首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
【JavaSE】接口 详解(下)
2024-04-21 15:00:05基础资料围观609次
Java资料网推荐【JavaSE】接口 详解(下)这篇文章给大家,欢迎收藏Java资料网享受知识的乐趣
前言
欢迎关注个人主页:逸狼
创造不易,可以点点赞吗~
如有错误,欢迎指出~
目录
接口实例运用
接口实现比较引用数据类型(对于引用类型数据来说,不能直接用大于小于号来比较)
代码举例理解
这里要比较两个对象的大小(指定某种方式比较,比如 年龄等)
比较对象的年龄
package demo6;
//接口Comparable 实现 比较引用类型数据的方法,这里面的comparable 的compareTo需要重写
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override//要重写这个方法
public int compareTo(Student o) {
/* if(this.age>o.age){//this表示当前对象,o表示传的参数
return 1;
}
else if(this.age<o.age){
return 0;
}
else{
return -1;
}*/
//代码改良
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1=new Student("zhangsan",20);
Student student2=new Student("lisi",5);
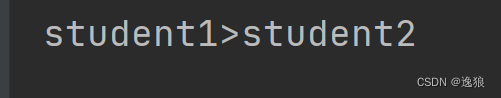
// 比较student1和student2,如果1大于2,返回大于0的数字,否则返回小于0的数字
if(student1.compareTo(student2)>0){//调用的是student1的比较方法,传的是参数是student2
System.out.println("student1>student2");
}
else{
System.out.println("student1<=student2");
}
}
}
测试结果
比较对象的姓名
name是String类型,Java里面自带了字符串比较方法compareTo,比较的是字符串的ASCII码值
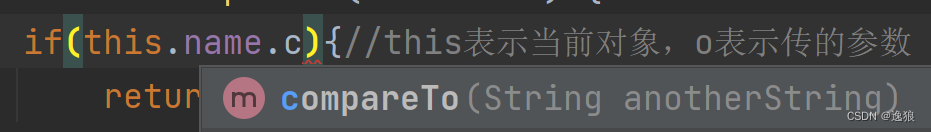
@Override//要重写这个方法
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if(this.name.compareTo(o.name)>0){//this表示当前对象,o表示传的参数
return 1;
}
else if(this.name.compareTo(o.name)==0){
return 0;
}
else{
return -1;
}这里有问题:Comparable接口有局限性(一旦这个类写死了比较方式,就不能随意更改)
利用冒泡排序实现Array.sort
public class Test6 {
//冒泡排序 模拟实现引用数据类型的排序
public static void mySort(Comparable[] comparable){
for (int i = 0; i < comparable.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < comparable.length-1-i; j++) {
if(comparable[j].compareTo(comparable[j+1])>0){
//交换
Comparable tmp=comparable[j];
comparable[j]=comparable[j+1];
comparable[j+1]=tmp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students=new Student[3];
students[0]=new Student("zhangsan",8);
students[1]=new Student("lisi",4);
students[2]=new Student("wangwu",10);
mySort(students);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students));
}
}代码结果(这里是根据学生的年龄排的结果)
年龄比较器
package demo;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.age-o2.age;
}
}姓名比较器
package demo;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class NameComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1,Student o2) {
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}
}
比较示例测试
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1=new Student("zhangsan",4);
Student student2=new Student("lisi",6);
//年龄比较器
AgeComparator ageComparator=new AgeComparator();
int ret=ageComparator.compare(student1,student2);
System.out.println(ret);
//名字比较器
NameComparator nameComparator=new NameComparator();
int ret2=nameComparator.compare(student1,student2);
System.out.println(ret2);
}clone接口
前提:任何一个对象默认都是继承Object类的(是所有类的父类)
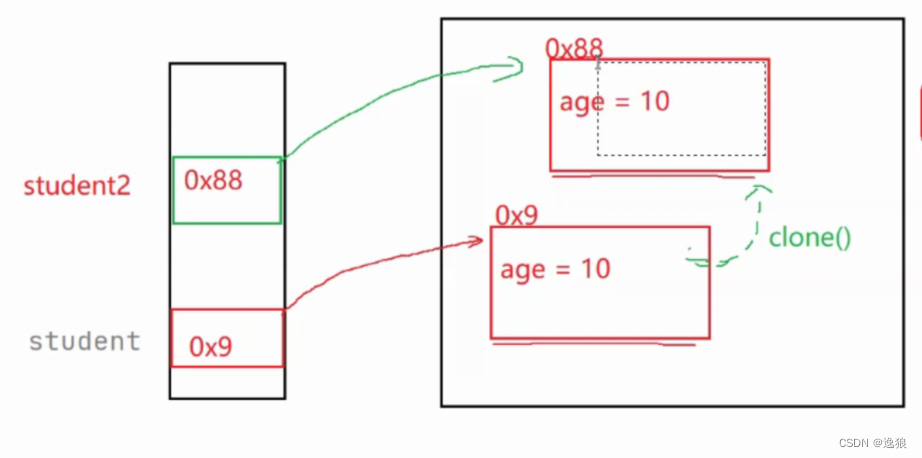
package demo3;
class Student implements Cloneable{//CloneNotSupportedException 必须实现Cloneable接口
public int age;
public Student(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();//Object中的clone方法使用了protected修饰,所以要重写,并用super访问
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student1=new Student(10);
Student student2=(Student)student1.clone() ;//clone是父类方法,在子类中使用要强制转换 (向下转型)
}
}
浅拷贝和深拷贝
浅拷贝
两个引用指向一个对象,如两个Student指向一个Money
图解
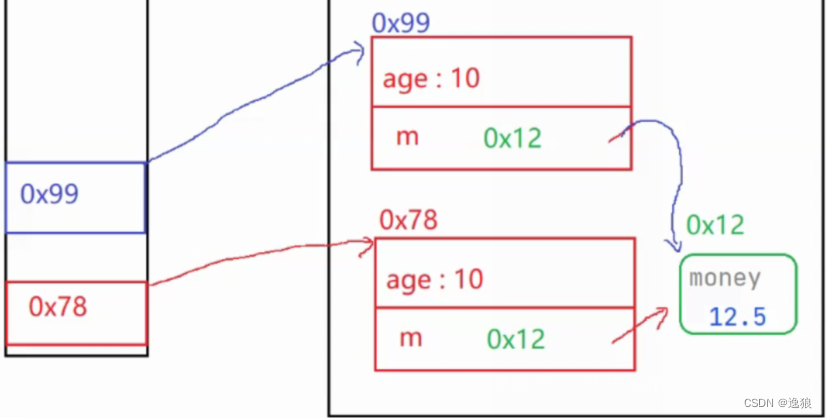
代码举例
package demo3;
class Money {
public double money=12.5;
}
class Student implements Cloneable{//CloneNotSupportedException 必须实现Cloneable接口
public int age;
public Money m=new Money();
public Student(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();//Object中的clone方法使用了protected修饰,所以要重写,并用super访问
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student1=new Student(10);
Student student2=(Student)student1.clone() ;//clone是父类方法,在子类中使用要强制转换 (向下转型)
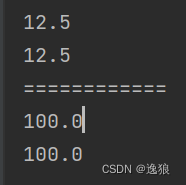
System.out.println(student1.m.money);//12.5
System.out.println(student2.m.money);//12.5
System.out.println("============");
student2.m.money=100;
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
}
}
打印结果
这里通过对象student2修改了money,而student1的money也被修改了
深拷贝
两个引用指向两个对象,如两个Student指向两个个Money
图解
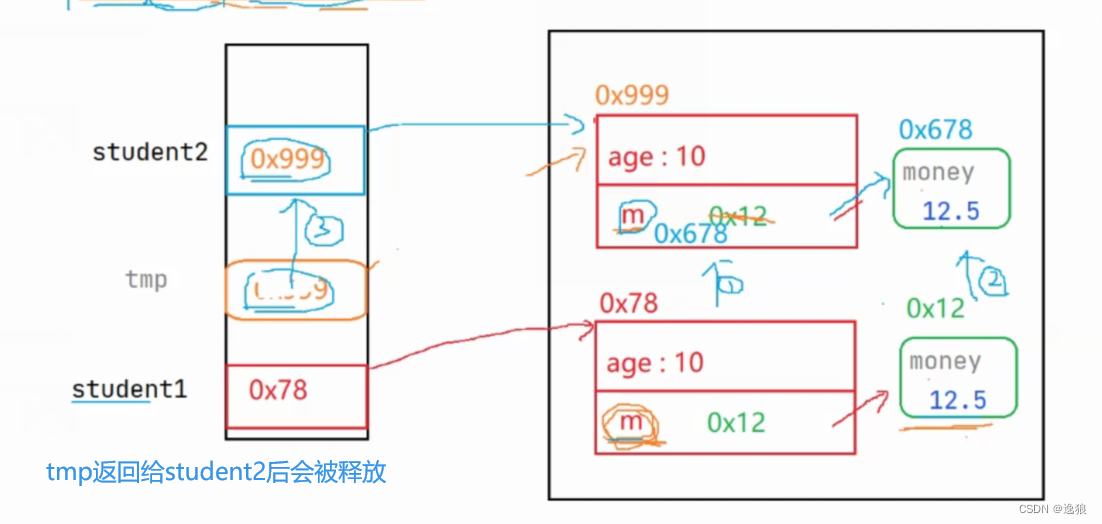
代码举例
package demo3;
class Money implements Cloneable{//表示Money支持克隆功能
public double money=12.5;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//要重写克隆方法
return super.clone();
}
}
class Student implements Cloneable{//CloneNotSupportedException 必须实现Cloneable接口
public int age;
public Money m=new Money();
public Student(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student tmp=(Student)super.clone();
tmp.m=(Money)this.m.clone();
return tmp;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student1=new Student(10);
Student student2=(Student)student1.clone() ;//clone是父类方法,在子类中使用要强制转换 (向下转型)
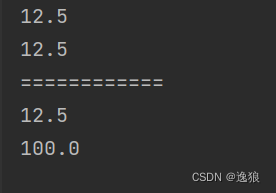
System.out.println(student1.m.money);//12.5
System.out.println(student2.m.money);//12.5
System.out.println("============");
student2.m.money=100;
System.out.println(student1.m.money);
System.out.println(student2.m.money);
}
}
打印结果
这里通过对象student2修改了money,student1的money不会被修改。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80898480/article/details/137380673
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签: