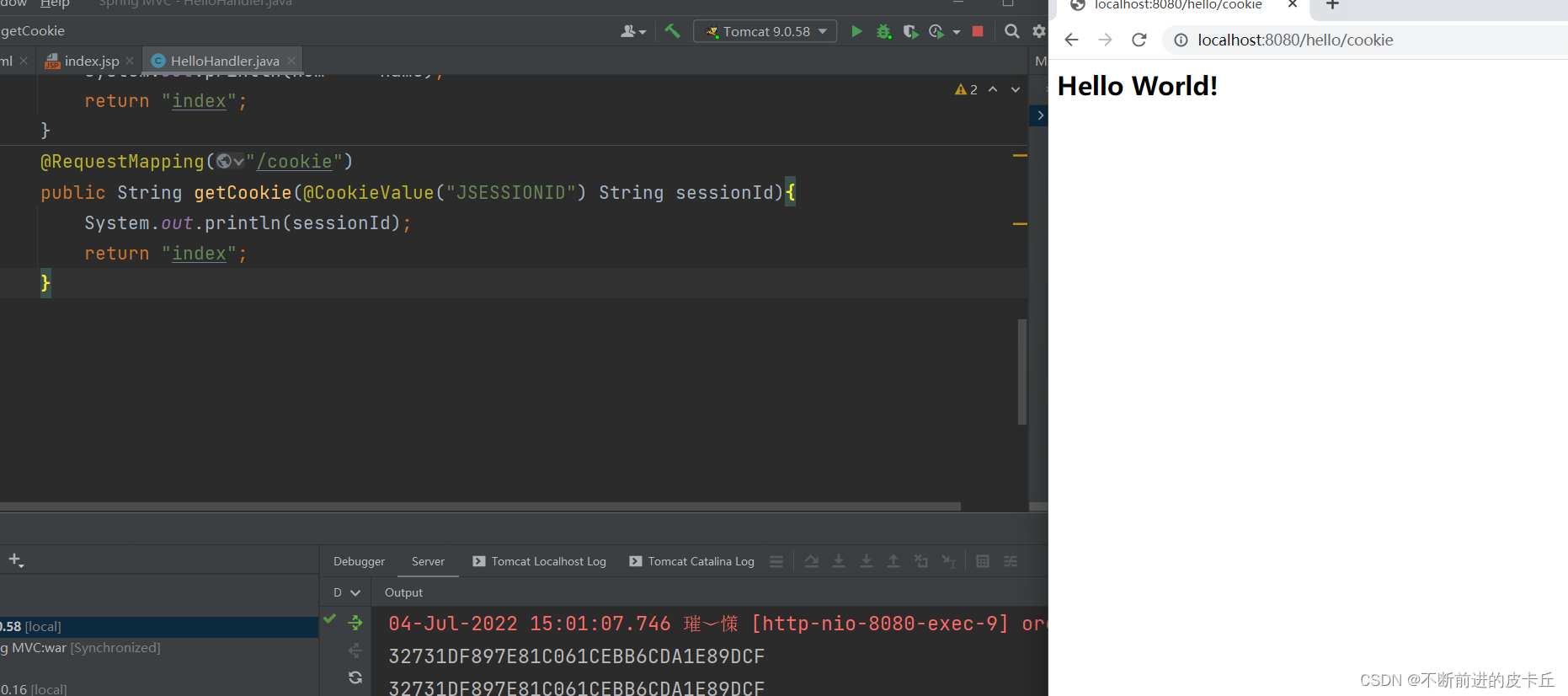
5.3映射Cookie
@RequestMapping("/cookie")
public String getCookie(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String sessionId){
System.out.println(sessionId);
return "index";
}
5.4使用POJO绑定参数
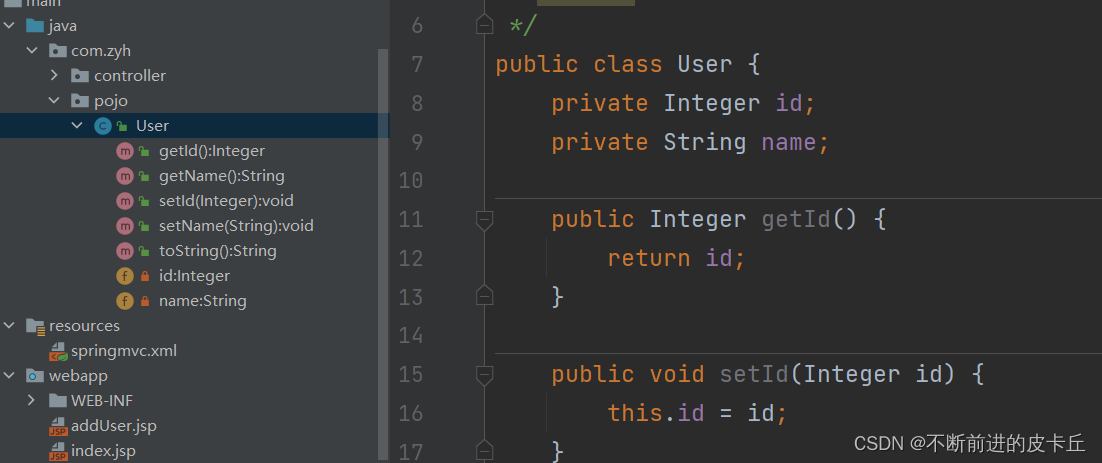
Spring MVC会根据请求参数名和POJO属性名进行匹配,自动为该对象填充属性值,并且支持属性级联
首先创建实体类
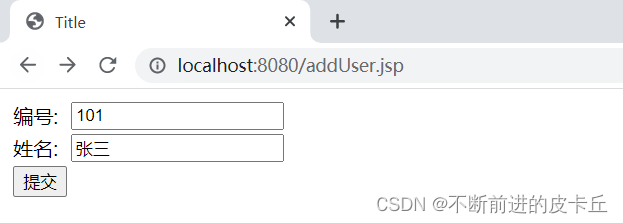
为了方便测试,写一个addUser.jsp页面
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 17614
Date: 2022-07-04
Time: 21:01
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/hello/add" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="id">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>姓名:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="name">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
然后在Handler中,编写相关方法
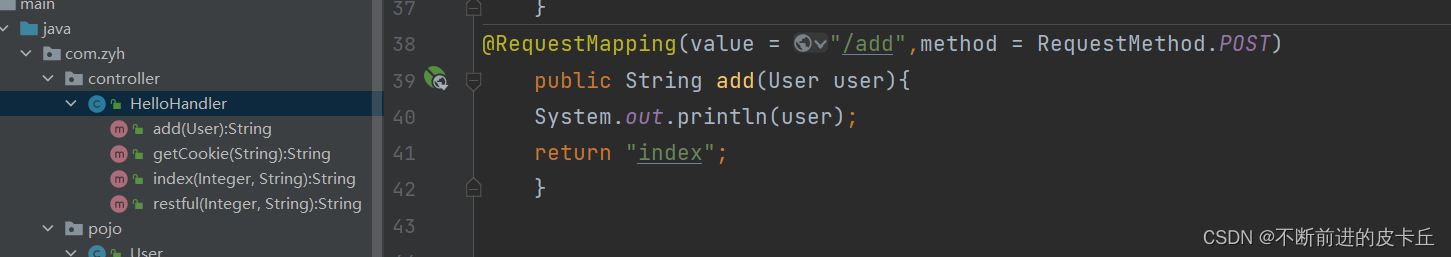
启动Tomcat服务器
结果发现出现乱码问题
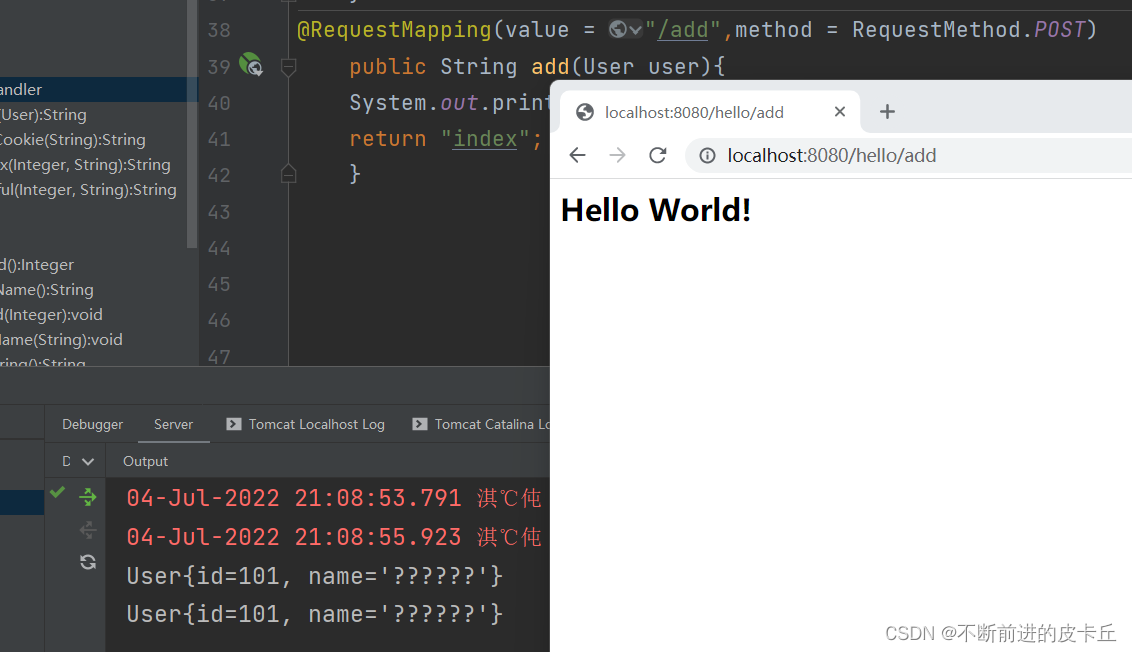
为了解决这个问题,我们只需要在web.xml配置文件中配置过滤器就可以了
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
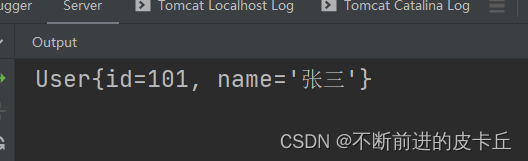
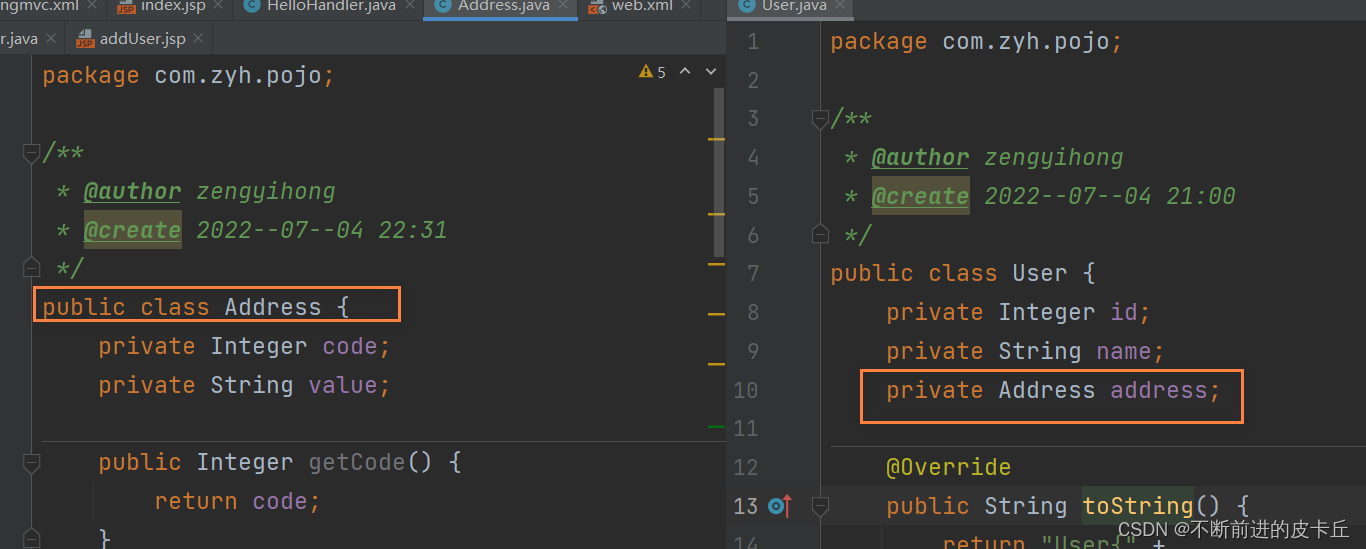
接下来看看属性级联是如何操作
addUser.jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 17614
Date: 2022-07-04
Time: 21:01
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/hello/add" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="id">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>姓名:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="name">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>地址编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="address.code">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>地址信息:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="address.value">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
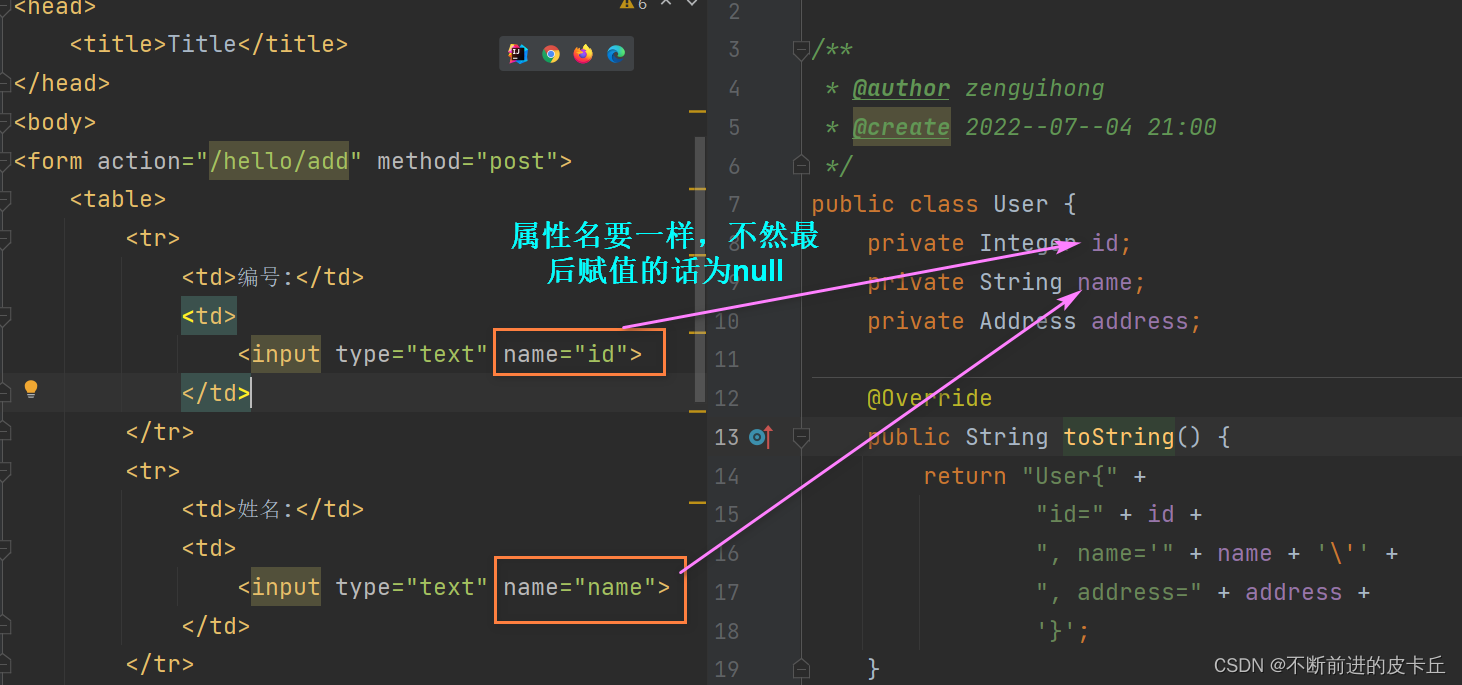
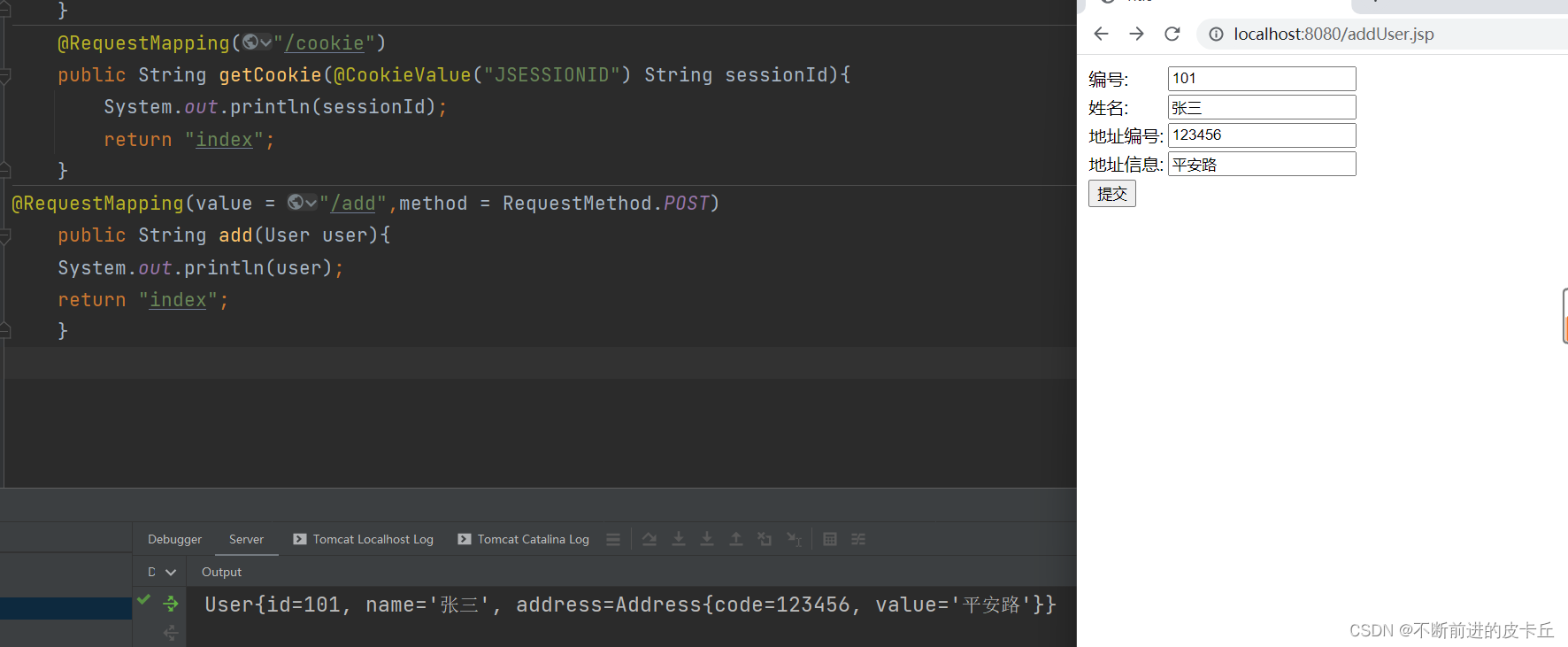
主体对象可以没有无参构造器,但是级联对象必须要有无参构造器
5.5JSP页面的转发和重定向
Spring MVC默认是通过转发的形式响应JSP,可以手动进行修改
@RequestMapping("/restful/{id}/{name}")
public String restful(@PathVariable("id") Integer num, @PathVariable("name") String name){
System.out.println(num+"-"+name);
return "index";
}
比如,我们想把它改成重定向的话
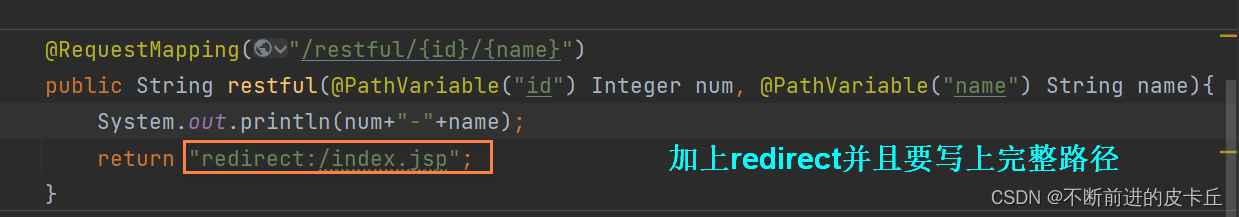
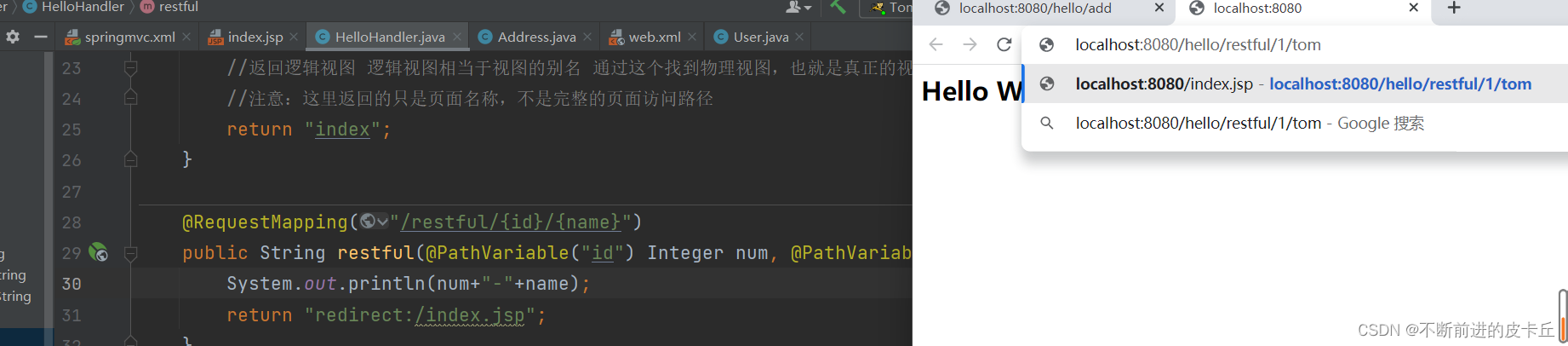
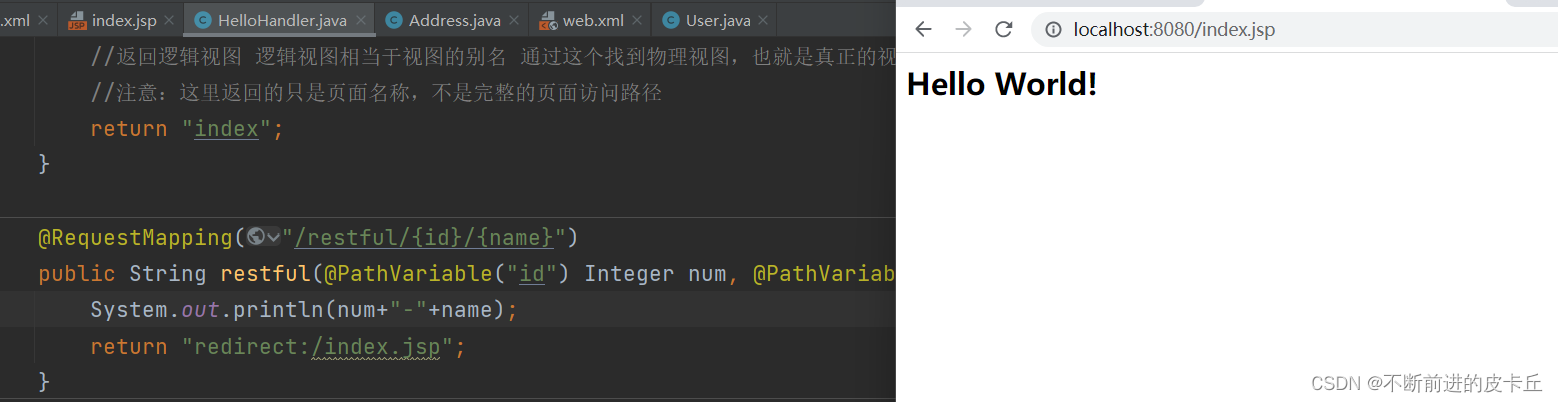
设置重定向的时候不能写逻辑视图,必须写明资源的物理路径,比如"rediect:/index.jsp"
转发
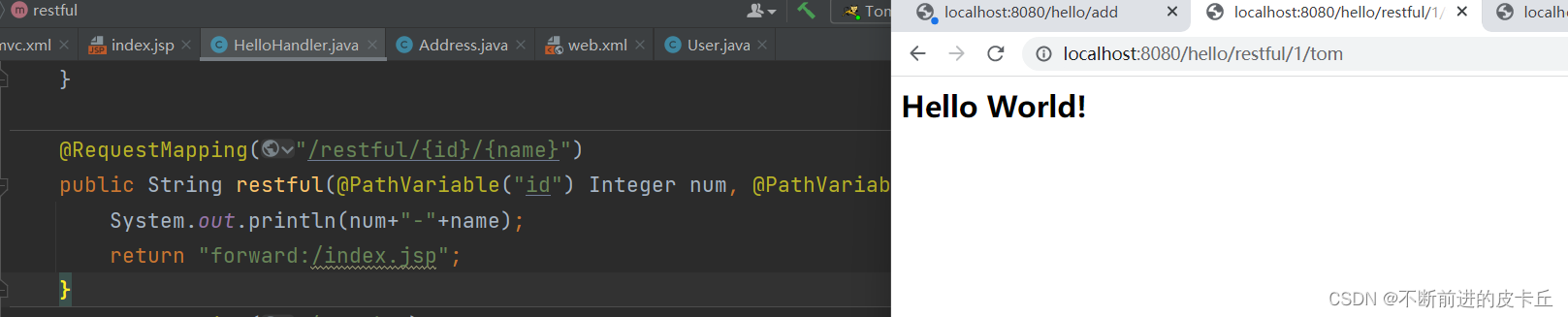
我们可以看到地址栏没变
六、Spring MVC数据绑定
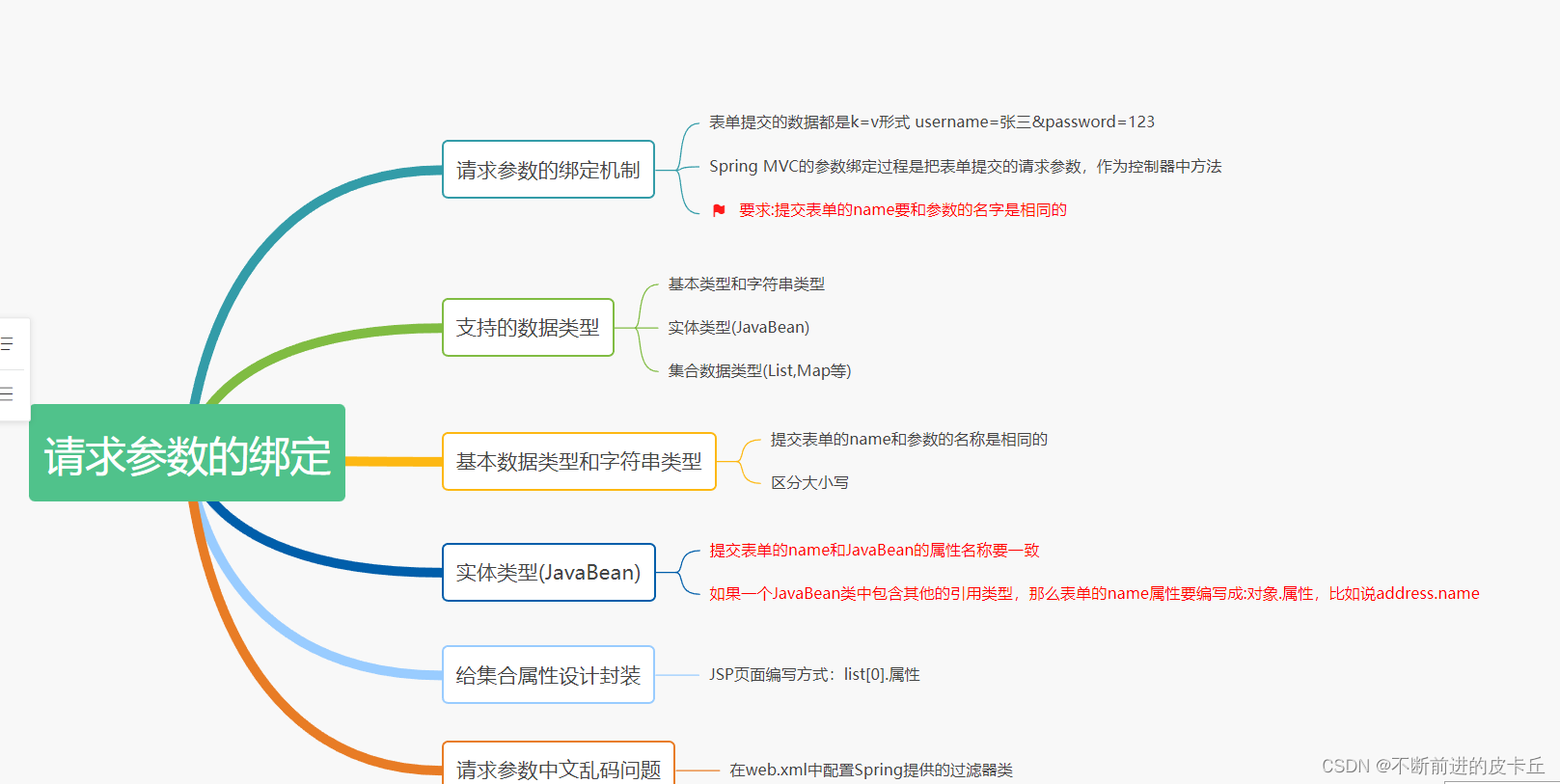
- 数据绑定:在后台业务方法中,直接获取前端HTTP请求中的参数
- HTTP请求传输的参数都是String类型的,Handler业务方法中的参数是开发者指定的参数类型,比如int,Object,所以需要进行数据类型的转换
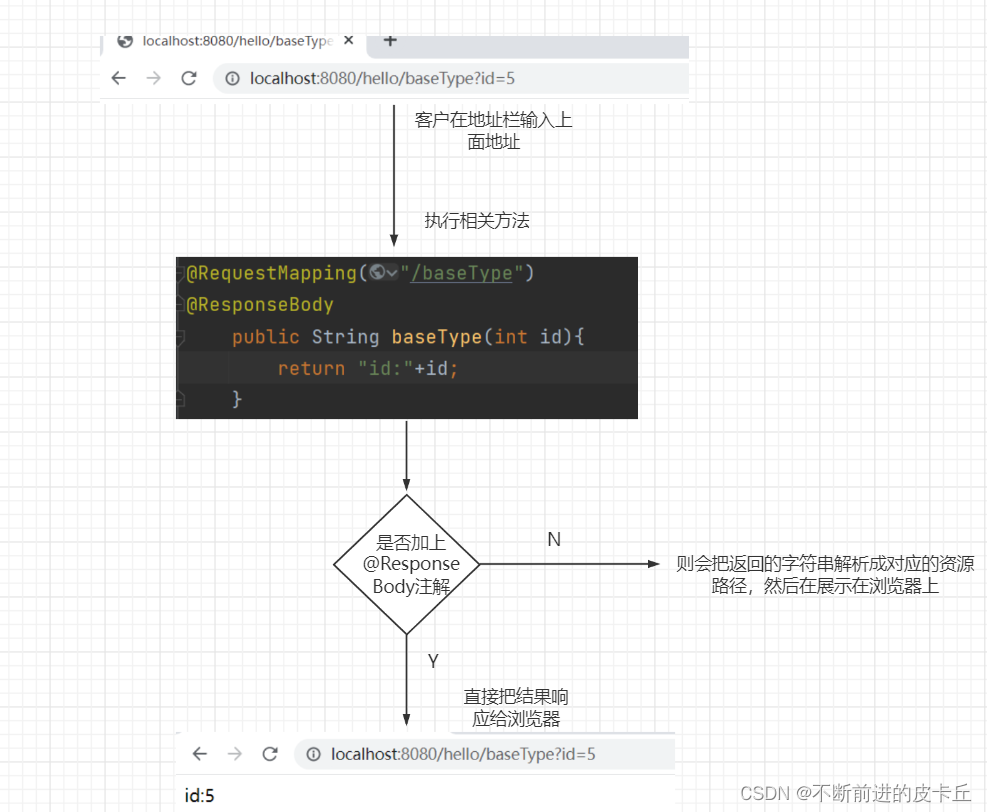
- Spring MVC的HandlerAdapter组件会在执行Handler业务方法之前,完成参数的绑定,开发者直接使用即可
6.1基本数据类型
@RequestMapping("/baseType")
@ResponseBody
public String baseType(int id){
return "id:"+id;
}
客户端HTTP请求中必须包含id参数,否则抛出500异常,因为id不能为null
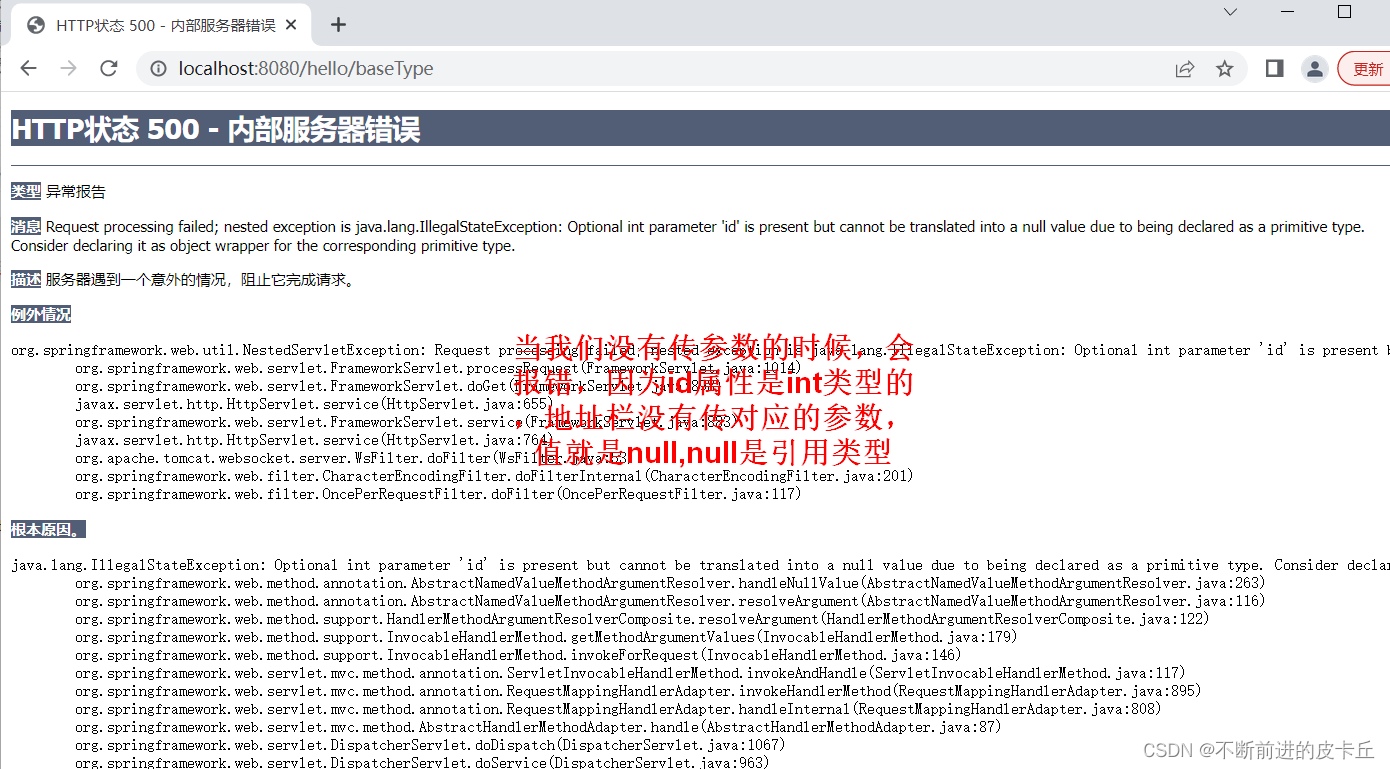
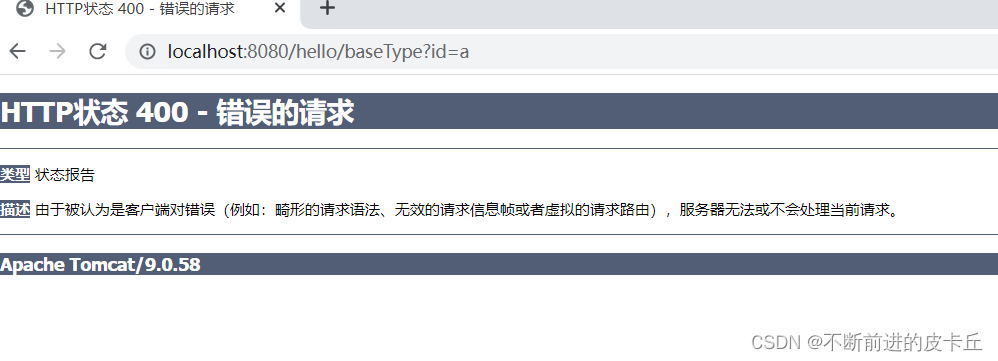
同时id的值必须为数值,而且必须为整数,否则抛出400异常
6.2包装类
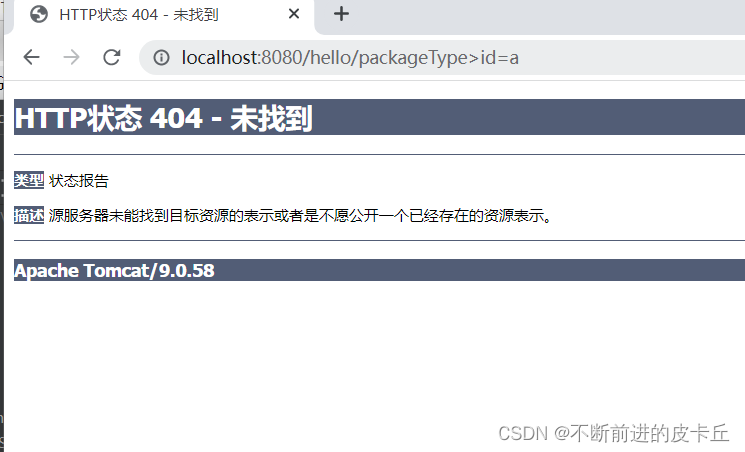
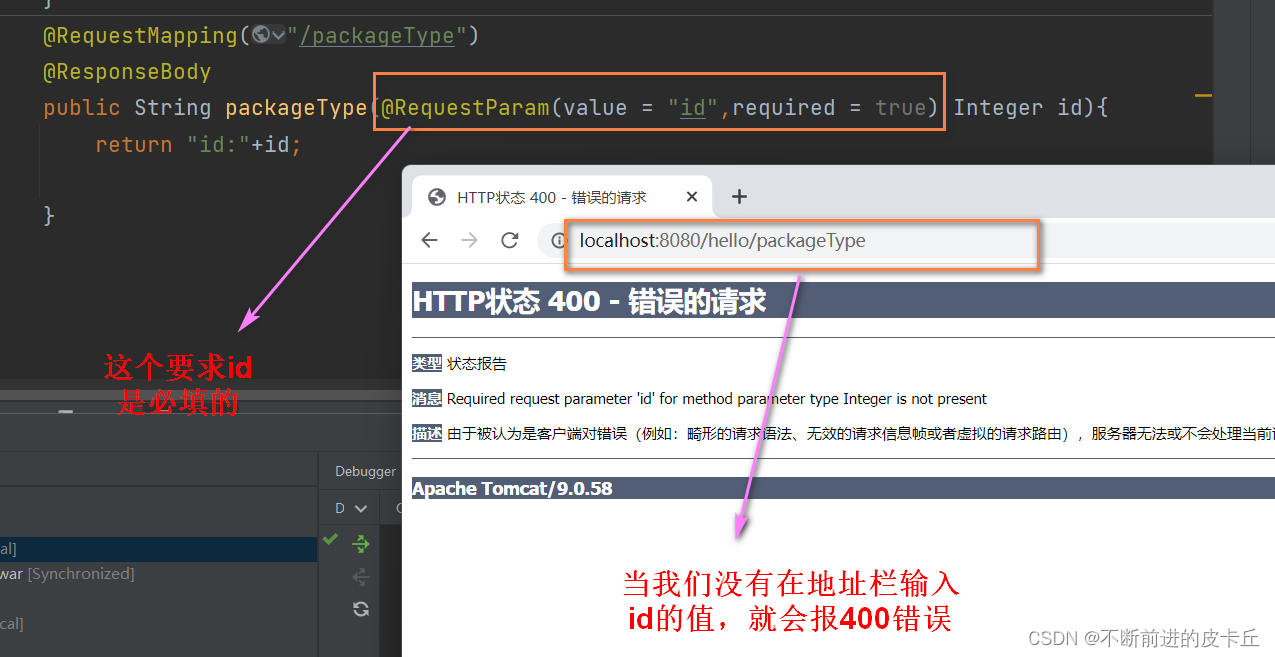
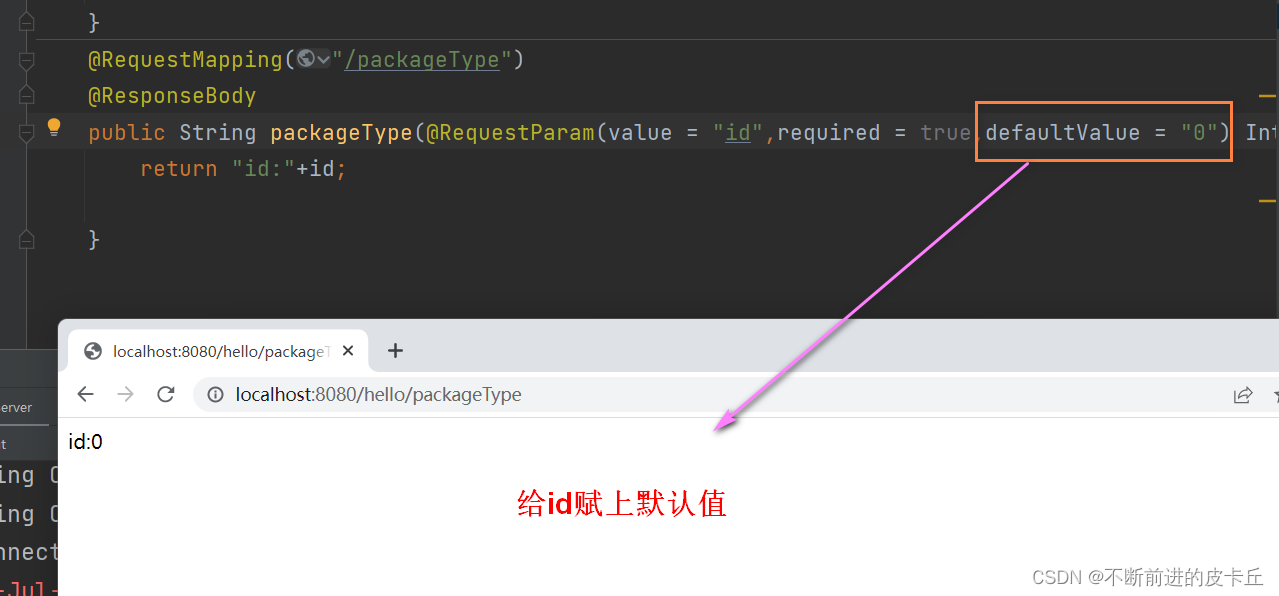
@RequestMapping("/packageType")
@ResponseBody
public String packageType(Integer id){
return "id:"+id;
}
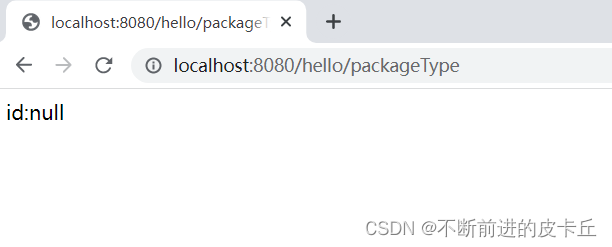
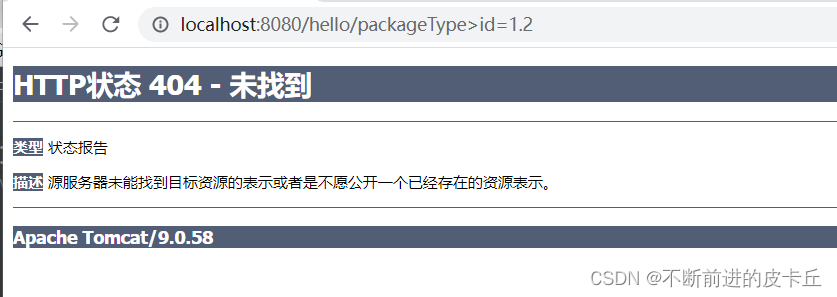
如果HTPP请求中没有包含id参数,不会报错,id的值就是null,会直接返回id:null给客户端,但是如果id=a,或者id=1.2,同样会抛出400异常,因为数据类型无法转换
- value=“id”:把HTTP请求中名字为id的参数和Handler业务方法中的形参进行映射
- required:true表示id参数必须填,false表示非必填
- defaultValue=“0”:表示当HTTP请求中没有id参数的时候,形参的默认值是0
6.3数组类型
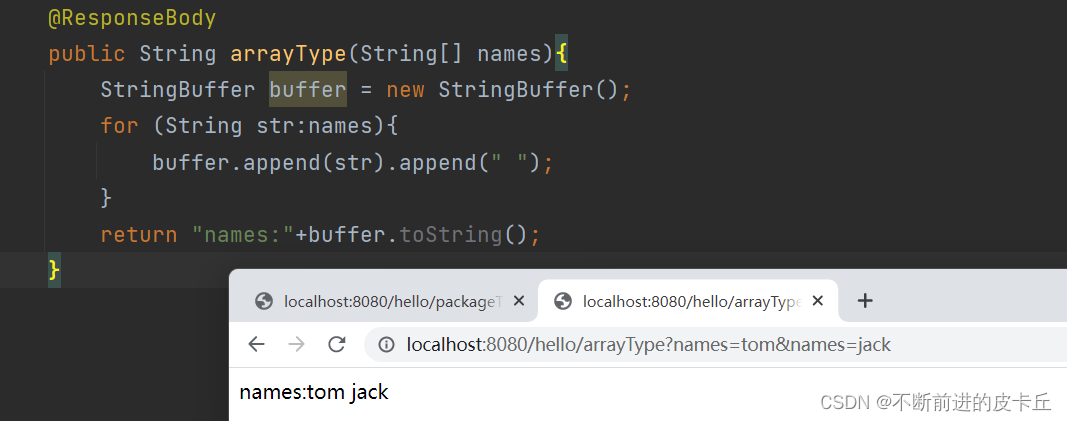
@RequestMapping("/arrayType")
@ResponseBody
public String arrayType(String[] names){
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
for (String str:names){
buffer.append(str).append(" ");
}
return "names:"+buffer.toString();
}
6.4POJO(java对象)
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Address {
private Integer code;
private String value;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"code=" + code +
", value='" + value + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 17614
Date: 2022-07-04
Time: 21:01
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/hello/add" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="id">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>姓名:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="name">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>地址编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="address.code">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>地址信息:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="address.value">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
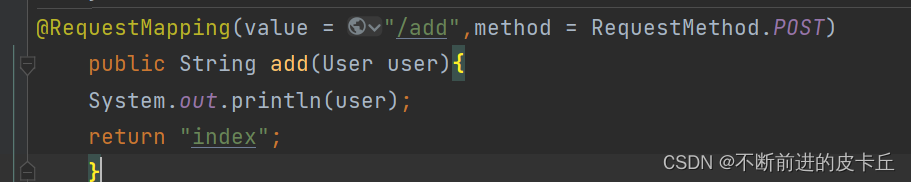
我们如果希望直接把User对象返回给浏览器展示的话
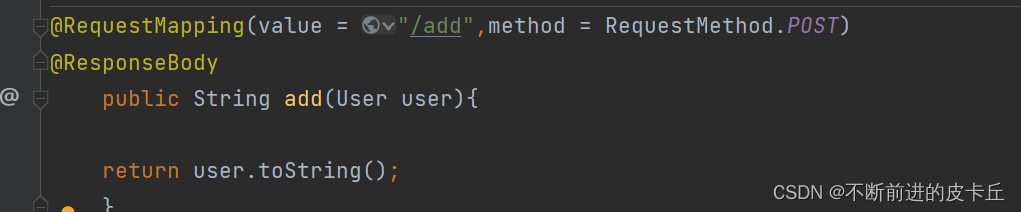

我们可以在springmvc.xml中添加一个消息转换器把中文乱码解决掉
前后端转换的数据称为消息
解决响应时乱码问题,springmvc.xml中配置转换器即可
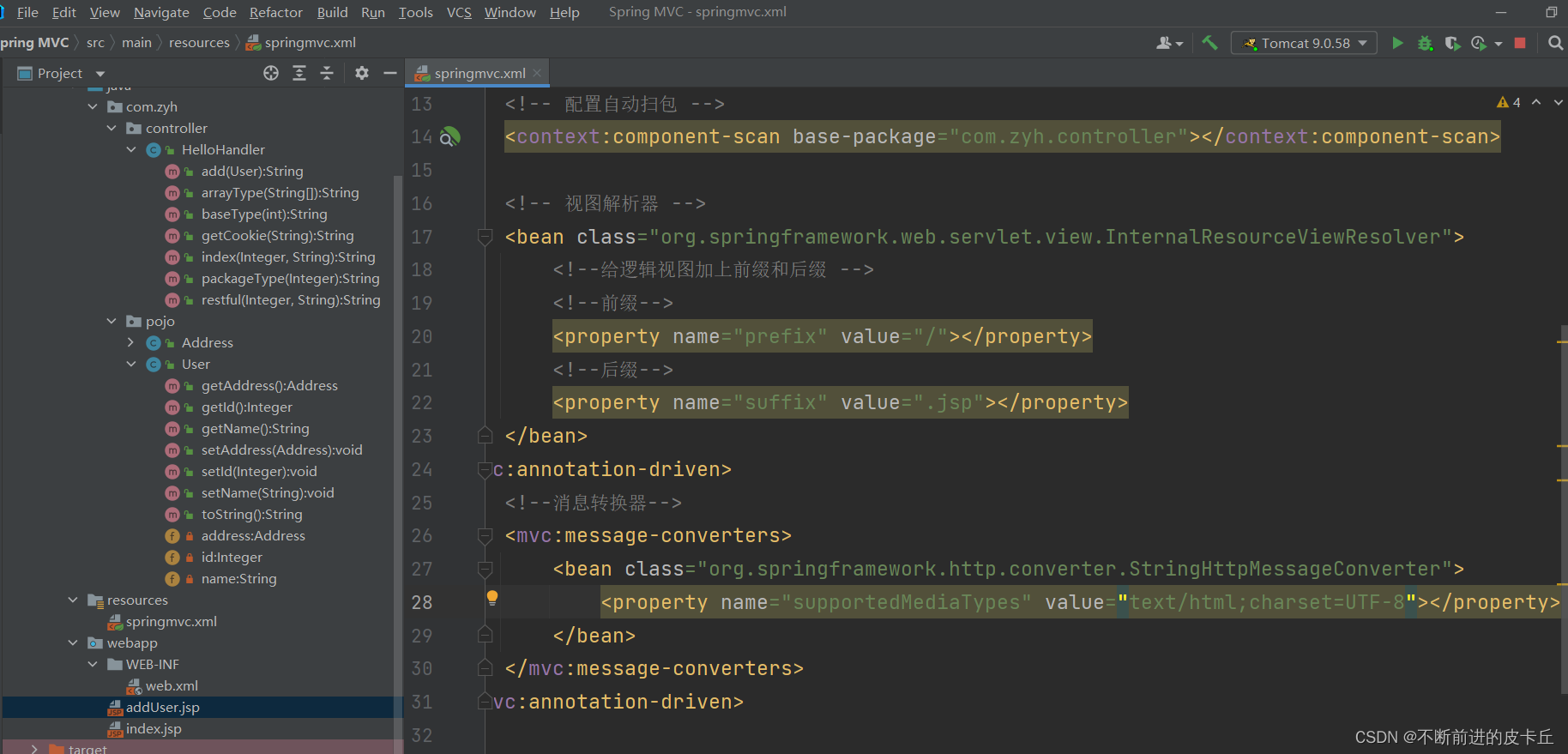
总结一下关于乱码的问题

6.5List
Spring MVC不支持List类型的直接转换,需要包装成Object
public class UserList {
private List<User> userList;
public List<User> getUserList() {
return userList;
}
public void setUserList(List<User> userList) {
this.userList = userList;
}
}
@RequestMapping("/listType")
@ResponseBody
public String listType(UserList userList){
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
for (User user:userList.getUserList()){
buffer.append(user);
}
return "用户:"+buffer.toString();
}
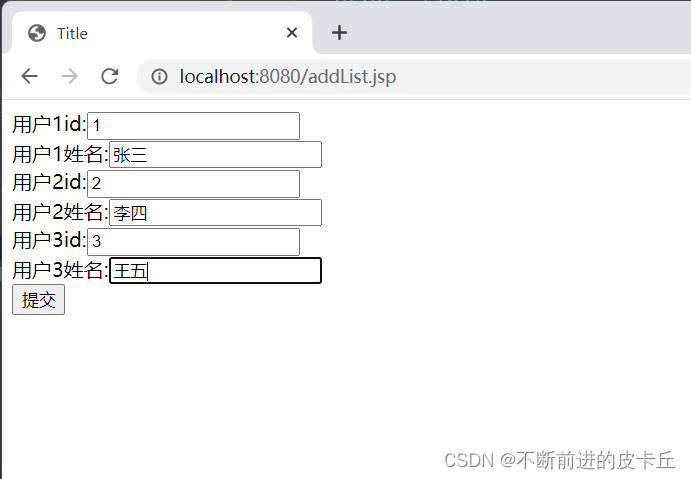
为了方便测试,我们要写一个表单
addList.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/hello/listType" method="post">
用户1id:<input type="text" name="userList[0].id"><br>
用户1姓名:<input type="text" name="userList[0].name"><br>
用户2id:<input type="text" name="userList[1].id"><br>
用户2姓名:<input type="text" name="userList[1].name"><br>
用户3id:<input type="text" name="userList[2].id"><br>
用户3姓名:<input type="text" name="userList[2].name"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
接下来进行测试
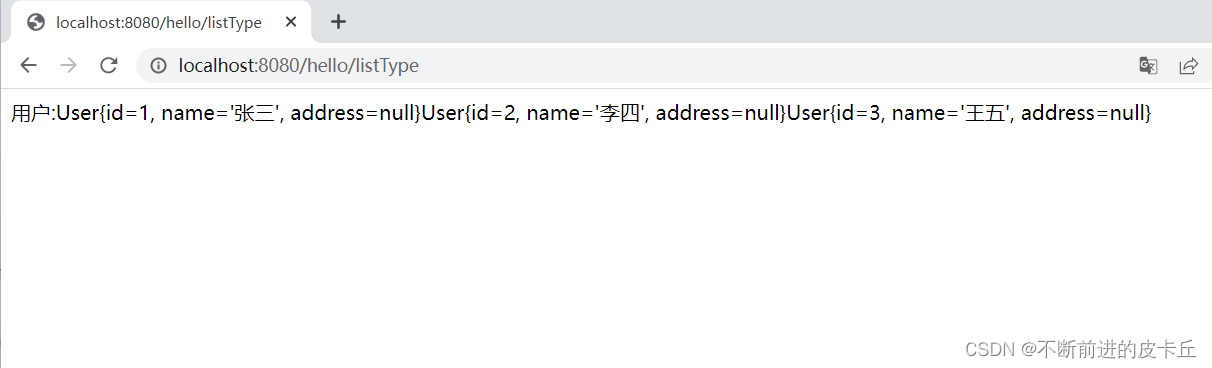
注意:User类一定要有无参构造,否则抛出异常
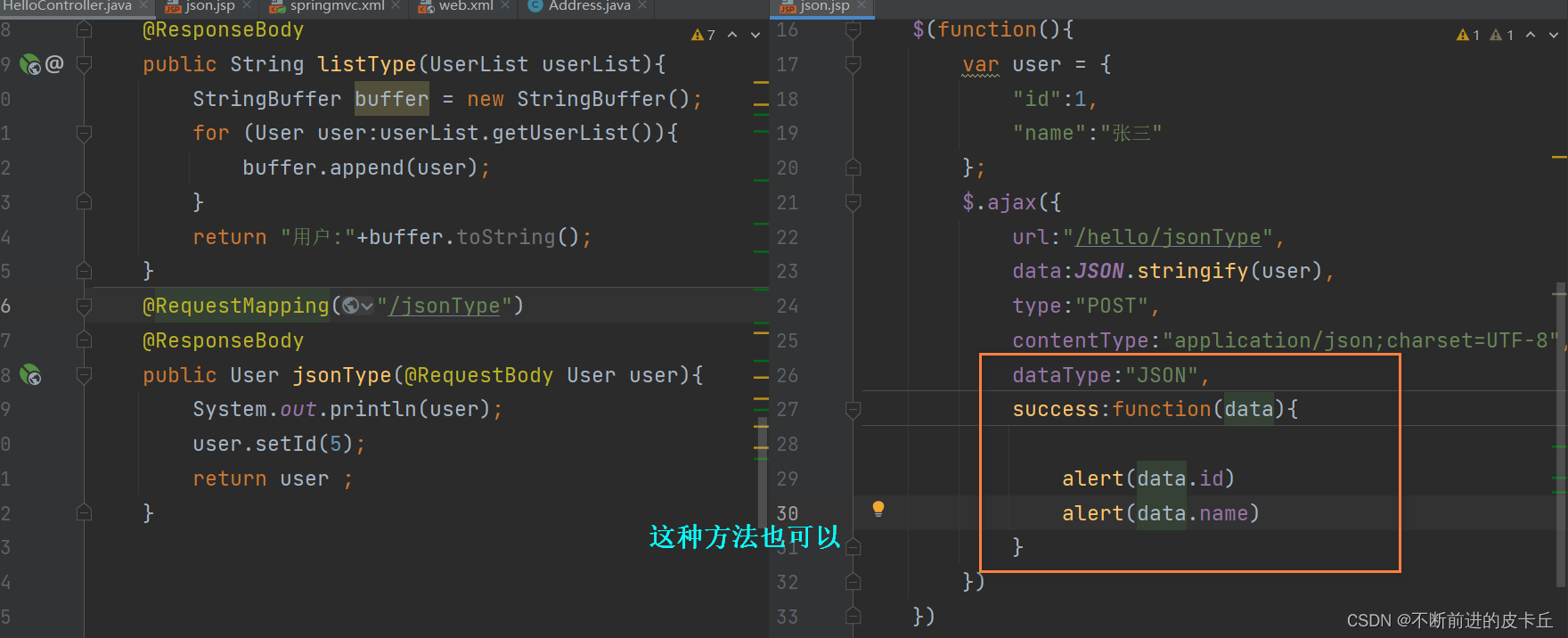
6.6JSON
- JSON数据必须用JSON.stringfy()方法转换成字符串
- contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8"不能省略
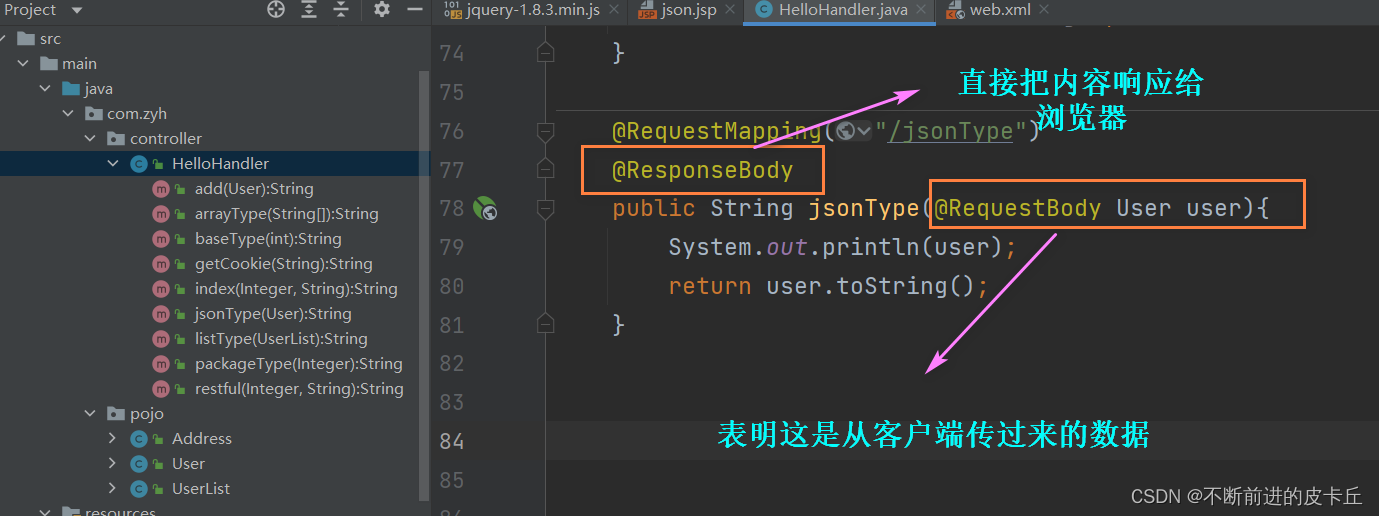
- @RequestBody注解
- 读取HTTP请求参数,通过Spring MVC提供的HttpMessageConverter接口把读取的参数转换为JSON、XML格式的数据,绑定到业务方法的形参
- 需要使用组件结合@RequestBody注解把JSON转为JavaBean,这里使用FastJson,其优势是如果属性为空,就不会将其转为JSON
- @ResponseBody注解
- 把业务方法返回的对象,通过HttpMessageConverter接口转为指定格式的数据,JSON、XML等,响应给客户端
因为要用到jQuery,所以,先把相关代码写进来,因为代码很长,我这边就不展示出来了
为了测试jQuery代码能不能使用,写一个json.jsp,然后在jsp中引入进来,写一个简单的代码测试一下
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.8.3.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function (){
alert(123);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
启动服务器
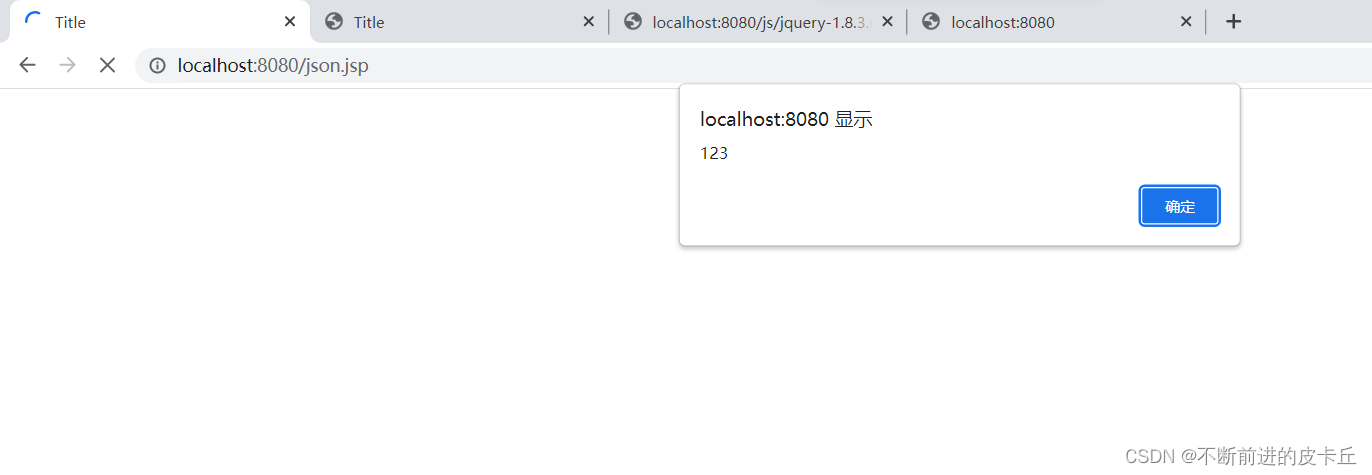
如果,访问的时候,能够弹框123,说明jQuery可以使用,否则说明无法使用
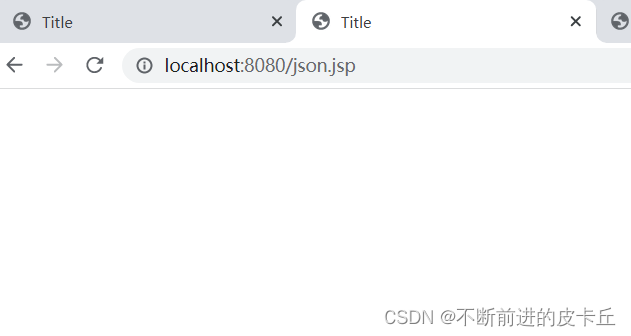
我们可以看到并没有弹窗,说明应该是哪里出了问题,jsp代码没有问题,问题应该是jQuery没有引进来,我们可以在浏览器用F12,检查一下
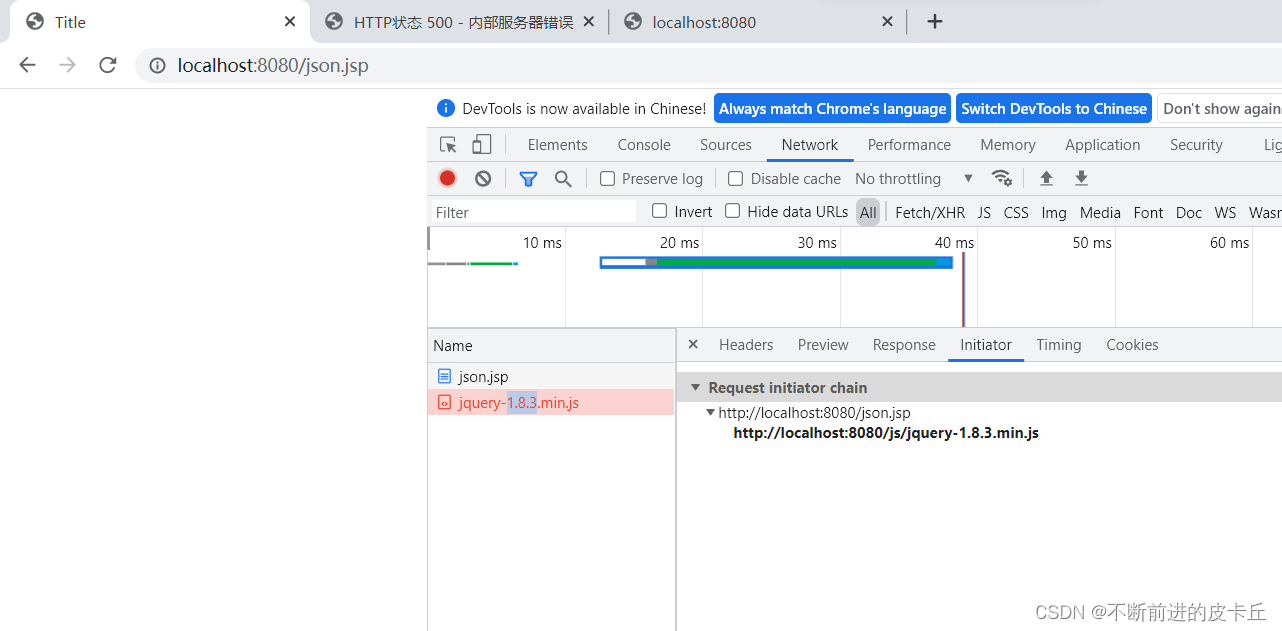
发现json.jsp没有问题,问题出在jQuery上面,报500错误
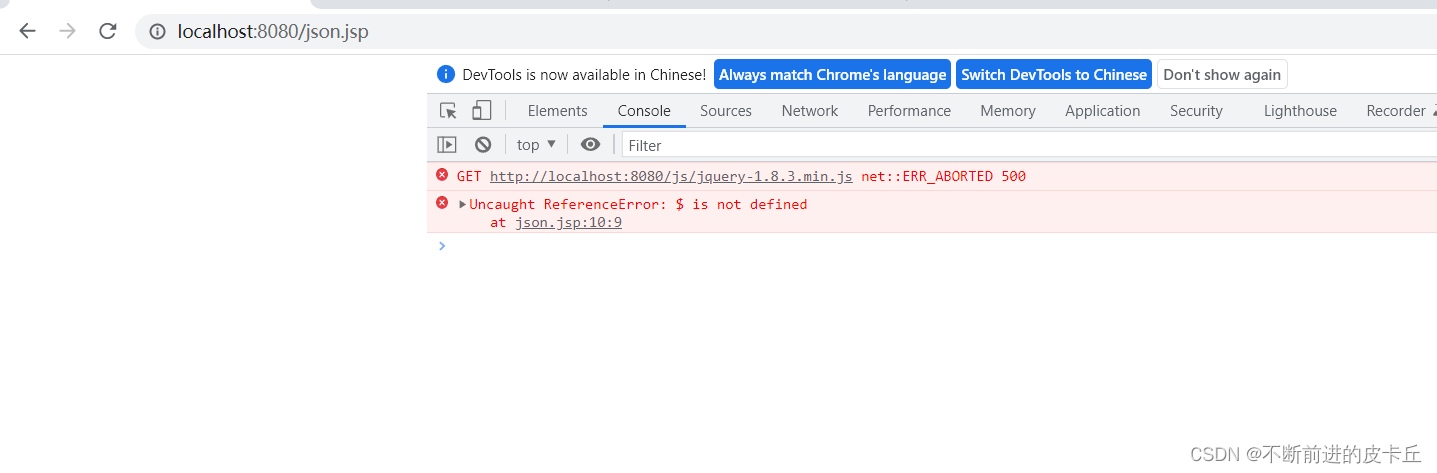
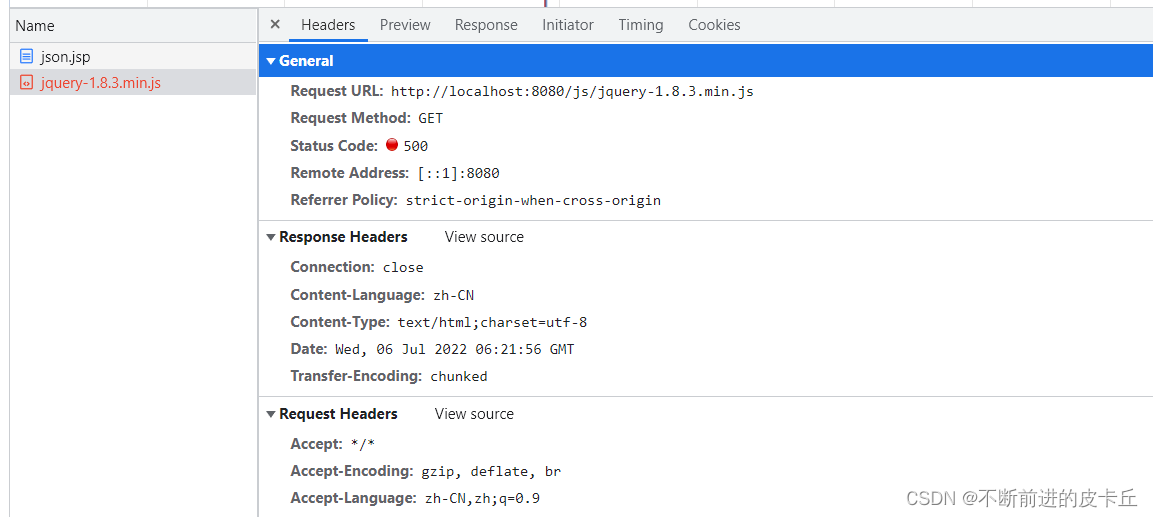
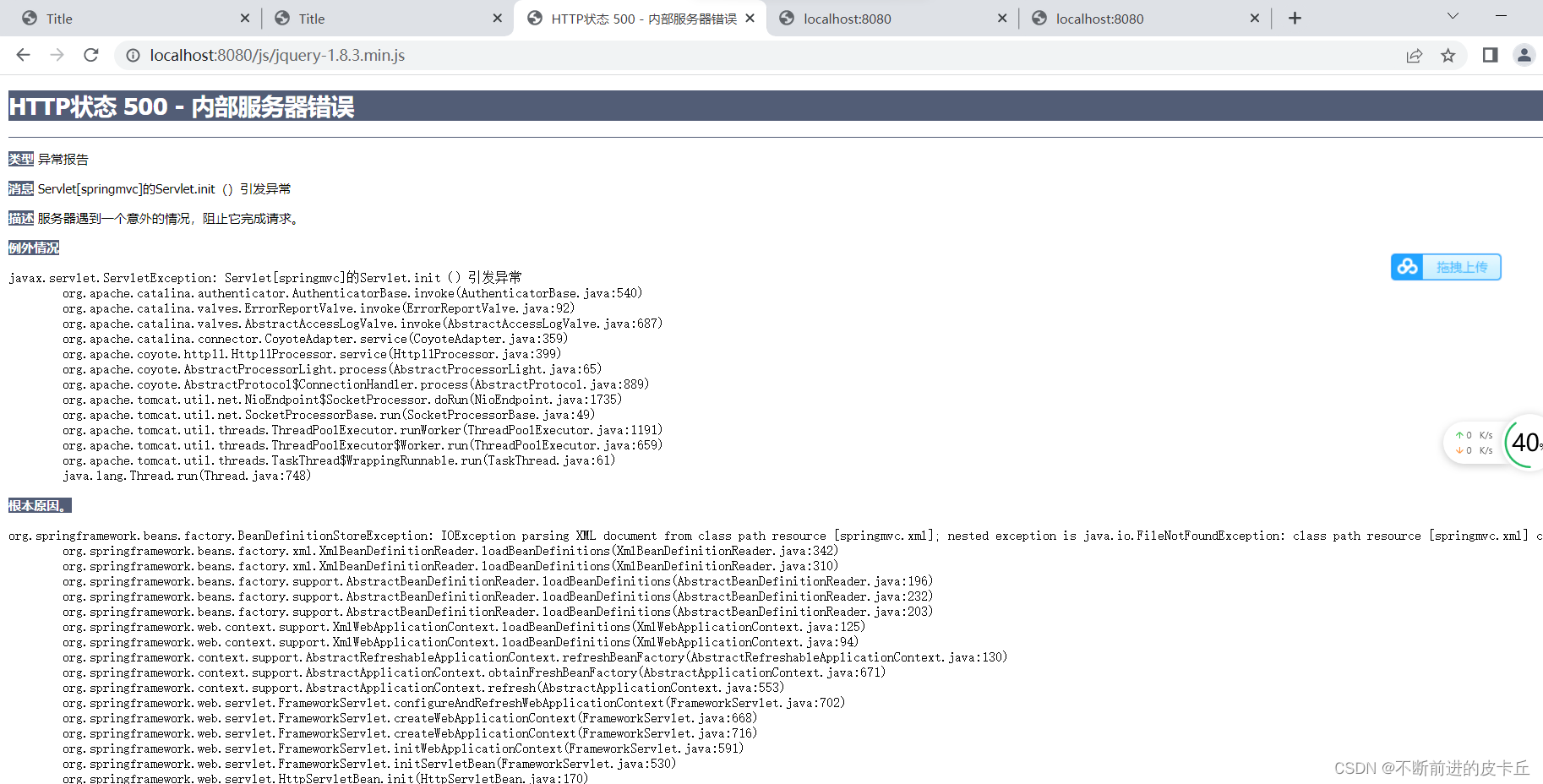
分析一下原因,因为我们刚开始在web.xml中,配置的是所有的请求都会被DispatcherServlet拦截映射,但是现在我们访问的是实际存在的资源,逻辑请求需要映射,但是物理请求是不需要映射的。这个时候,它会把我们的物理请求也进行映射,在配置文件加上下面的代码就可以了
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.js</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
解决好上面的问题后,我们就可以开始写代码了
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.8.3.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
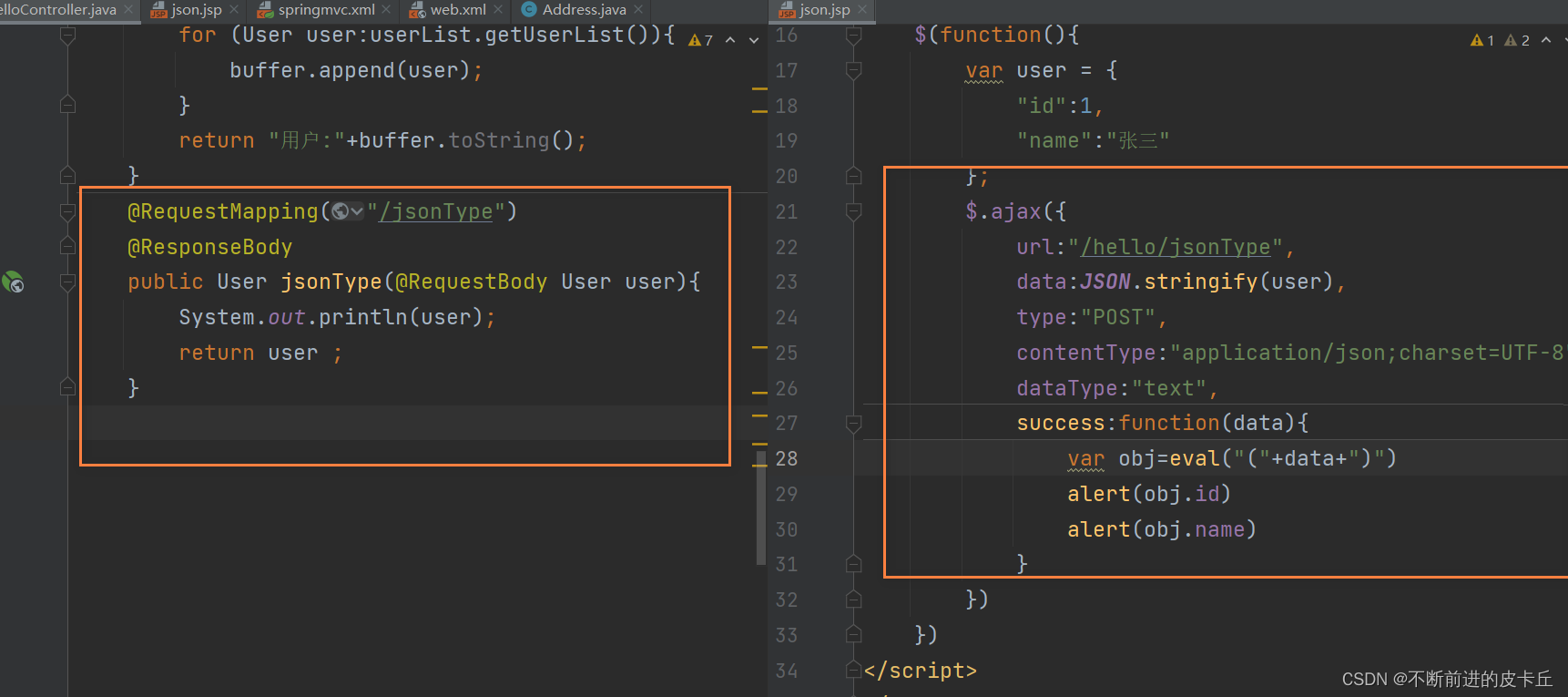
$(function(){
var user = {
"id":1,
"name":"张三"
};
$.ajax({
url:"/hello/jsonType",
data:JSON.stringify(user),
type:"POST",
contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8",
dataType:"text",
success:function(data){
alert(data.id)
alert(data.name)
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
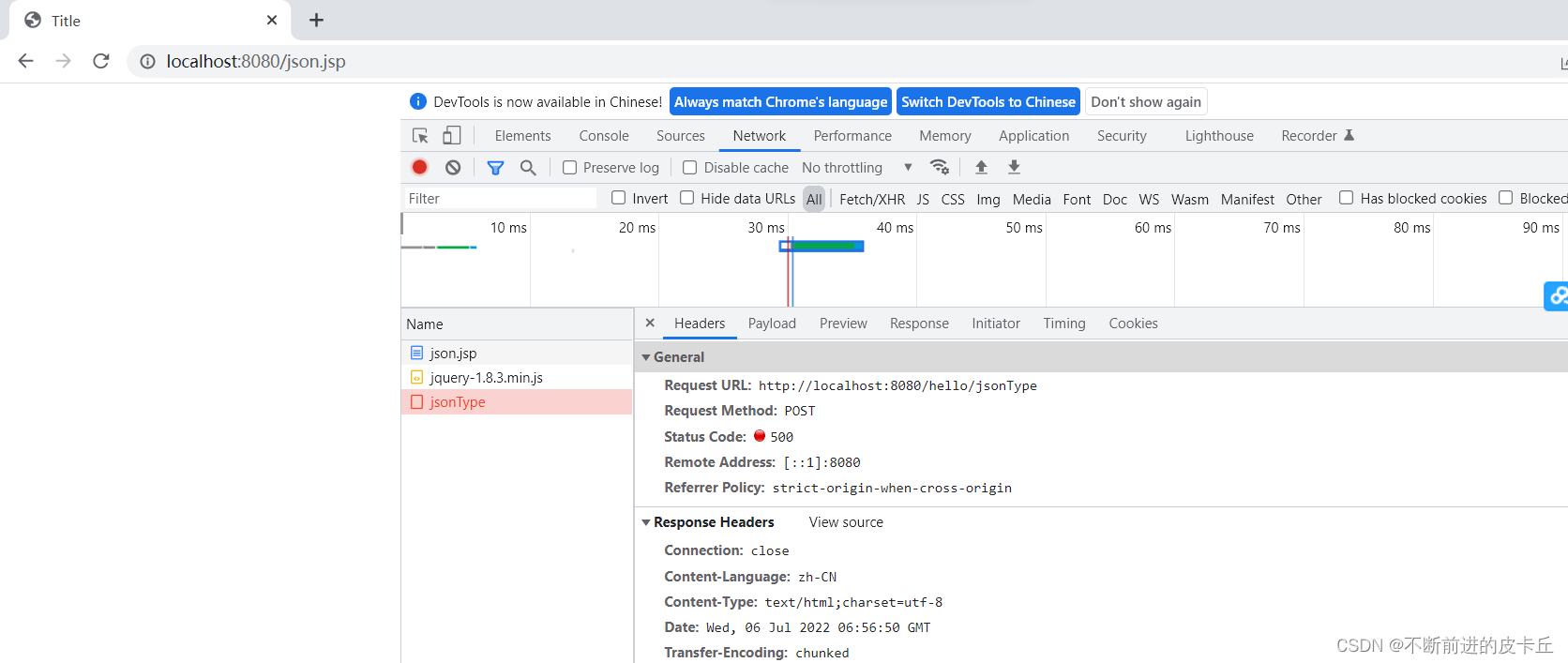
我们发现出错了,打断点发现此时Ajax请求没有进入到我们刚刚写的方法。
因为我们现在传的参数是json格式的,json格式就需要我们在后端把json格式解析成Java对象,这里我们仅仅加上@RequestBody注解是不够的,我们需要借助第三方工具把json解析成Java对象,这里用到的工具是fastjson,所以我们要在pom.xml中,把相关依赖导入进来
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.75</version>
</dependency>
导入进来后,还需要在springmvc的配置文件中进行配置
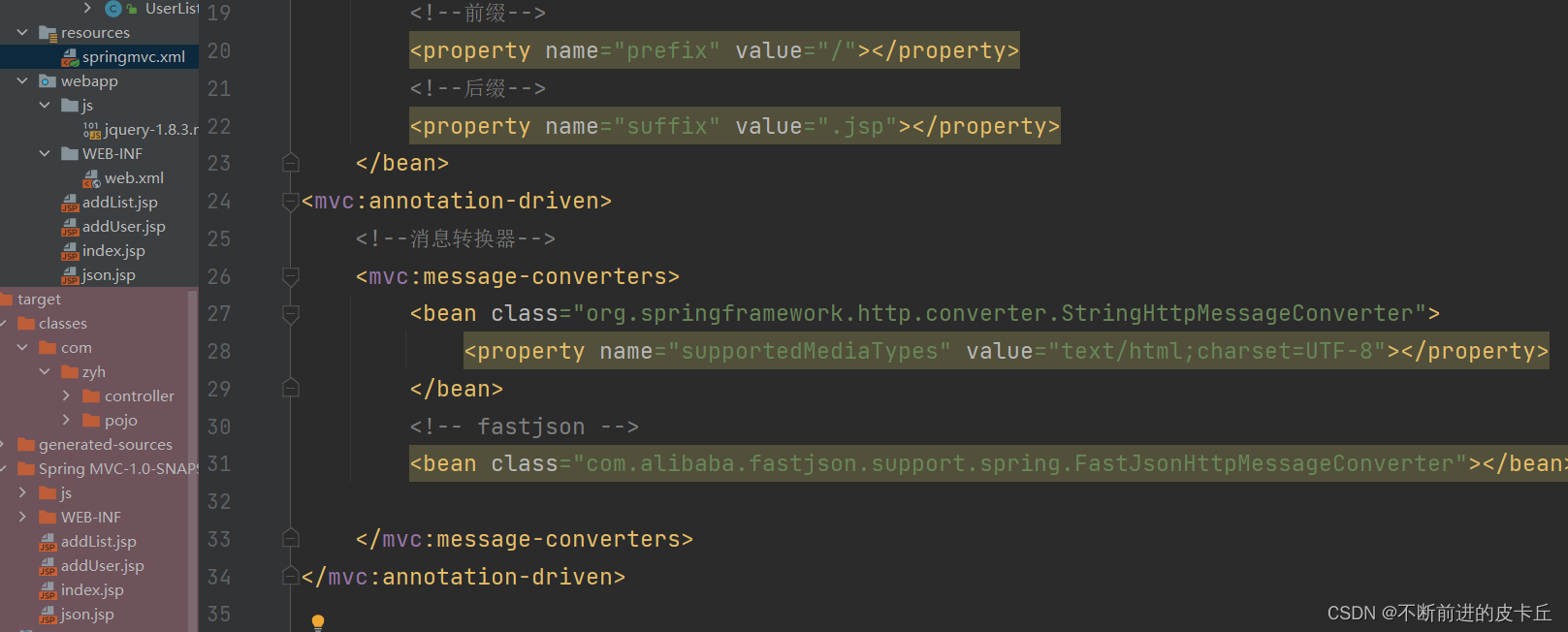
springmvc.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zyh.controller"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!--给逻辑视图加上前缀和后缀 -->
<!--前缀-->
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<!--后缀-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--消息转换器 -->
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8"></property>
</bean>
<!--fastjson -->
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
</beans>
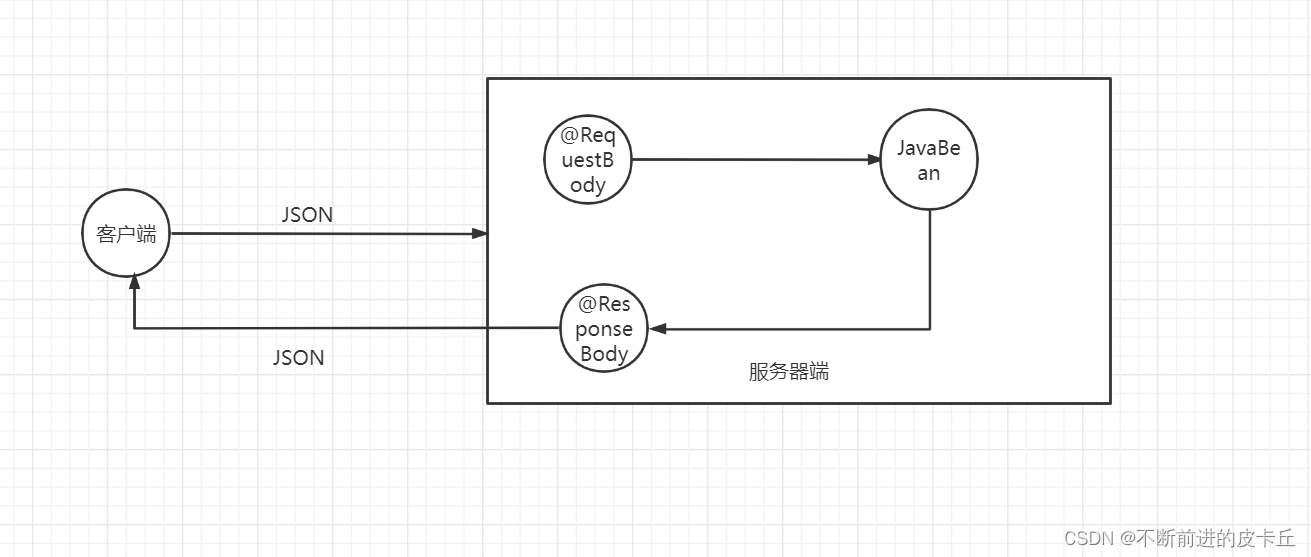
七、Spring MVC视图层解析
调用Web资源给域对象传值
- page
- request
- session
- application
业务数据的绑定是指把业务数据绑定给JSP域对象,业务数据的绑定是由ViewResolver来完成的,开发时,我们先添加业务数据,再交给ViewResolver来绑定,我们重点是学习如何添加业务数据,Spring MVC提供了下面几种方式来添加业务数据:
- Map
- Model
- ModelAndView
- @SessionAttribue
- @ModelAttribute
- Servlet的API
7.1业务数据绑定到request域对象
7.1.1Map
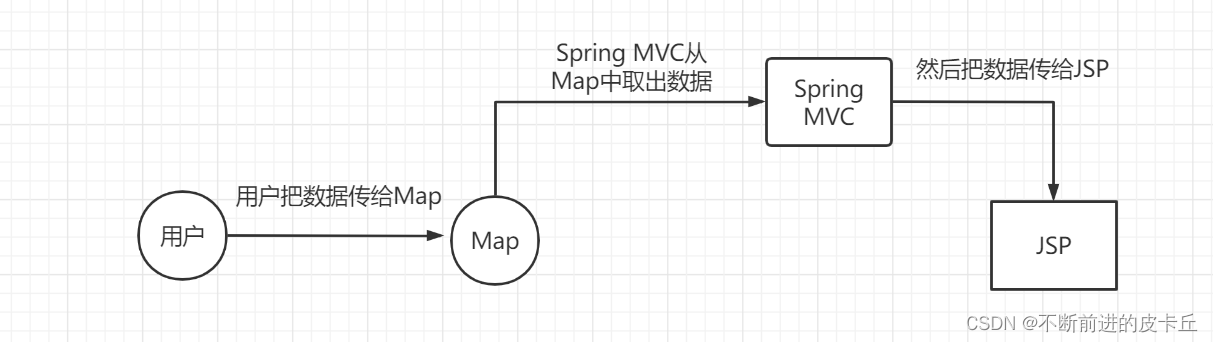
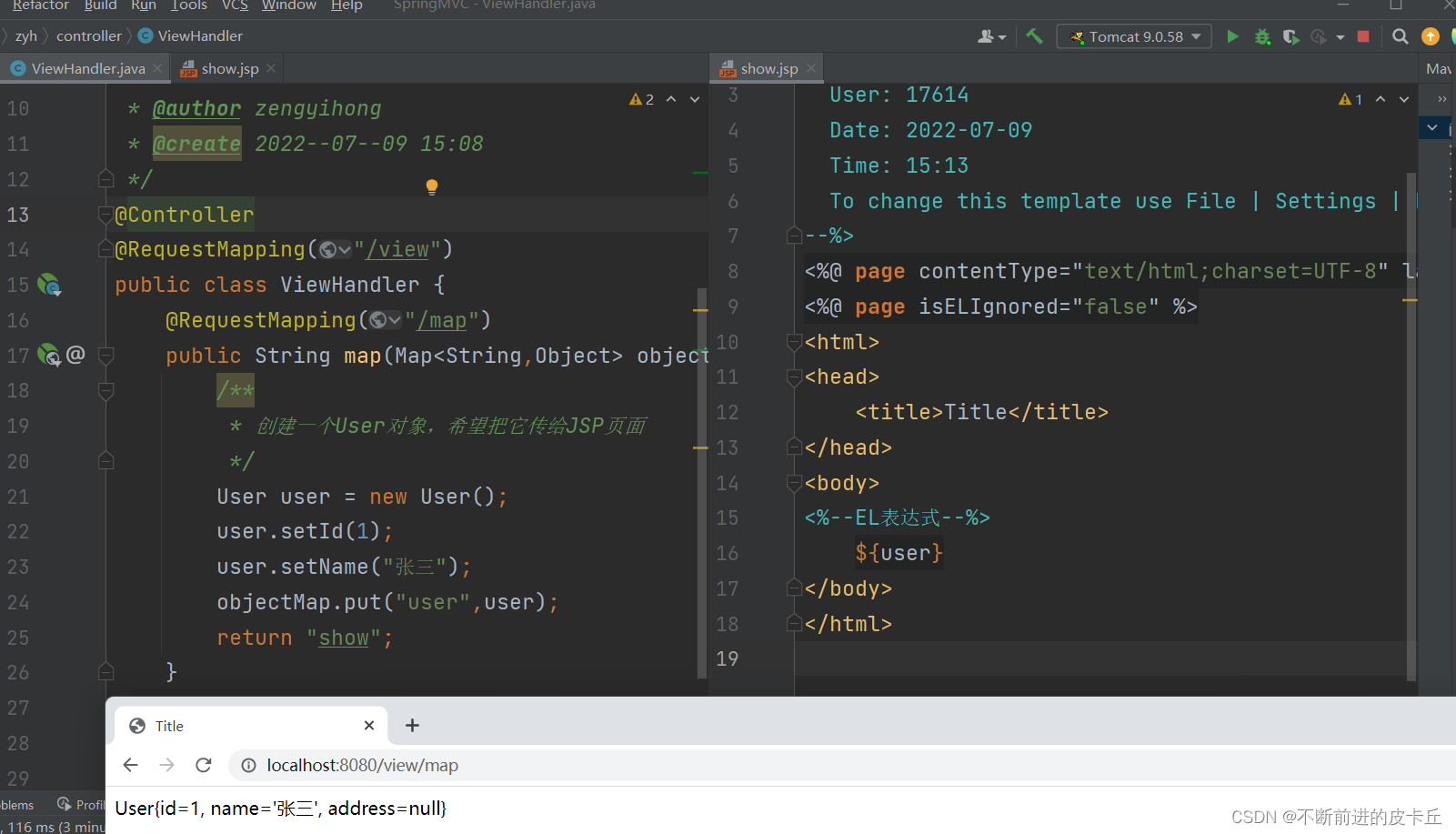
Spring MVC在调用业务方法之前会先创建一个隐含对象作为业务数据的存储容器,设置业务方法的入参为Map类型,Spring MVC会把隐含对象的引用传递给入参
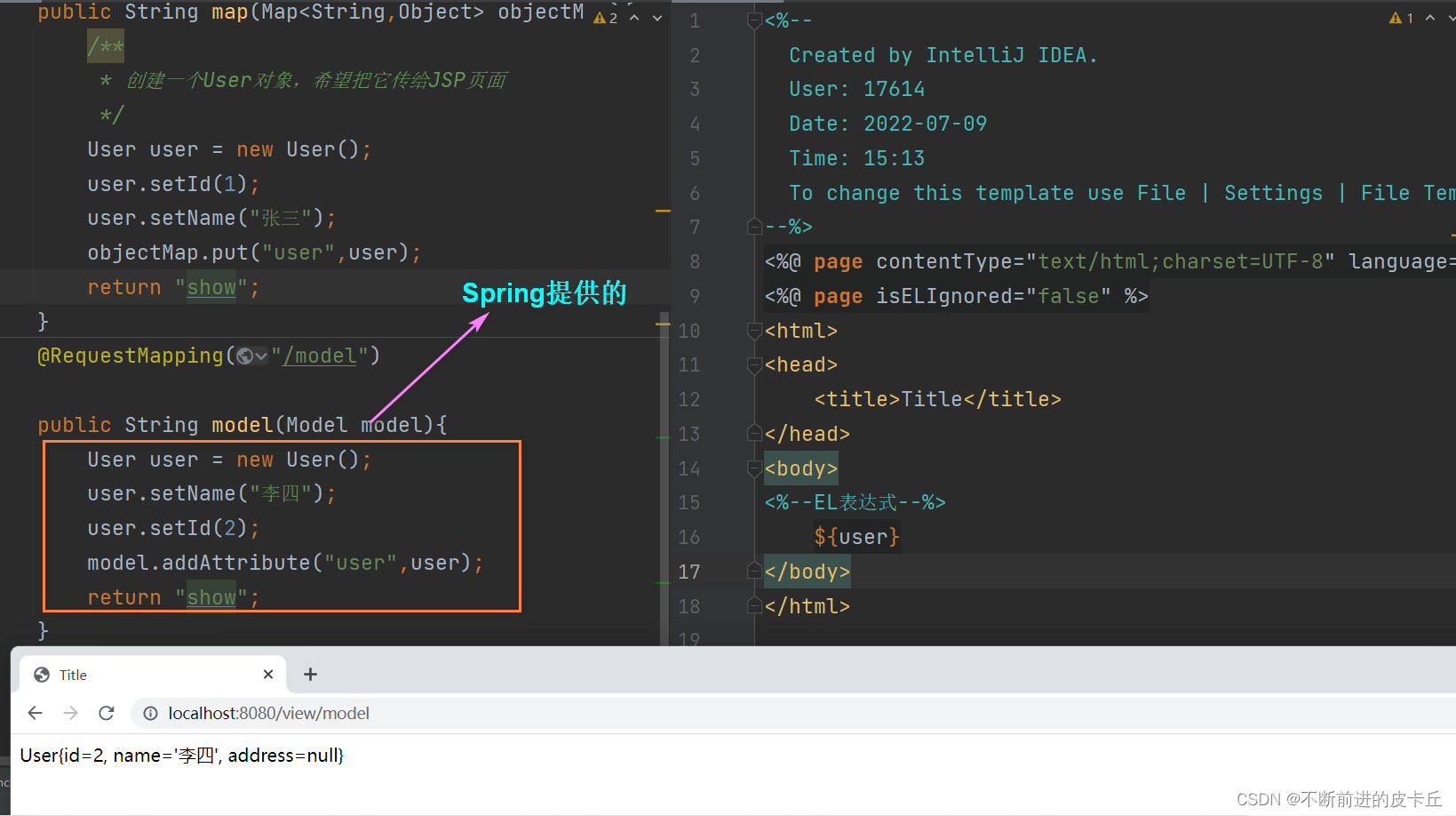
7.1.2 Model
Model和Map类似,业务方法通过入参来完成业务数据的绑定
7.1.3ModelAndView
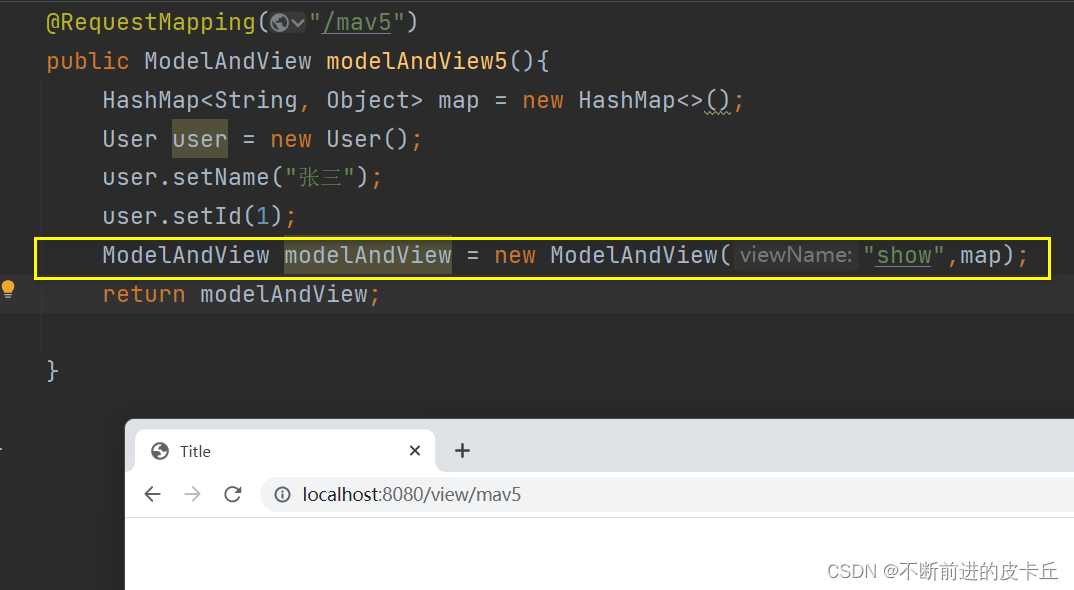
和Map,Model不同的是,ModelAndView不仅包含业务数据,同时也封装了视图信息,如果使用ModelAndView来处理业务数据,业务方法的返回值必须是ModelAndView对象
业务方法中对ModelAndView进行两个操作:
- 填充业务数据
- 绑定视图信息
第一种方式
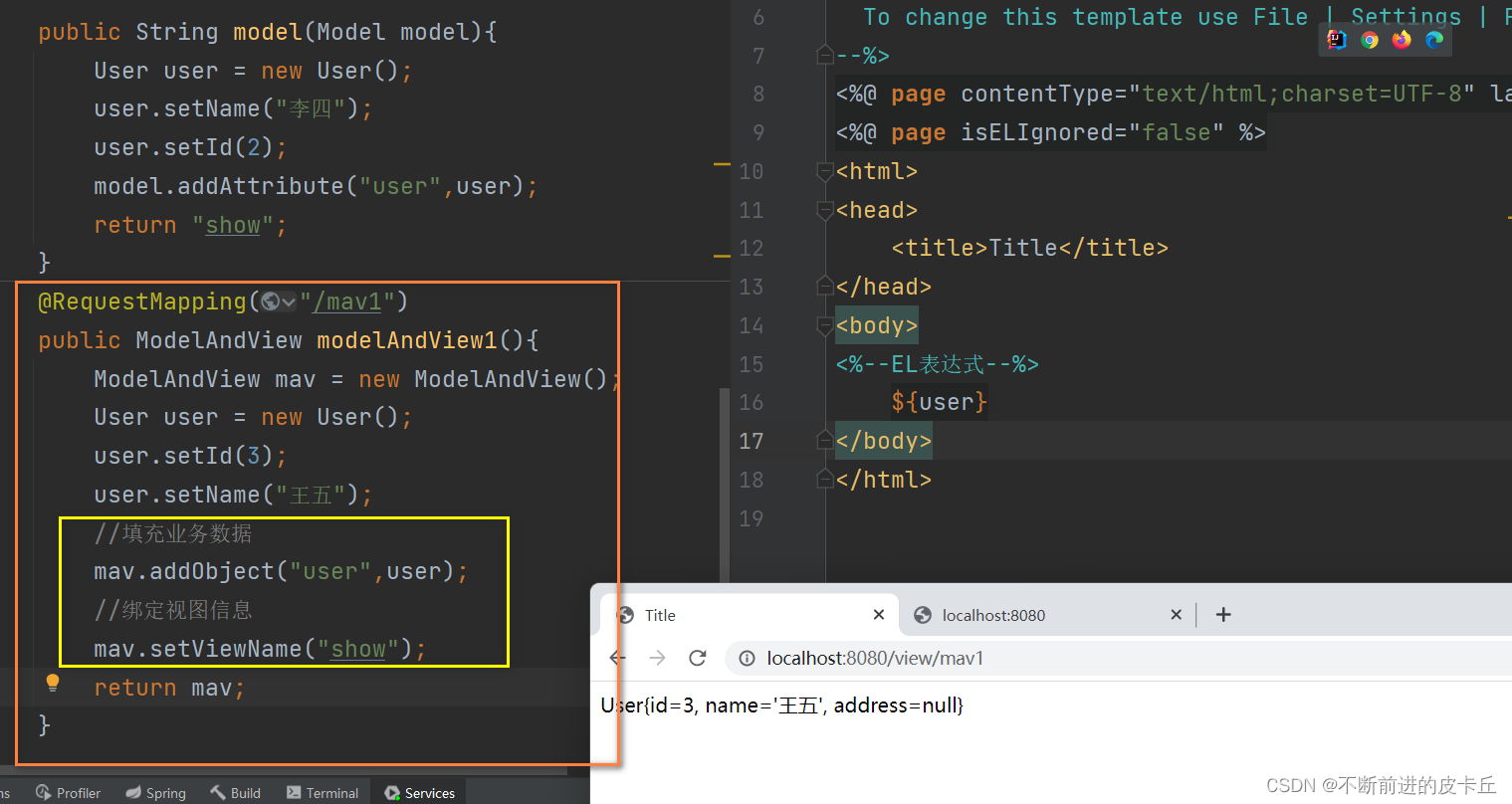
第二种方式
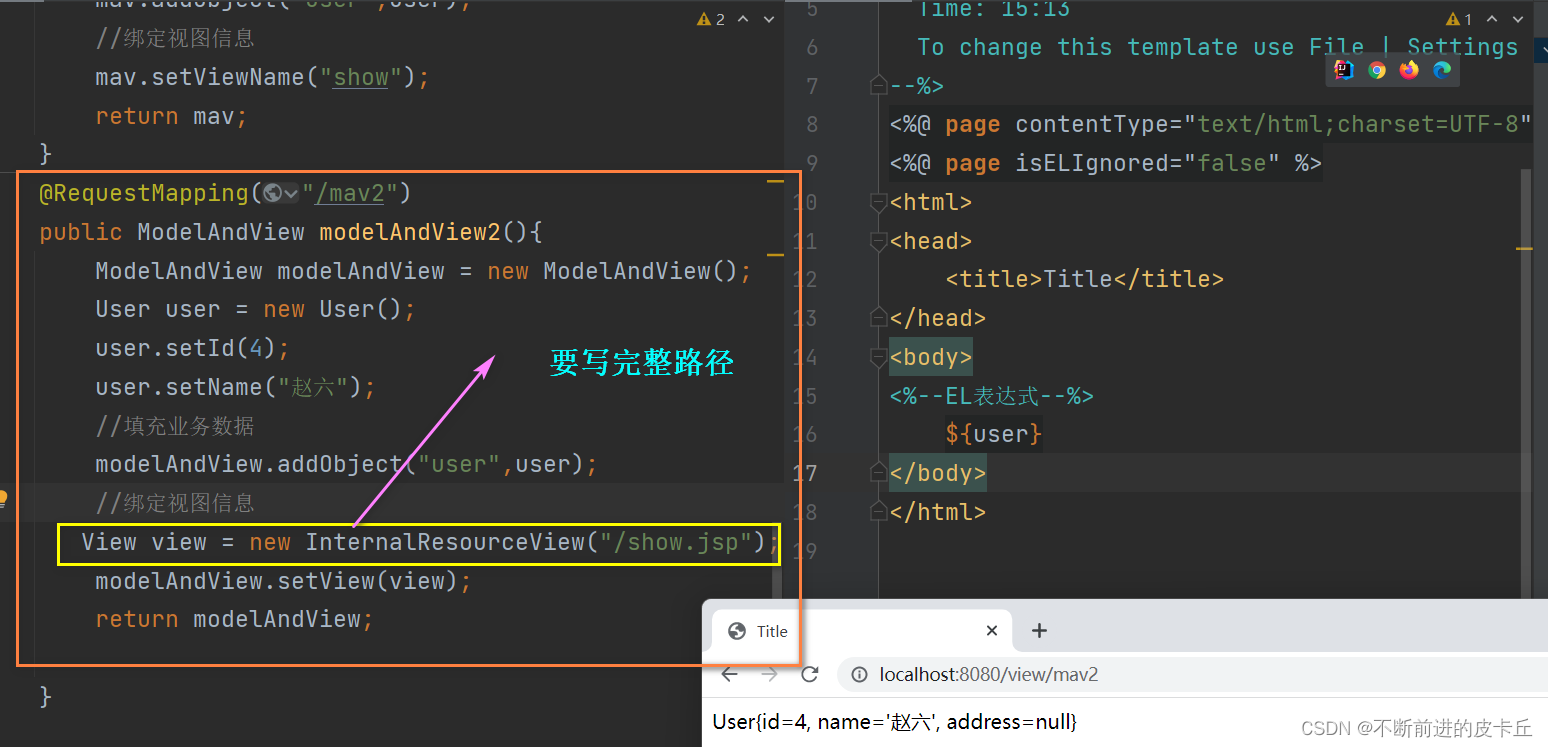
第三种方式
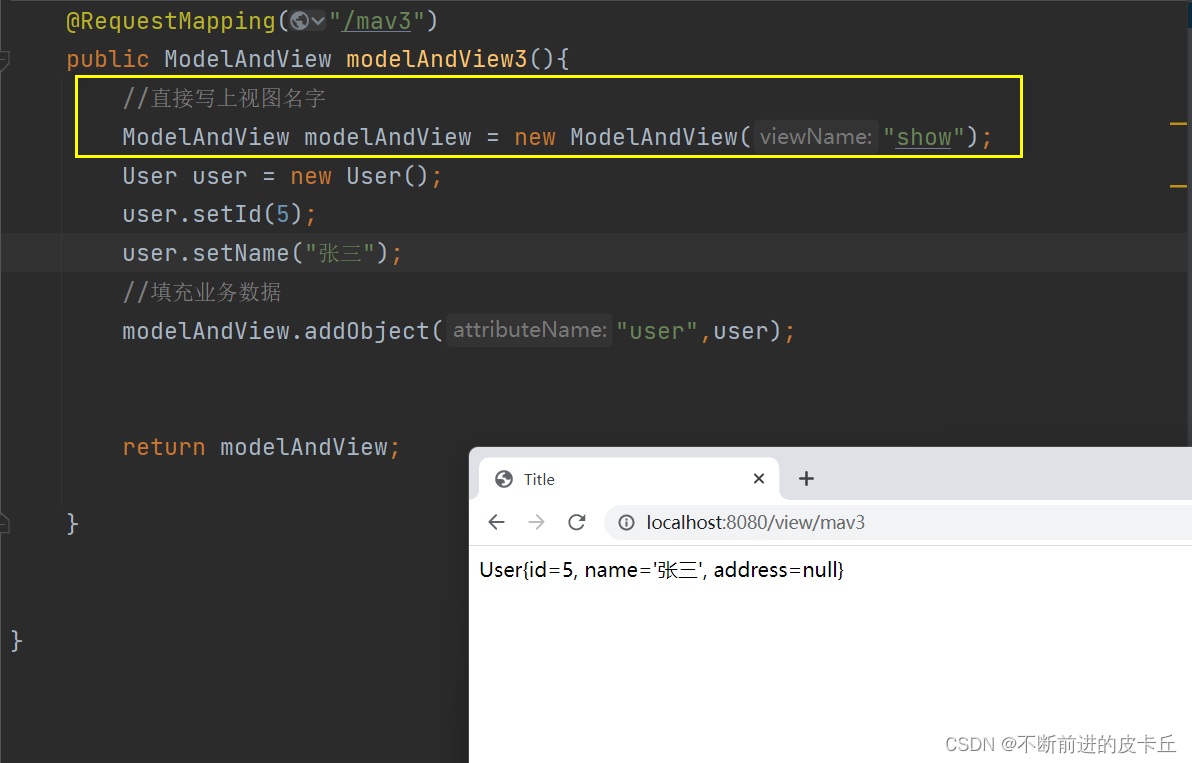
第四种方式
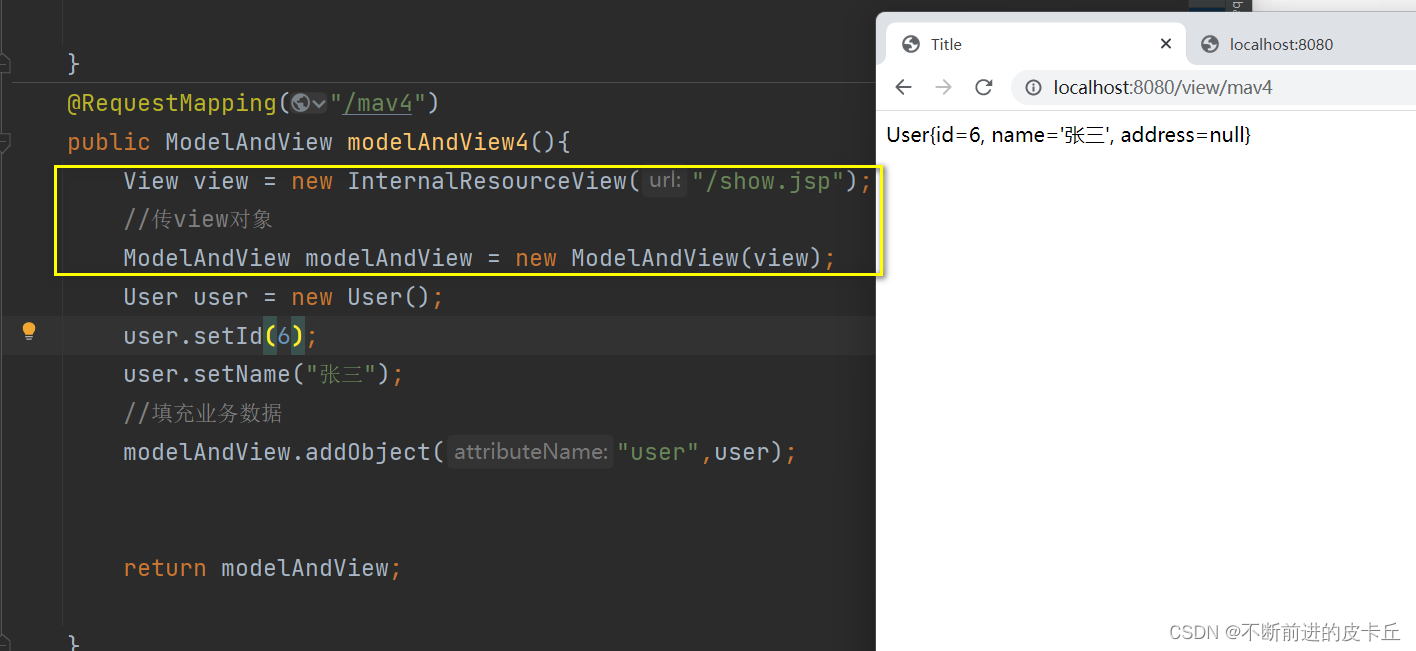
第五种方式
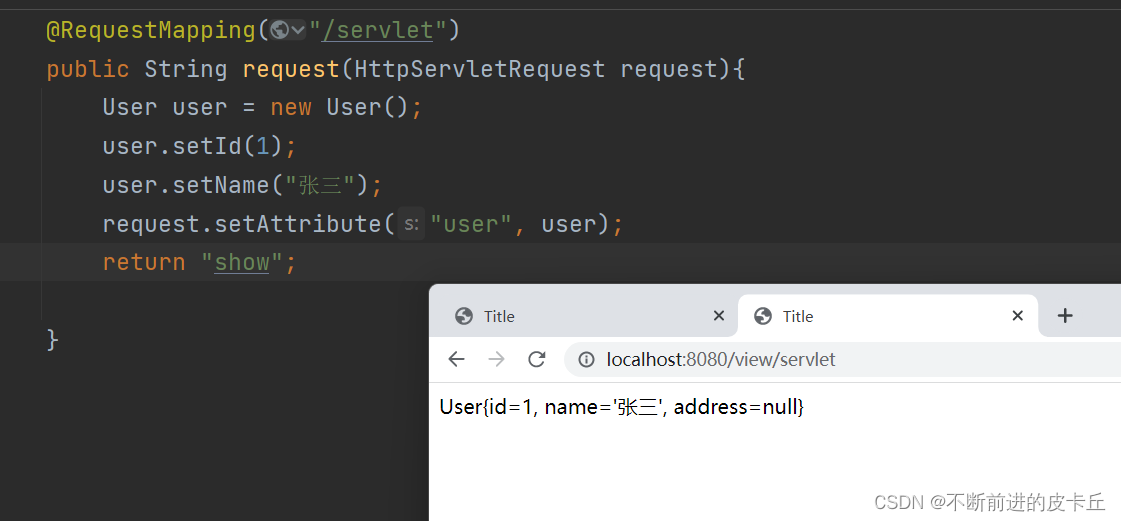
7.1.4 Servlet的API
Spring MVC可以在业务方法种直接获取Servlet原生Web资源,只需要在方法定义时添加HttpServletRequest输入参数就可以,在方法体种直接使用request对象
先在pom.xml导入相关依赖
<!--导入servlet API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
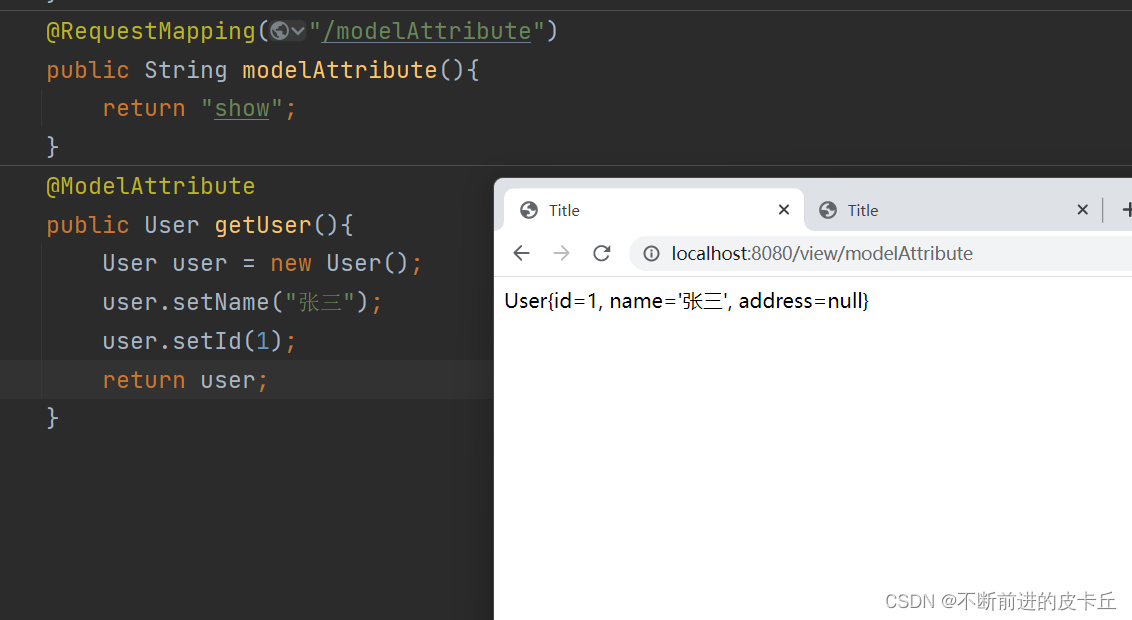
7.1.5@ModelAttribute
Spring MVC还可以通过@ModelAttribute注解的方式添加业务数据,具体使用步骤如下:
- 定义一个方法,这个方法用来填充到业务数据中的对象
- 给该方法添加@ModelAttribute注解,不是响应请求的业务方法
- @ModelAttribute注解的作用,将请求参数绑定到Model对象。被@ModelAttribute注释的方法会在Controller每个方法执行前被执行(如果在一个Controller映射到多个URL时,要谨慎使用)。
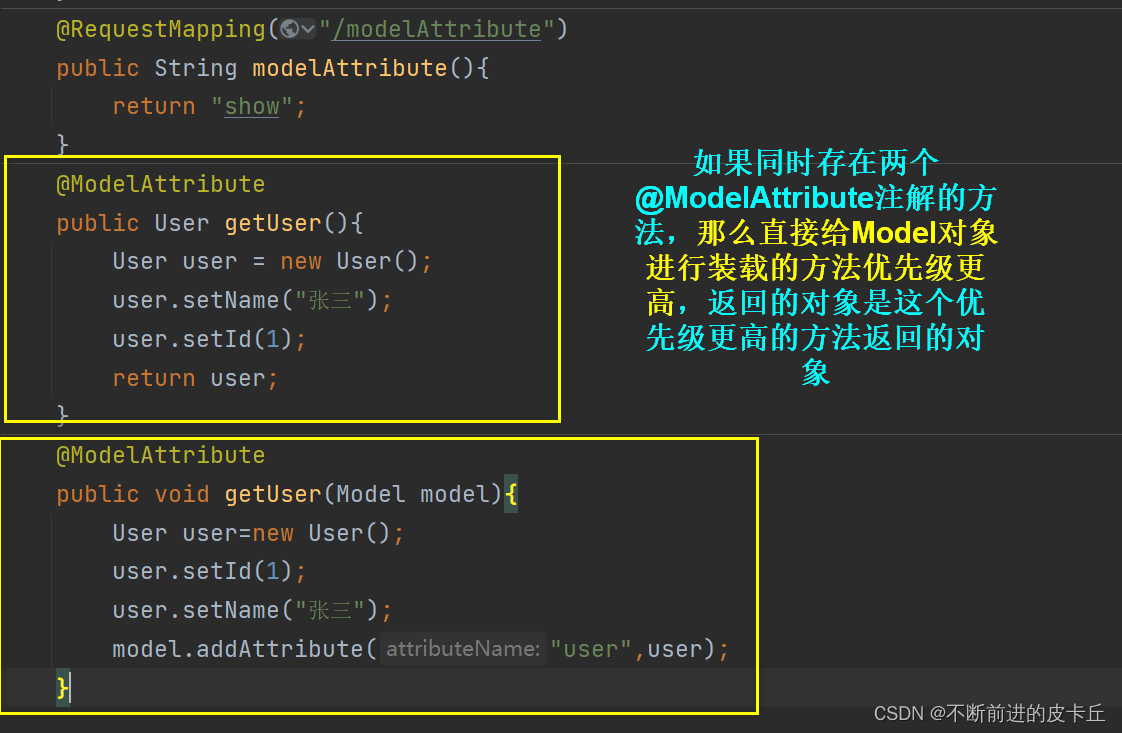
@ModelAttribute的作用是当Handler接收到一个客户端请求以后,不管调用哪一个业务方法,都会优先调用被@ModelAttribute注解修饰的方法,并且把其返回值作为业务数据,再到业务方法,此时业务方法只需要返回视图信息就可以了,不需要返回业务数据,即使返回业务数据,也会被@ModelAttribute注解修饰的方法返回的数据所覆盖
域中的对象以key-value的形式存储,此时key默认值是业务数据所对应的类的类名首字母小写以后的结果
如果getUser没有返回值,则必须手动在该方法中填充业务数据,使用Map或者Model均可。
@ModelAttribute
public void getUser(Model model){
User user=new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("张三");
model.addAttribute("user",user);
}
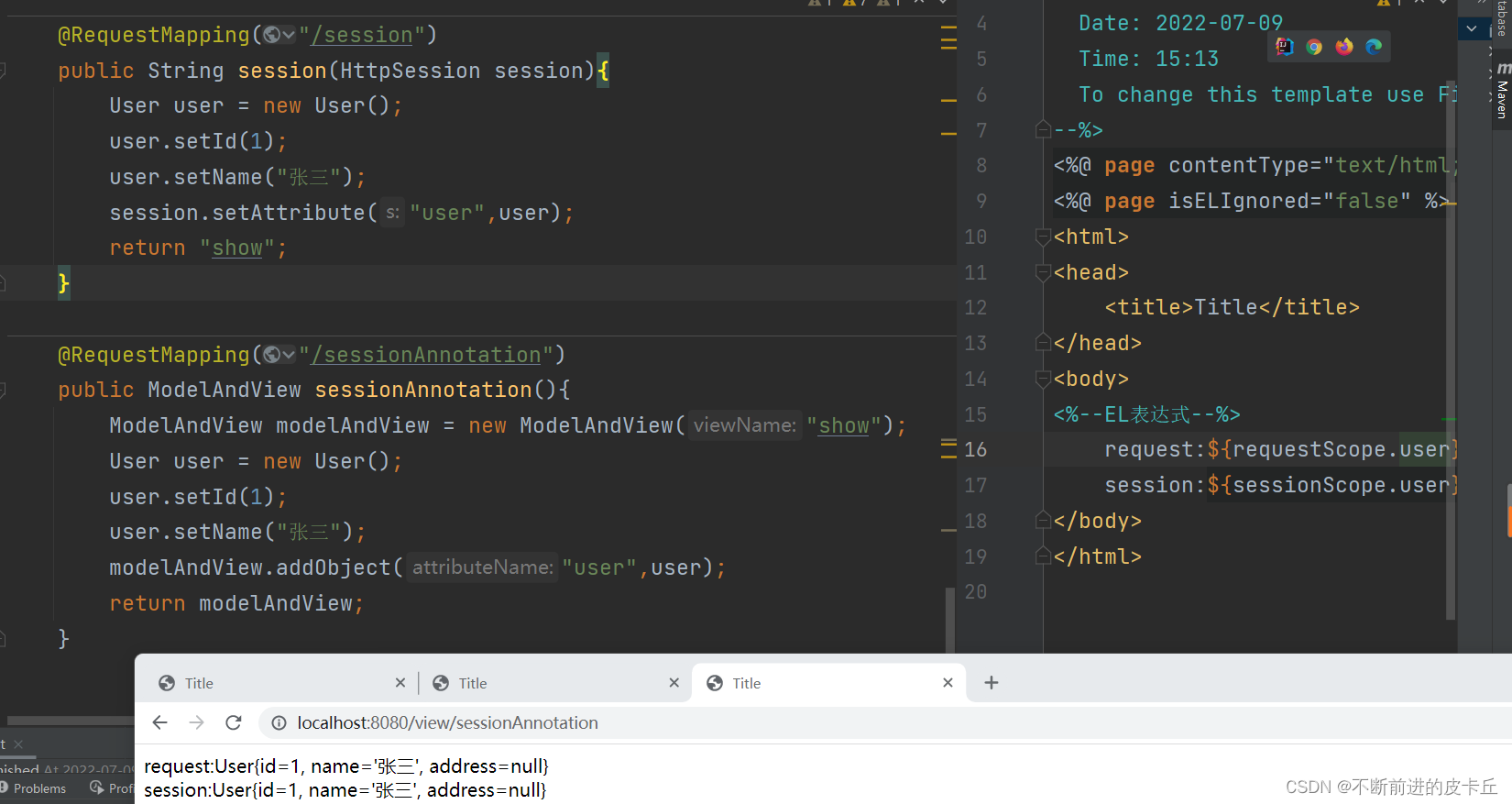
7.2业务数据绑定到Session域对象
7.2.1使用原生的Servlet API
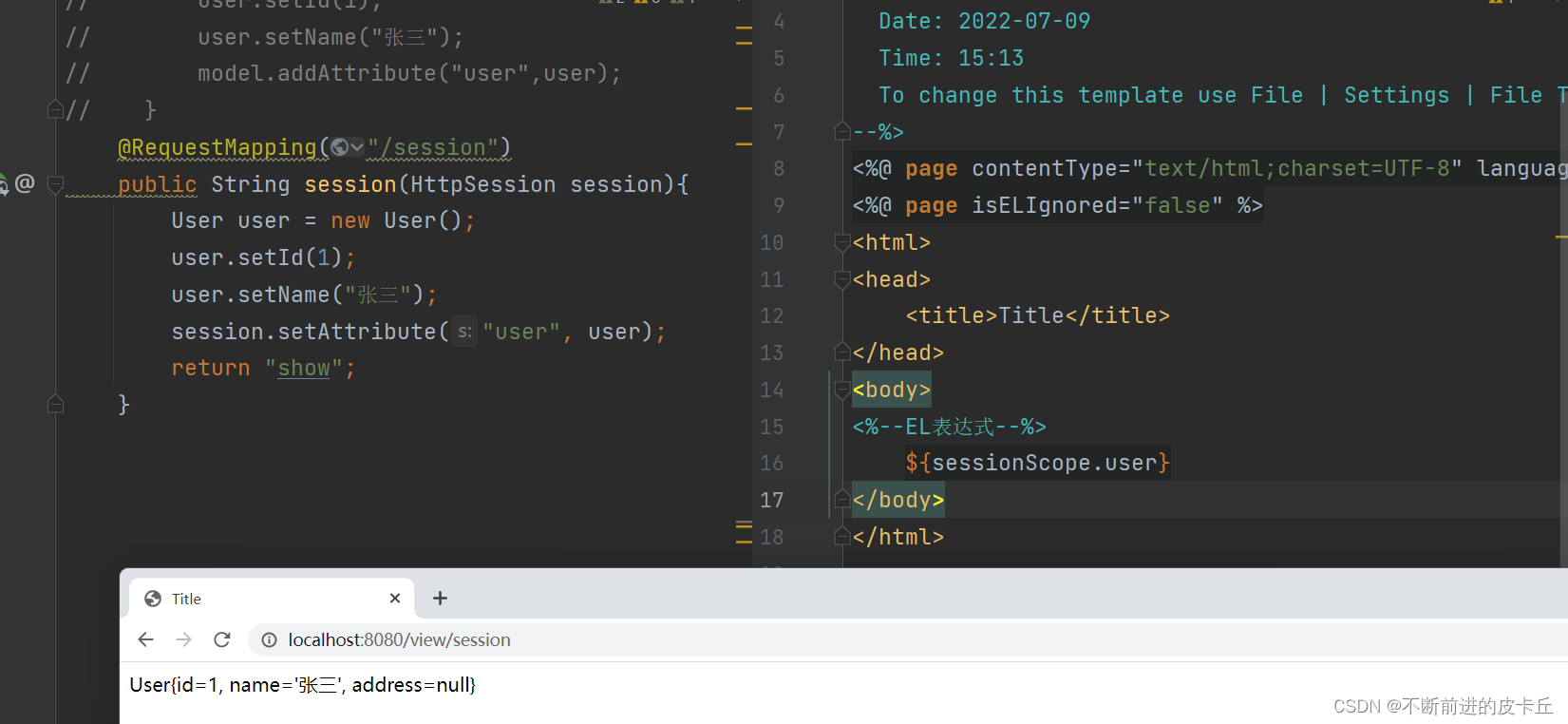
7.2.2@SessionAttribute
@SessionAttribute这个注解不是给方法添加的,而是给类添加的
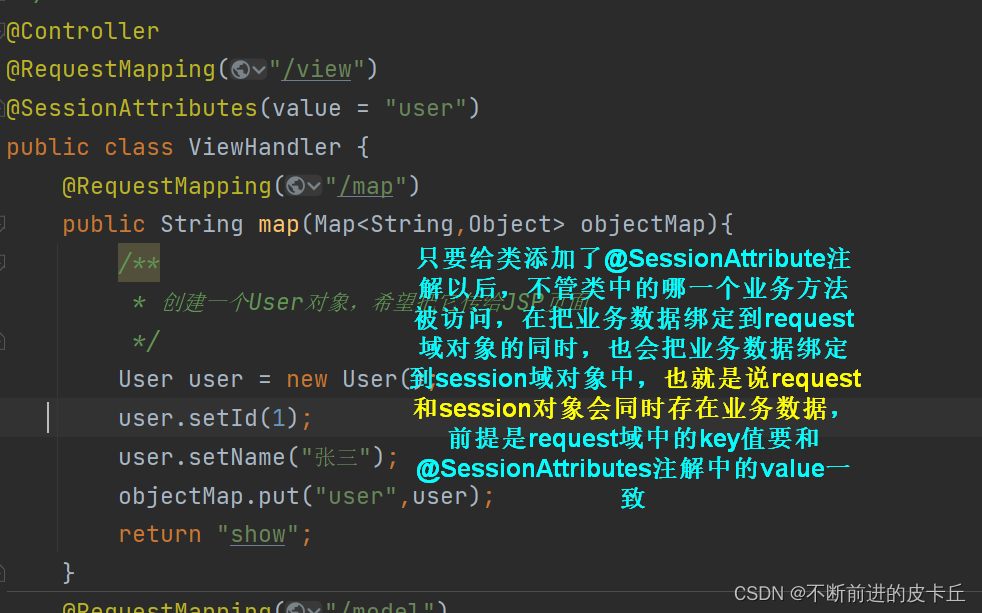
@SessionAttributes除了可以通过key值绑定,也可以通过业务数据的数据类型进行绑定
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(type=User.class)
public class ViewHandler{
...
}
@SessionAttributes可以同时绑定多个业务数据
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(type={User.class,Address.class})
public class ViewHandler{
...
}
或者
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value={"user","address"})
public class ViewHandler{
...
}
八、 Spring MVC自定义数据类型转换器
Spring MVC默认情况下可以对基本类型进行类型转换,例如可以将String转换为Integer,Double,Float等。但是Spring MVC并不能转换日期类型(java.util.Date),如果希望把字符串参数转换为日期类型,必须自定义类型转换器
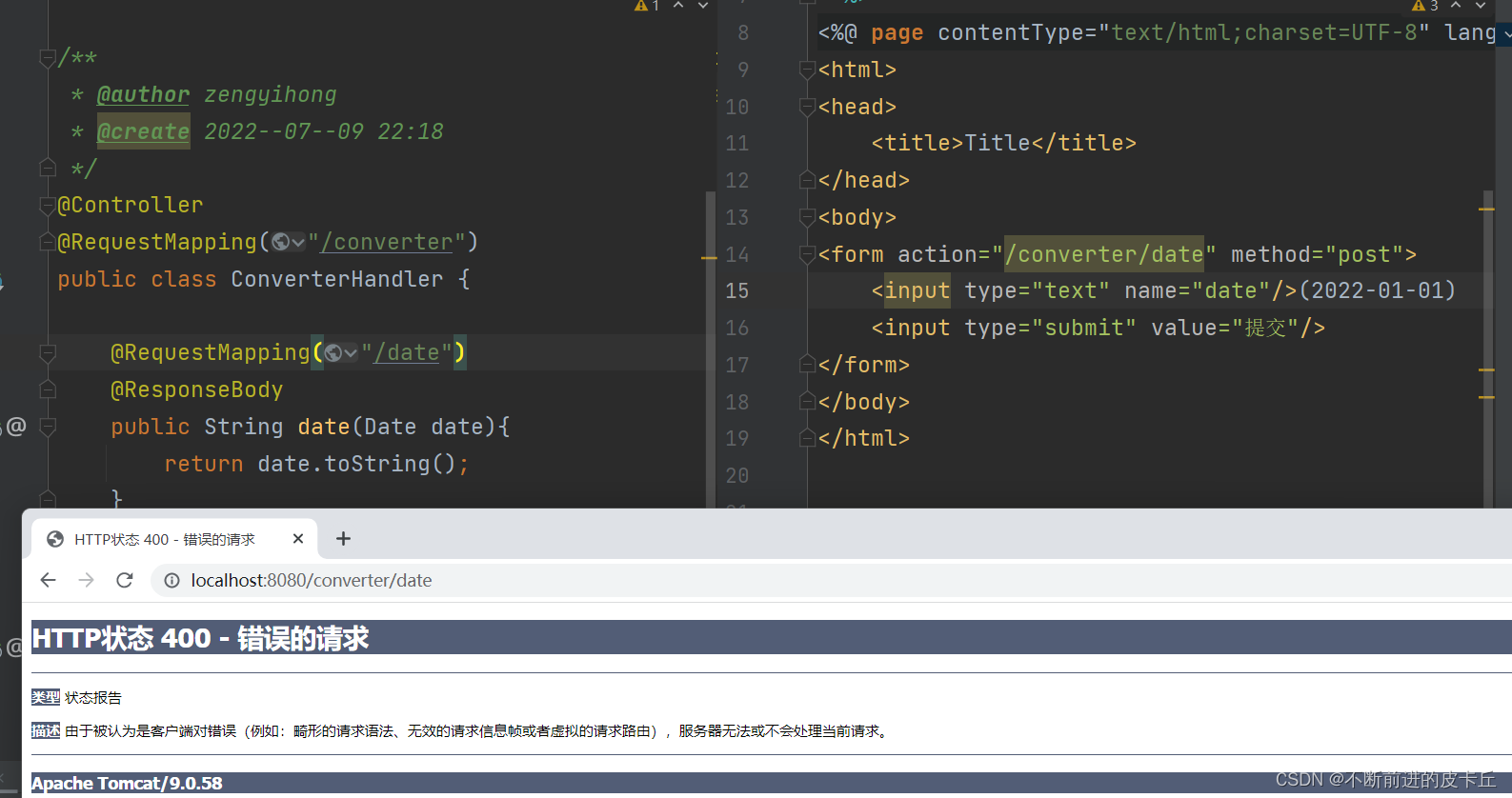
1.创建DateConverter类,并且实现org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter接口,这样它就成为了一个自定义数据类型转换器,需要指定泛型<String,Date>,表示把String类型转为Date类型
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
private String pattern;
public DateConverter(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
@Override
public Date convert(String s) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(this.pattern);
try {
return simpleDateFormat.parse(s);
} catch (ParseException e | java.text.ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
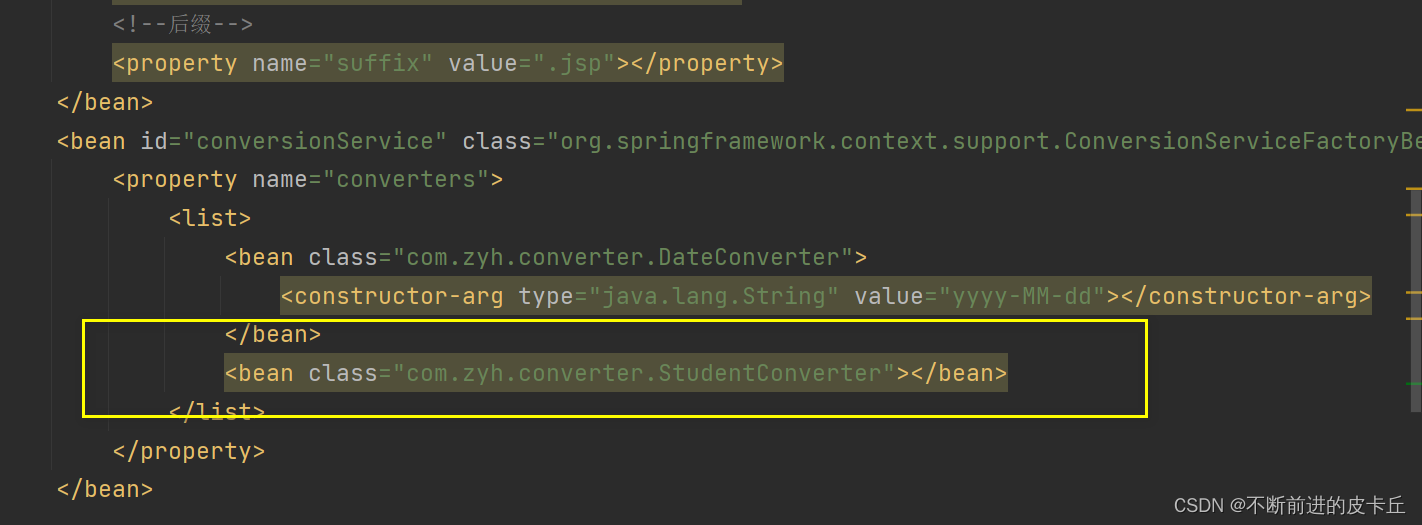
2.在springmvc.xml中配置conversionService bean,这个bean是org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean的实例化对象,同时bean中必须包含一个converters属性,在其中注册所有需要使用的自定义转换器
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="com.zyh.converter.DateConverter">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="yyyy-MM-dd"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
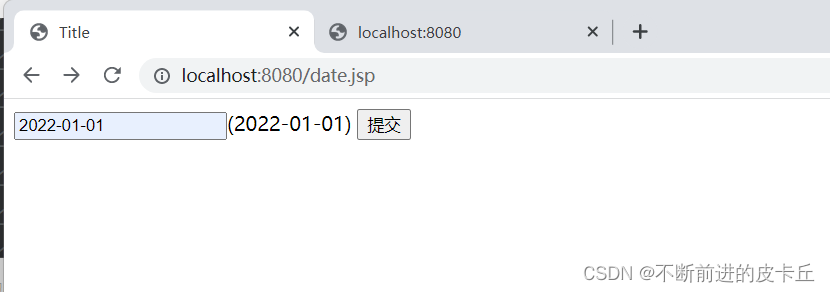
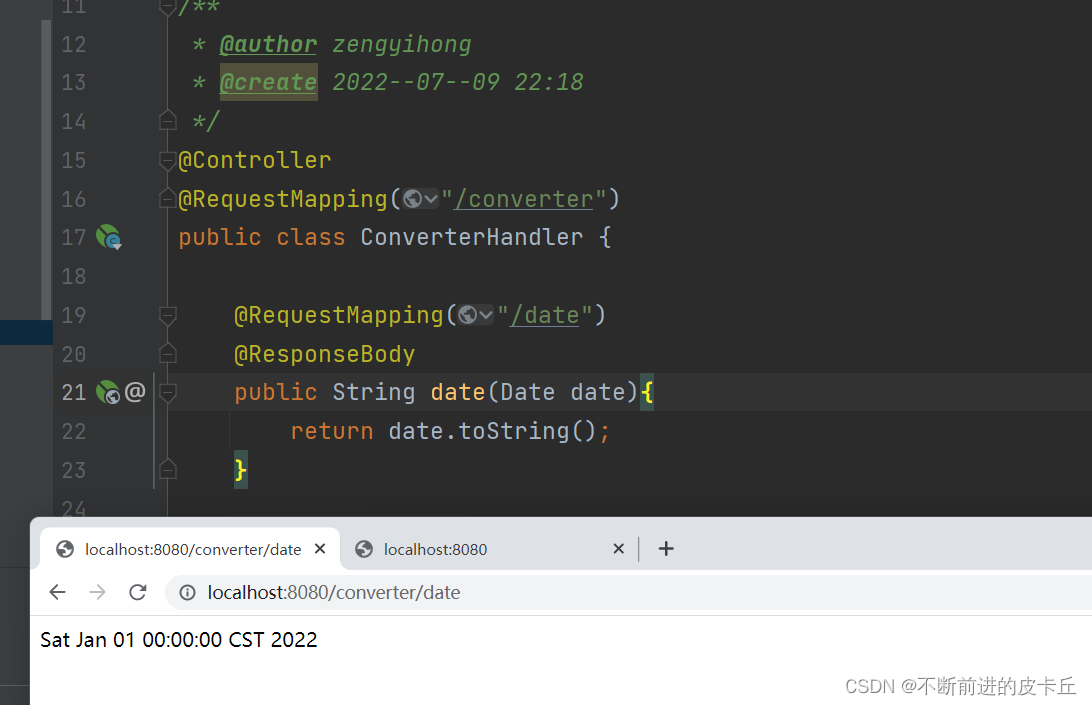
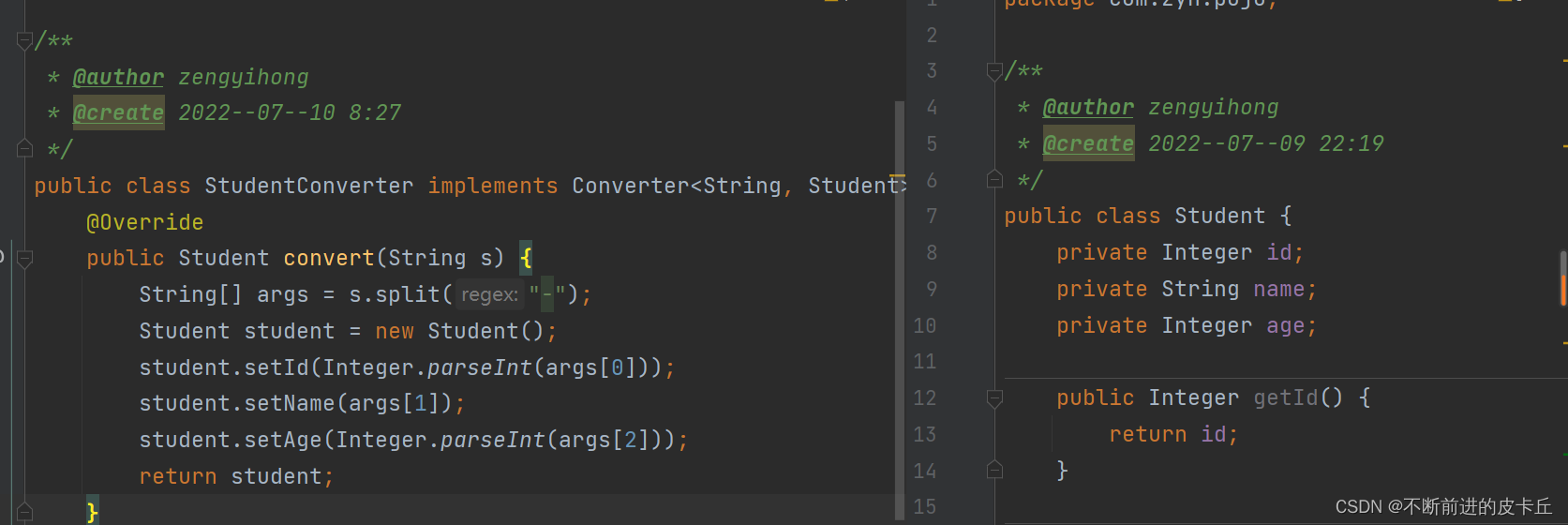
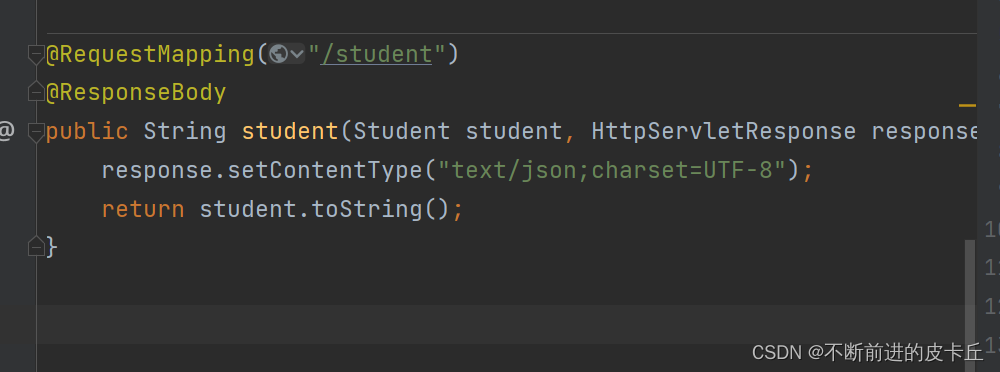
我们也可以自定义类
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/converter/student" method="post">
<input type="text" name="student"/>(1-张三-22)<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
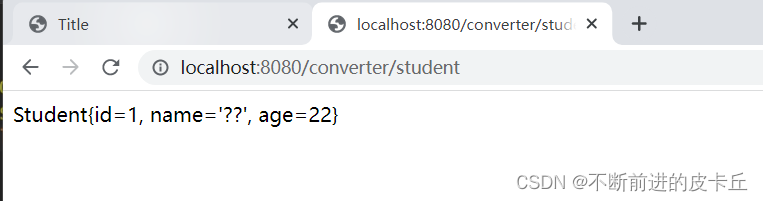
接下来看看怎么解决中文乱码问题(搞了好久都要崩溃了)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zyh.controller"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!--给逻辑视图加上前缀和后缀 -->
<!--前缀-->
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<!--后缀-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="com.zyh.converter.DateConverter">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="yyyy-MM-dd"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="com.zyh.converter.StudentConverter"></bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService">
<!--消息转换器 -->
<mvc:message-converters>
<!-- 解决中文乱码问题 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8"></property>
</bean>
<!--fastjson -->
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
</beans>
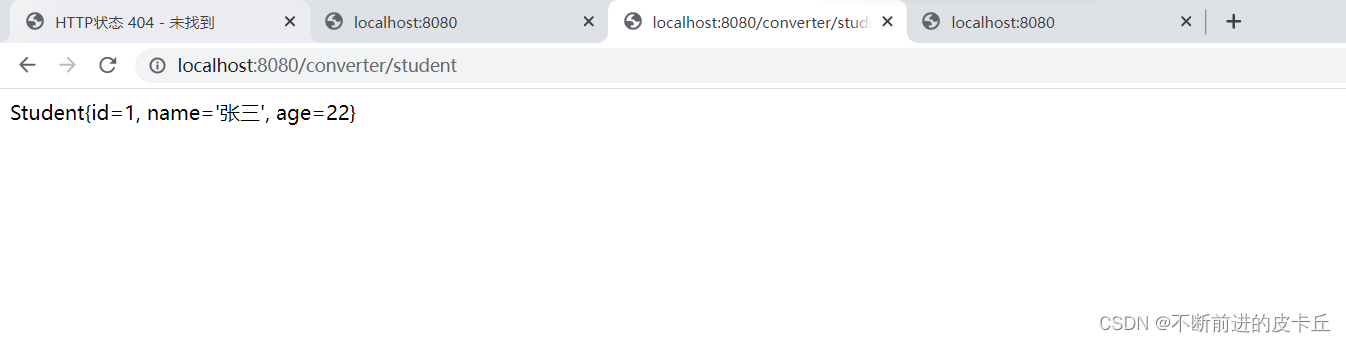
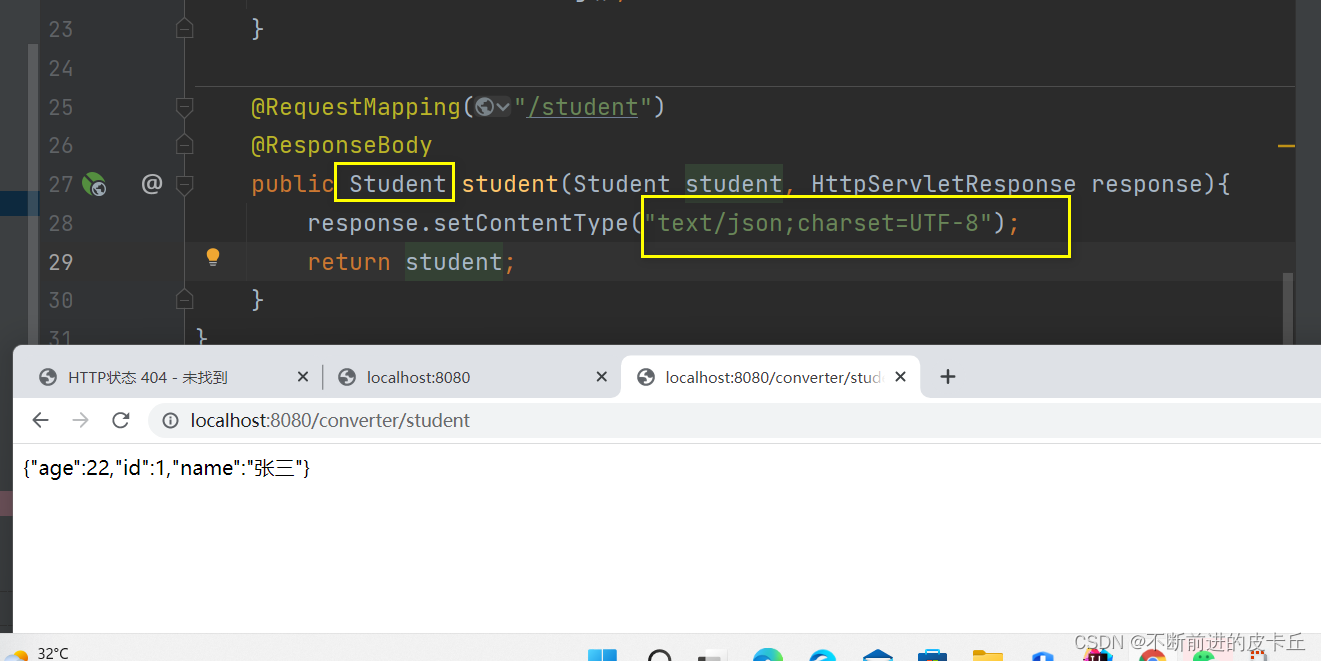
如果我们想要在浏览器显示的是JSON格式,中文乱码需要在业务方法中通过设置response的编码方式来解决,springmvc.xml的bean不起作用,如果不需要把业务数据转换成json格式,springmvc.xml的配置可以起到中文乱码的作用
九、Spring MVC和RESTful的集成
9.1初识RESTful
- RESTful是什么
- RESTful是当前比较流行的一种互联网软件架构模型,通过统一的规范来完成不同终端的数据访问和交换,REST全称是Representaional State Transfer(资源表现层状态转换)
- RESTful的优点:结构清晰,有统一的标准、扩展性好
- Resources
- 资源指的是网络中的某一个具体文件,类型不限,可以是文本、图片、音频、视频、数据流等,是网络中真实存在的一个实体
- 如何获取?可以通过统一资源标识符找到这个实体,URI,每一个资源都有特定的URI,通过URI可以找到一个具体的资源
- 这里涉及到http协议的uri和url,推荐大家看这篇文章HTTP 协议详解 —— URI、HTTP protocol、HTTP headers

- Pepresentation
- 资源表现层,资源的具体表现形式,比如一段文字,可以使用TXT,JSON,HTML,XML等不同的形式来描述
- State Transfer
- 状态转化是指客户端和服务端之间的数据交换,因为HTTP请求不能传输数据的状态,所有的状态都保存在服务端,如果客户端希望访问服务端的数据,就需要使其发生状态改变,同时这种状态转化是建立在表现层,完成转换就表示资源的表现形式发生了改变
9.2RESTful的特点
1.URL传参更加简洁
- 传统形式URL: http://localhost:8080/findById?id=1
- RESTful风格URL: http://localhost:8080/findById/1
2.完成不同终端之间的资源共享,RESTful提供了一套规范,不同终端之间只要遵守这个规范,就可以实现数据交互。
RESTful具体来说是四种表现形式,HTTP请求中四种请求类型(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)分别表示四种常规操作,CRUD
- GET用来获取资源
- POST用来创建资源
- PUT用来修改资源
- DELETE用来删除资源
两个终端要完成数据交互,基于RESTful的方式,增删改查操作分别需要使用不同的HTTP请求类型来访问。
传统的web开发中form表单只支持GET和POST请求,如何解决呢?我们可以通过添加HiddenHttpMethodFilter过滤器,可以把POST请求转为PUT或者DELETE
@Component
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class RESTHandler {
// @RequestMapping(value = "/find",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/find")
@ResponseBody
public String find(){
return "Hello";
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(){
}
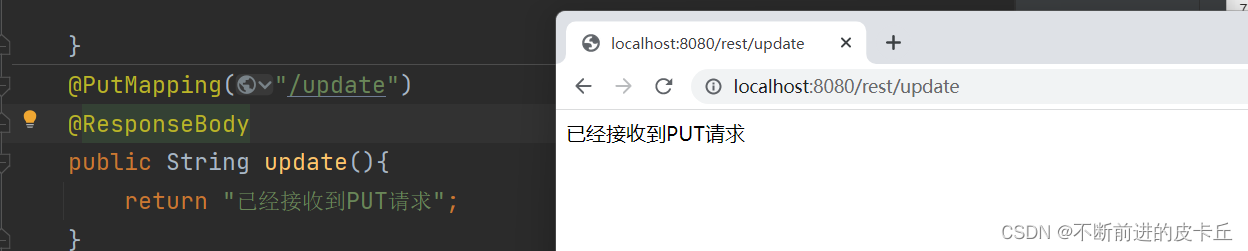
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(){
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public void delete(){
}
}
9.3HiddenHttpMethodFilter的实现原理
HiddenHttpMethodFilter检测请求参数是否包含_method参数,如果包含则取出它的值,并且判断请求类型之后完成请求类型的转换,然后继续传递
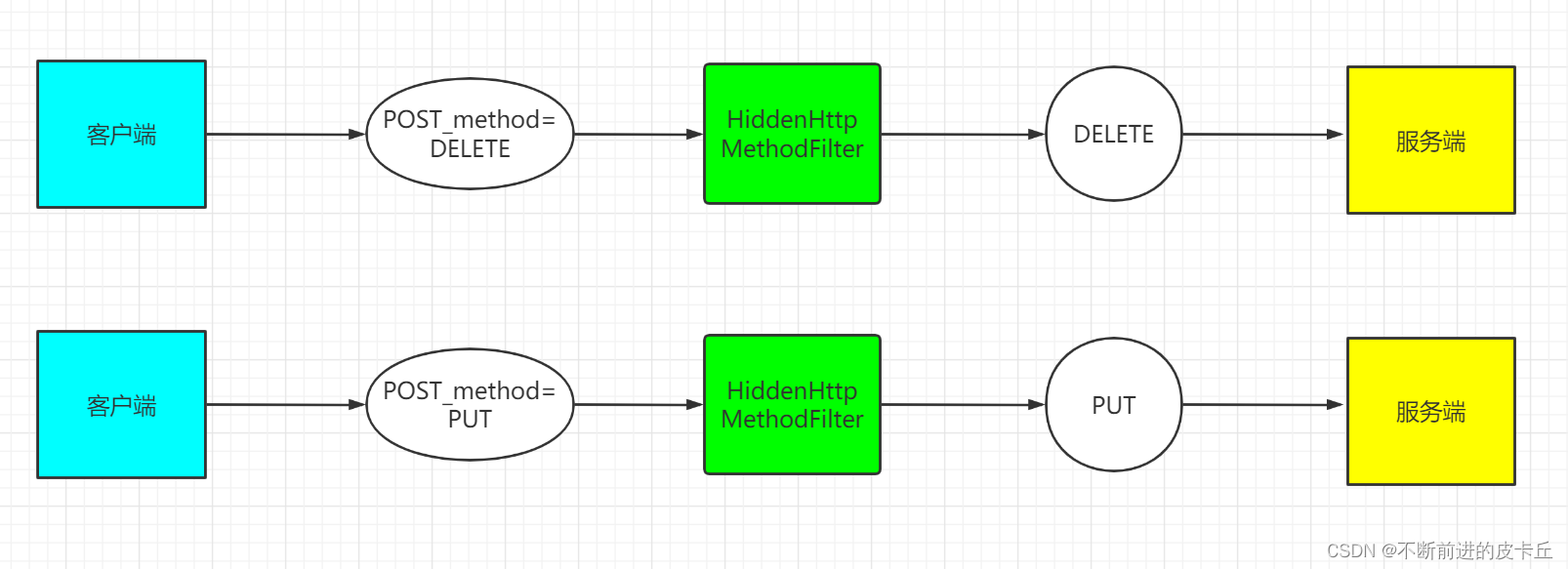
实现步骤:
1.在form表单中添加隐藏域标签,name为_method,value为PUT或DELETE
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/rest/update" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
2.在web.xml中配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
接下来用一个小案例练练手
9.4Spring MVC和RESTful整合
这个整合没有连接数据库
需求分析
- 添加课程:成功则返回全部课程信息
- 查询课程:通过id查询对应课程信息
- 修改课程:成功则返回修改之后的全部课程信息
- 删除课程:成功则返回删除之后的全部课程信息
记得在pom.xml添加JSTL的依赖
代码实现
1.JSP
- 添加课程:add.jsp
- 修改课程:edit.jsp
- 课程展示:courseList.jsp
2.Course实体类
public class Courese{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private double price;
还有对应的set,get方法,构造器
}
3.CourseRepository
@Repository
public class CourseRepository {
private Map<Integer, Course> map;
public CourseRepository(){
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, new Course(1,"语文",70.0));
map.put(2, new Course(2,"数学",80.0));
map.put(3, new Course(3,"英语",90.0));
}
public Collection<Course> findAll(){
return map.values();
}
public Course findById(Integer id){
return map.get(id);
}
public void saveOrUpdate(Course course){
map.put(course.getId(), course);
}
public void deleteById(Integer id){
map.remove(id);
}
}
4.CourseController
package com.zyh.controller;
import com.zyh.pojo.Course;
import com.zyh.repository.CourseRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* @author zengyihong
* @create 2022--07--11 16:14
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/course")
public class CourseController {
@Autowired
private CourseRepository courseRepository;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public ModelAndView findAll() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("courseList");
modelAndView.addObject("list", courseRepository.findAll());
return modelAndView;
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public String deleteById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
courseRepository.deleteById(id);
return "redirect:/course/findAll";
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public String save(Course course) {
courseRepository.saveOrUpdate(course);
/**
* 添加信息后要求返回列表页面
* 重定向
*/
return "redirect:/course/findAll";
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public ModelAndView findById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("edit");
modelAndView.addObject("courser", courseRepository.findById(id));
return modelAndView;
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public String update(Course course){
courseRepository.saveOrUpdate(course);
return "redirect:/course/findAll";
}
}
JSP
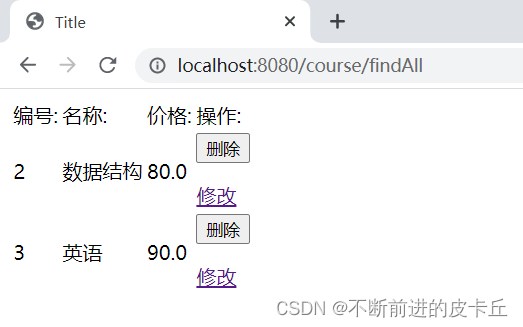
courseList.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td>编号:</td>
<td>名称:</td>
<td>价格:</td>
<td>操作:</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="course">
<tr>
<td>${course.id}</td>
<td>${course.name}</td>
<td>${course.price}</td>
<td>
<form action="/course/deleteById/${course.id}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
<input type="submit" value="删除">
</form>
<a href="/course/findById/${course.id}">修改</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
save.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/course/save" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>课程编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="id">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>课程名称:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>课程价格:</td>
<td> <input type="text" name="price"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</td>
<td>
<input type="reset" value="重置">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
edit.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/course/update" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT"/>
<table>
<tr>
<td>课程编号:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="id" value="${courser.id}">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>课程名称:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="name" value="${courser.name}">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>课程价格:</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="price" value="${courser.price}">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
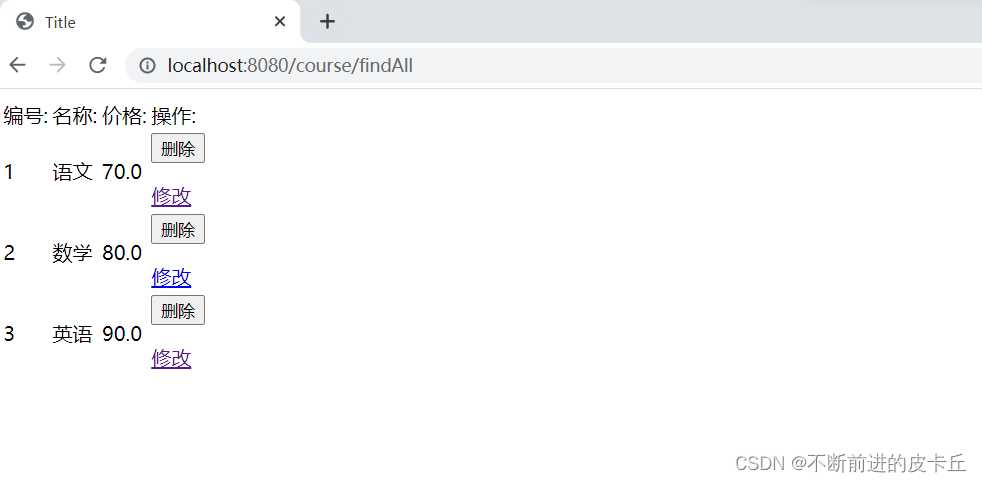
点击删除
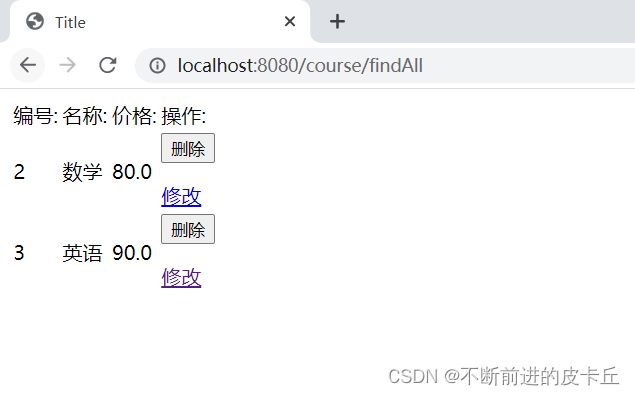
点击修改
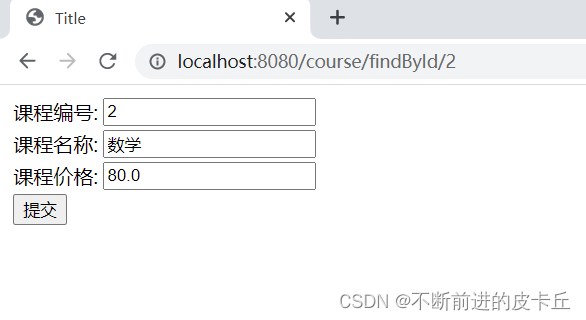
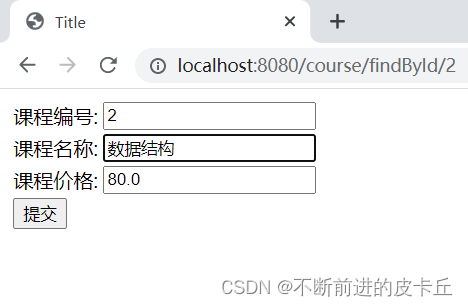
点提交
十、文件的上传下载
10.1文件上传
10.1.1单文件上传
1.底层使用的是Apache fileupload 组件完成上传功能,Spring MVC只是对其进行了封装,简化开发,pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
springmvc.xml
为了把二进制数据解析成对象
<!-- 文件的上传-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"></bean>
2.JSP页面
- input的type属性设置为file
- form表单的method设置为post
- form表单的enctype设置为multipart/form-data
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/file/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="img"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
<!-- 加上/代表从根目录也就是8080开始找 -->
</form>
<img src="${src}"/>
</body>
</html>
@Component
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileHandler {
/**
* 文件是以二进制流传输的
* @param img
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("img") MultipartFile img, HttpServletRequest request){
if (img.getSize()>0){
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
String filename = img.getOriginalFilename();
File descFile=new File(path, filename);
try {
img.transferTo(descFile);
request.setAttribute("src", "/file/"+filename);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return "upload";
}
}
然后选择文件
提交
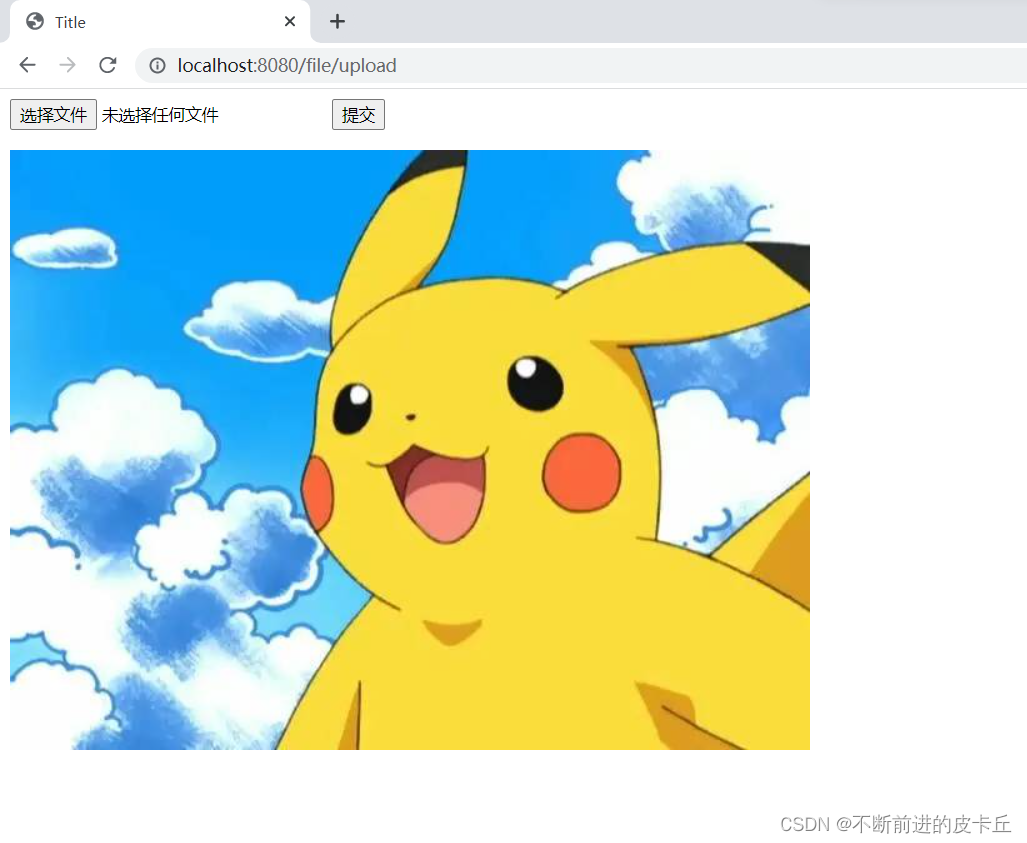
10.1.2多文件上传
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>多文件上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/file/uploads" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
file1:<input type="file" name="imgs"/><br>
file2:<input type="file" name="imgs"/><br>
file3:<input type="file" name="imgs"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
<c:forEach items="${pathList}" var="path">
<img src="${path}" width="300px">
</c:forEach>
@PostMapping("/uploads")
public String uploads(@RequestParam("imgs") MultipartFile[] imgs,HttpServletRequest request){
List<String> pathList=new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile img:imgs){
if (img.getSize()>0){
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
String filename = img.getOriginalFilename();
File descFile=new File(path, filename);
try {
img.transferTo(descFile);
pathList.add("/file/"+filename);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
request.setAttribute("pathList", pathList);
return "uploads";
}
10.2文件下载
JSP页面通过超链接点击进行下载
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>文件下载</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/file/download?fileName=皮卡丘.jpg">皮卡丘.jpg</a>
<a href="/file/download?fileName=柯南.png">柯南.png</a>
<a href="/file/download?fileName=springmvc.png">springmvc.png</a>
</body>
</html>
Handler
/**
* 根据文件的名字进行下载
*/
@GetMapping("/download")
public void download(String fileName,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
if (fileName!=null){
String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
File file=new File(path,fileName);
OutputStream out=null;
if (file.exists()){
//设置下载文件
response.setContentType("applicationContext/force-download");
//设置文件名
response.setHeader("Context-Disposition", "attachment;filename="+fileName);
try {
out=response.getOutputStream();
out.write(FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file));
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (out!=null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
十一、拦截器
11.1过滤器、监听器、拦截器的对比
- Servlet:处理Reequest请求和Response响应
- 过滤器(Filter):对Request请求起到过滤作用,作用在Servlet之前,如果配置为/*可以为所有的资源(servlet、js/css静态资源等)进行过滤处理
- 监听器(Listener):实现了javax.servlet.ServletContextListener接口的服务器端组件,它随Web应用的启动而启动,只初始化一次,然后一直监视,随Web应用的停止而销毁
- 作用一:做初始化工作,web应用中spring容器启动ContextLoaderListener
- 作用二:监听web中的特定事件,比如HttpSession,ServletRequest的创建和销毁;变量的创建、销毁和修改等可以在某些动作 前后增加处理,实现监控,比如说统计在线人数,利用HttpSessionListener等
- 拦截器(Interceptor):是Spring MVC、Struts等表现层框架自己的,不会拦截jsp/html/css/image等的访问,只会拦截访问的控制器方法(Handler)
- servlet、filter、listener是配置在web.xml中,interceptor是配置在表现层框架自己的配置文件中
- 在Handler业务逻辑执行之前拦截一次
- 在Handler逻辑执行完但是还没有跳转页面之前拦截一次
- 在跳转页面后拦截一次
11.2拦截器基本概念
Spring MVC中的拦截器(Interceptor)类似于Servlet中的过滤器(Filter),它主要用于拦截用户请求并作相应的处理。例如通过拦截器可以进行权限验证、记录请求信息的日志、判断用户是否登录等。
要使用Spring MVC中的拦截器,就需要对拦截器类进行定义和配置。通常拦截器类可以通过两种方式来定义。
- 通过实现HandlerInterceptor接口
- 继承HandlerInterceptor接口的实现类(如:HandlerInterceptorAdapter)来定义。
11.3拦截器的实现
通过实现HandlerInterceptor接口
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 在目标Handler(方法)执行前执行
* 返回true:执行Handler方法
* 返回false:阻止目标Handler方法执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("目标Handler执行前执行MyInterceptor---->preHandle方法...");
return true;
}
/**
* 在目标Handler(方法)执行后,视图生成前执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("目标Handler执行后,视图执行前执行MyInterceptor---->postHandle方法...");
}
/**
* 在目标方法执行后,视图生成后执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param ex
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("目标Handler执行后,视图执行后执行MyInterceptor---->afterCompletion方法...");
}
}
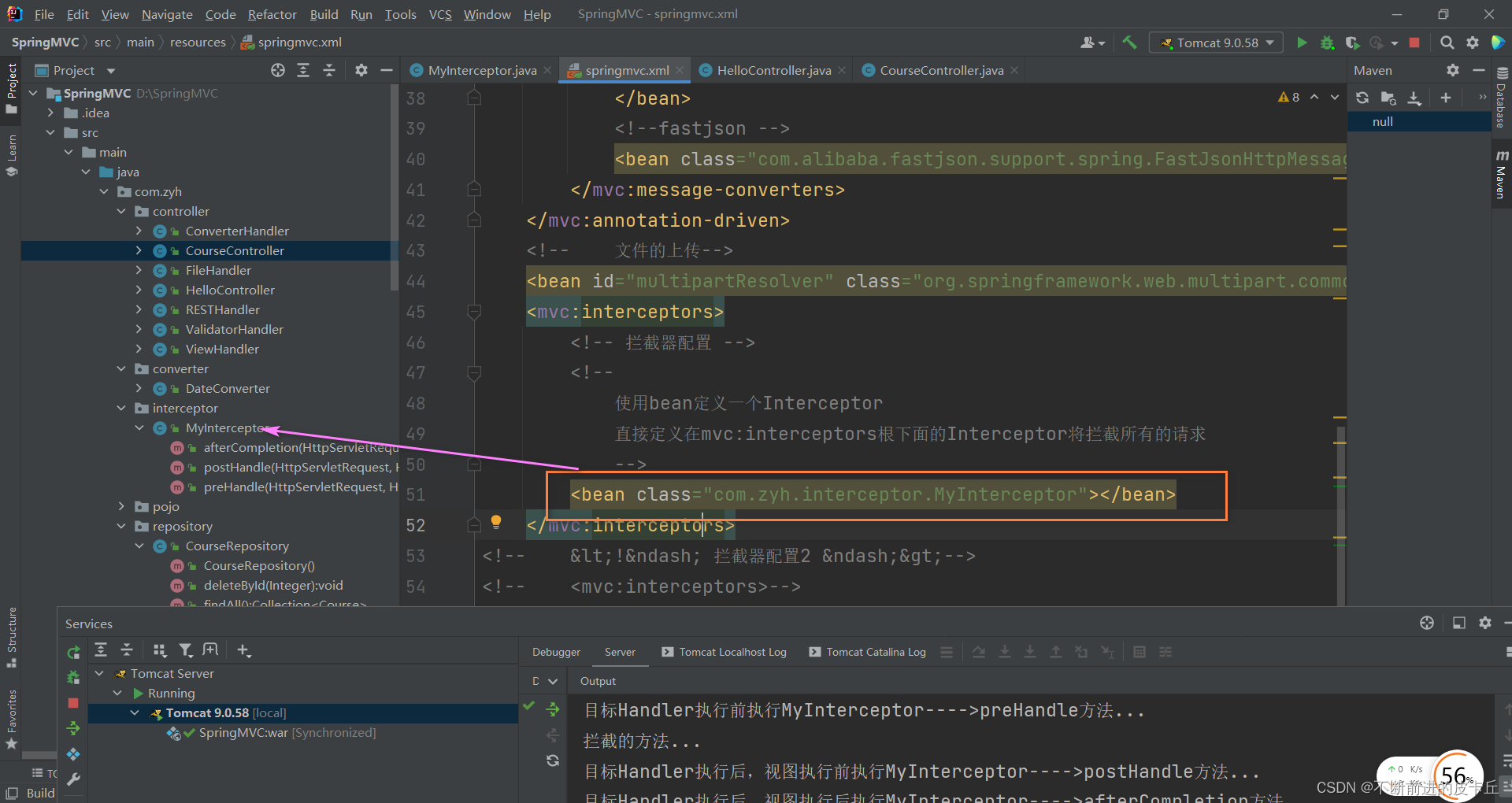
拦截器配置1
<mvc:interceptors>
<!-- 拦截器配置 -->
<!--
使用bean定义一个Interceptor
直接定义在mvc:interceptors根下面的Interceptor将拦截所有的请求
-->
<bean class="com.zyh.interceptor.MyInterceptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptors>
拦截器配置方式2
<!-- 拦截器配置2 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--定义在mvc:interceptor下面,可以自定义需要拦截的请求
如果有多个拦截器满足拦截处理的要求,则依据配置的先后顺序来执行
-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--通过mvc:mapping配置需要拦截的资源。支持通配符,可以配置多个 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <!-- /**表示拦截所有的请求-->
<!--通过mvc:exclude-mapping配置不需要拦截的资源。支持通配符,可以配置多个 -->
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/hello/*"/> <!-- /hello/*表示放行hello路径下的请求 -->
<bean class="com.zyh.interceptor.MyInterceptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
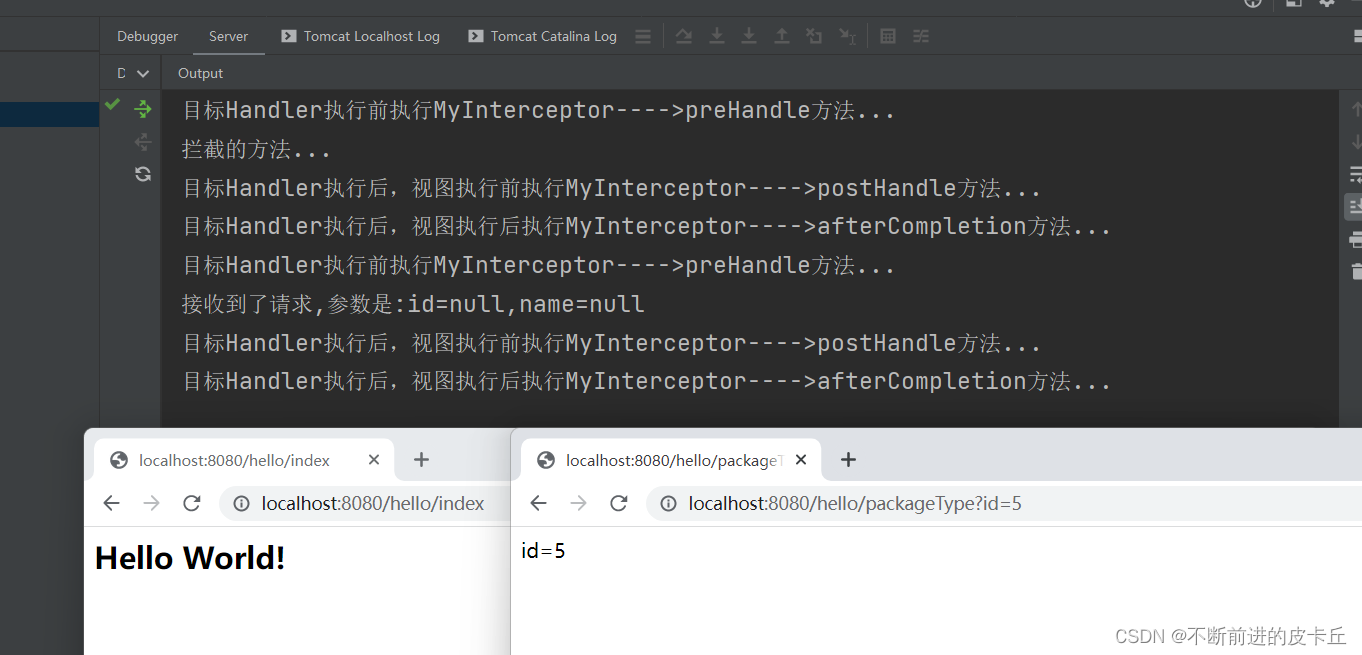
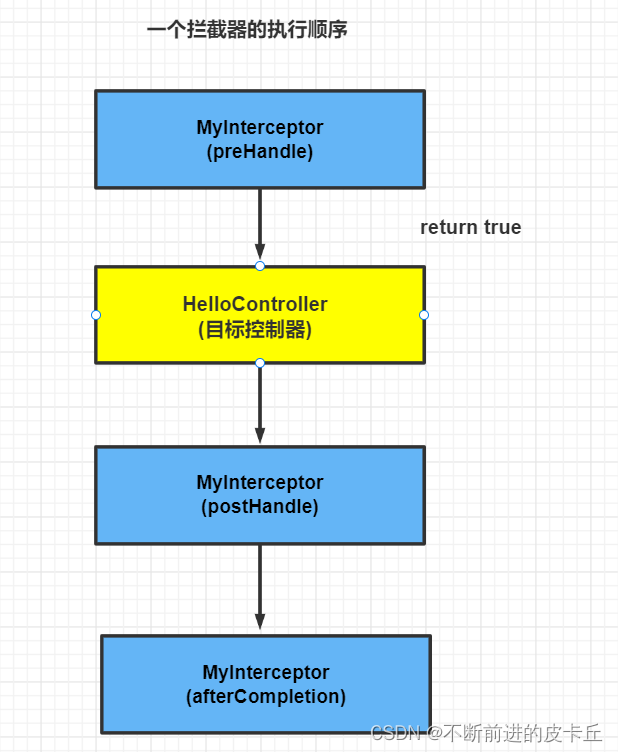
11.4多个拦截器的实现
Spring MVC框架支持多个拦截器的配置,从而构成拦截器链,对客户端进行多次拦截操作
过滤器配置
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.zyh.interceptor.MyInterceptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.zyh.interceptor.MyInterceptor2"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
自定义第二个过滤器
public class MyInterceptor2 implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 在目标Handler(方法)执行前执行
* 返回true:执行Handler方法
* 返回false:阻止目标Handler方法执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("2.目标Handler执行前执行MyInterceptor2---->preHandle方法...");
return true;
}
/**
* 在目标Handler(方法)执行后,视图生成前执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("3.目标Handler执行后,视图执行前执行MyInterceptor2---->postHandle方法...");
}
/**
* 在目标方法执行后,视图生成后执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param ex
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("5.目标Handler执行后,视图执行后执行MyInterceptor2---->afterCompletion方法...");
}
}
Handler
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@Controller
public class HelloContro
@RequestMapping("/packageType")
@ResponseBody
public String packageType(@RequestParam(value = "id", required = true) Integer id) {
System.out.println("拦截的方法...");
return "id=" + id;
}
}
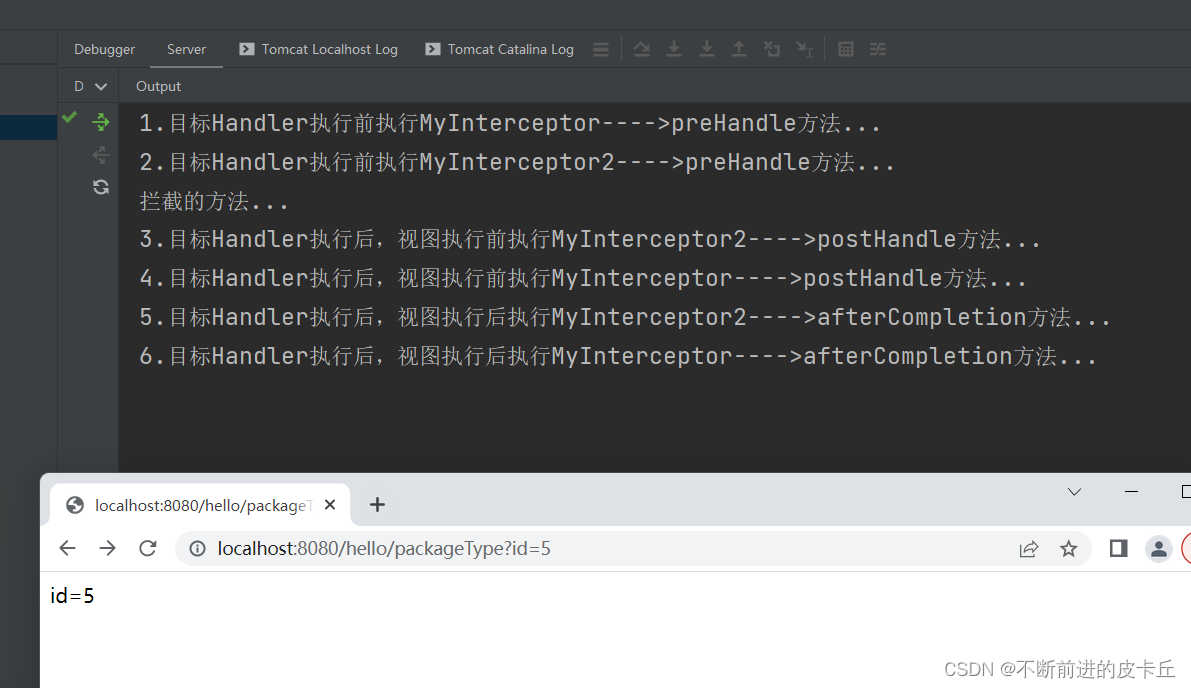
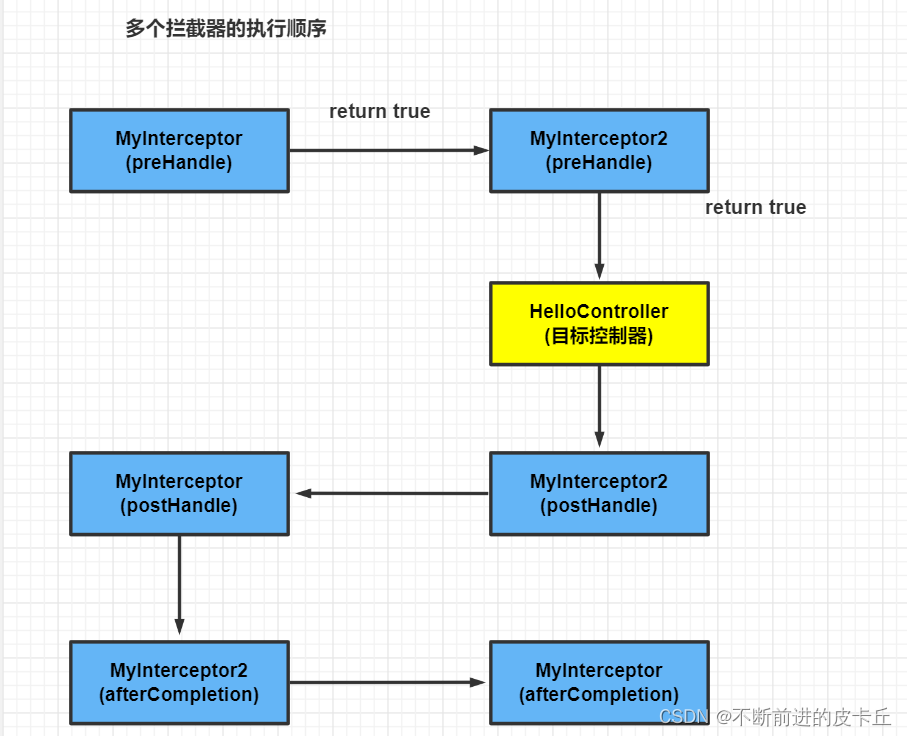
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签: