首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
Java之String类
2023-10-29 17:56:20基础资料围观671次

作者简介: zoro-1,目前大二,正在学习Java,数据结构等
作者主页: zoro-1的主页
欢迎大家点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐ 加关注哦!💖💖
Java之String类
String的构造
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用常量串构造
String s1 = "hello bit";
System.out.println(s1);
// 直接newString对象
String s2 = new String("hello bit");
System.out.println(s1);
// 使用字符数组进行构造
char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o','b','i','t'};
String s3 = new String(array);
System.out.println(s1);
}
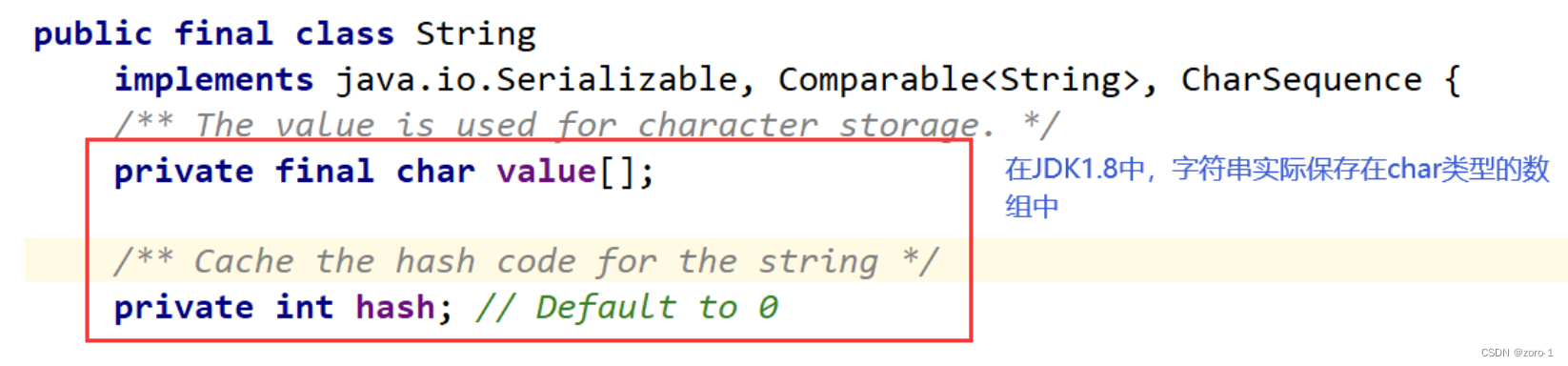
String底层
String是引用类型,内部并不存储字符串本身,在String类的实现源码中,String类实例变量如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
// s1和s2引用的是不同对象 s1和s3引用的是同一对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("world");
String s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1.length()); // 获取字符串长度---输出5
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // 如果字符串长度为0,返回true,否则返回false
}
String之间的比较
比较内容
以下是一个例子,比较两个字符串变量的内容是否相等:
str1 = "hello"
str2 = "world"
if str1 == str2:
print("The strings are equal.")
else:
print("The strings are not equal.")
输出结果为:
The strings are not equal.
这是因为str1变量包含的字符串与str2变量包含的字符串不同,因此它们的内容不相等。以下是一个例子,比较两个字符串变量的内容是否相等:
str1 = "hello"
str2 = "world"
if str1 == str2:
print("The strings are equal.")
else:
print("The strings are not equal.")
输出结果为:
The strings are not equal.
这是因为str1变量包含的字符串与str2变量包含的字符串不同,因此它们的内容不相等。以下是一个例子,比较两个字符串变量的内容是否相等:
str1 = "hello"
str2 = "world"
if str1 == str2:
print("The strings are equal.")
else:
print("The strings are not equal.")
输出结果为:
The strings are not equal.
这是因为str1变量包含的字符串与str2变量包含的字符串不同,因此它们的内容不相等。
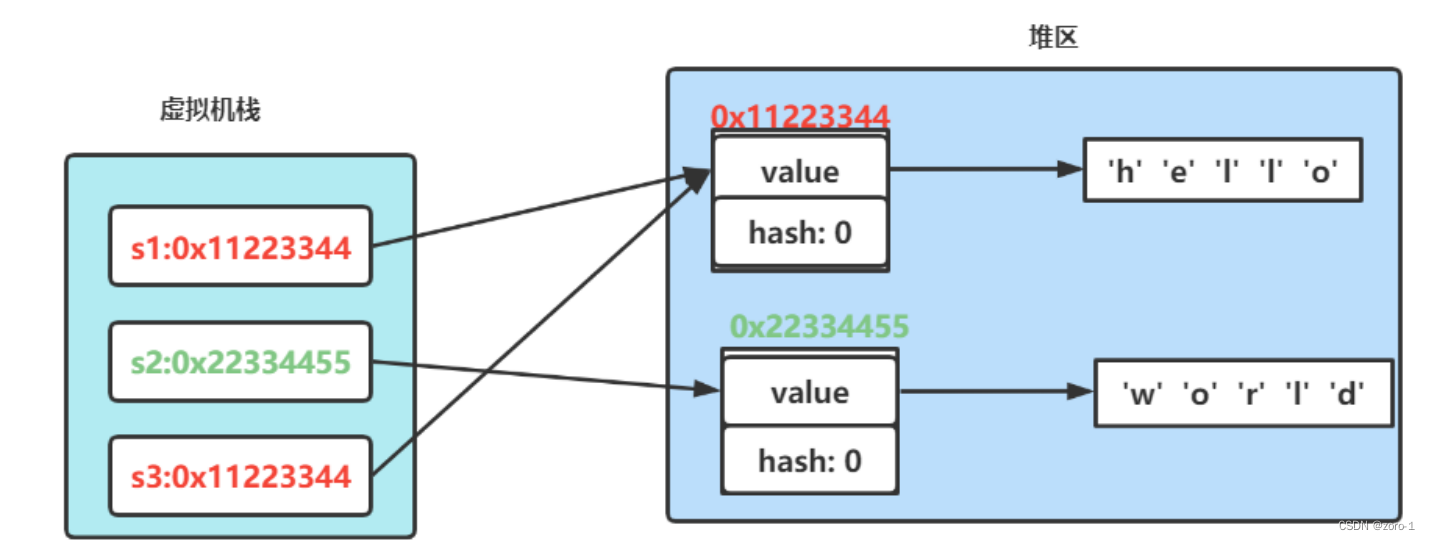
比较地址
假设有两个String对象,分别为str1和str2,它们的值都为"Hello"。
当我们使用"=="运算符比较这两个字符串时,实际上比较的是它们在内存中的地址。
例如:
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "Hello";
if (str1 == str2) {
System.out.println("str1和str2的地址相同");
} else {
System.out.println("str1和str2的地址不同");
}
输出结果为"str1和str2的地址相同",因为在Java中,如果两个字符串的值相同,则它们会被存储在同一个字符串常量池中,因此它们的地址是相同的。但是,如果我们使用new关键字创建字符串对象,则它们的地址是不同的,例如:
String str1 = new String("Hello");
String str2 = new String("Hello");
if (str1 == str2) {
System.out.println("str1和str2的地址相同");
} else {
System.out.println("str1和str2的地址不同");
}
输出结果为"str1和str2的地址不同",因为每个字符串对象都有自己的地址空间,它们并不指向同一个地址。
字符串查找相关方法
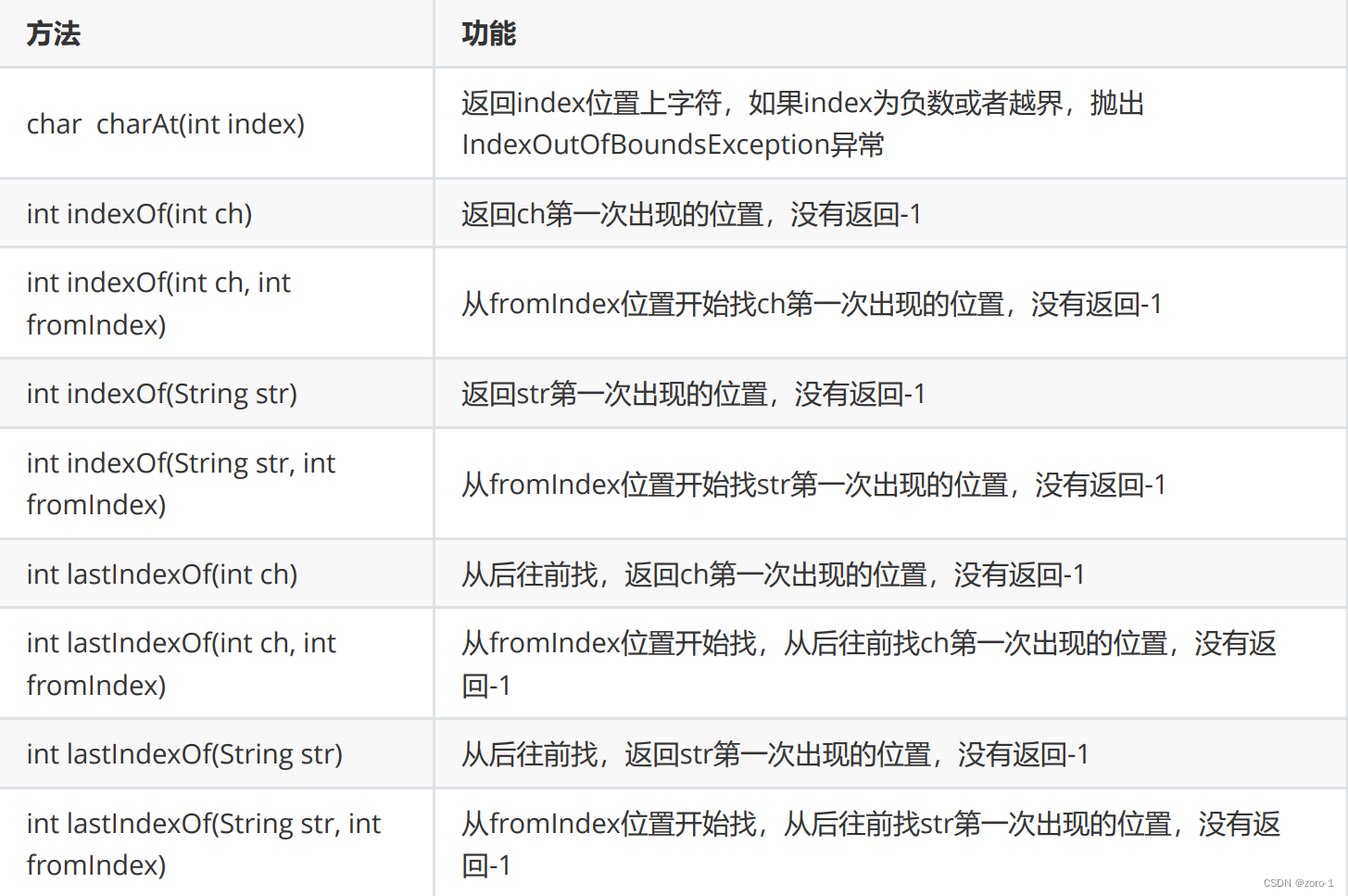
代码演示
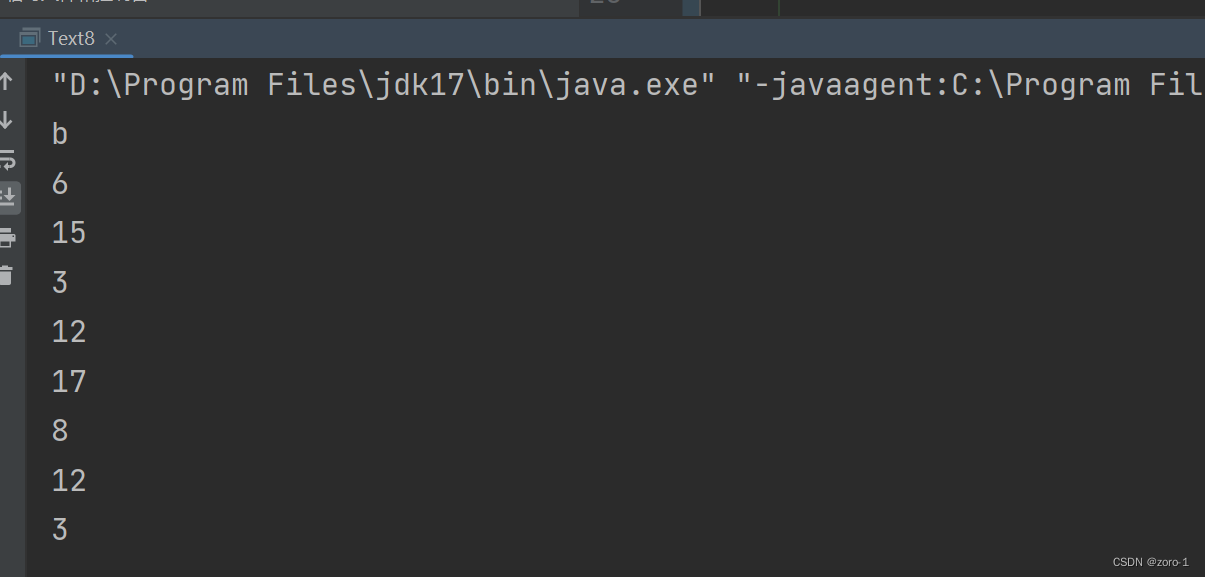
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); //'b
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10));// 15
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); //3
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); // 12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c'));// 17
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); // 8
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb")); // 12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10)); // 3
代码执行结果:
字符串转化
数值类和字符串转化
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); // 'b'
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10)); // 15
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); // 3
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); // 12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c')); // 17
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); // 8
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb")); // 12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10)); // 3
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字转字符串
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型,这个后面会讲到
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}
}
字符串大小写转化
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO"; // 小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); // 大写转小写
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}
字符串转数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello"; // 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println(); // 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2); }
字符串格式化
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);
System.out.println(s);
}
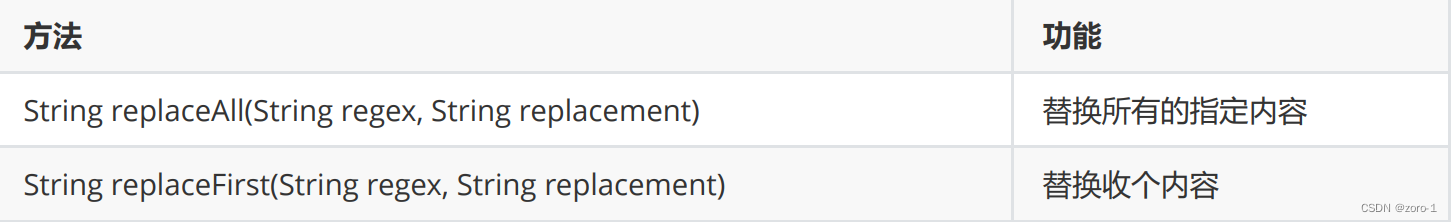
字符串替换
代码演示:
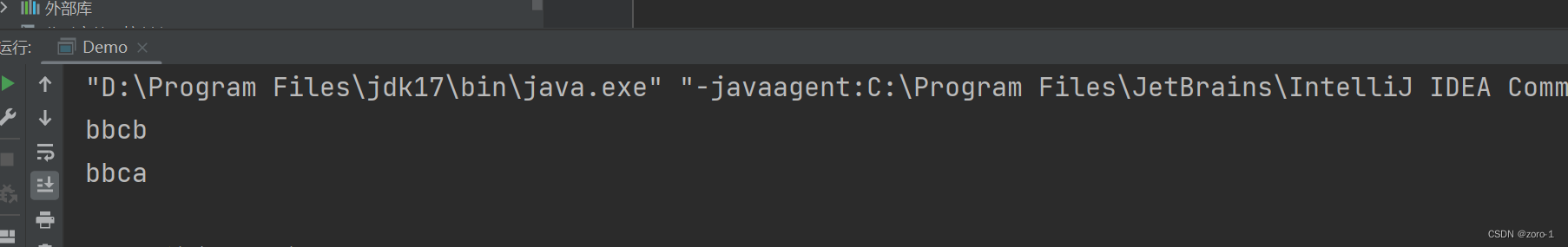
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="abca";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("a","b"));
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("a","b"));
}
}
代码运行结果:
字符串拆分
代码演示:
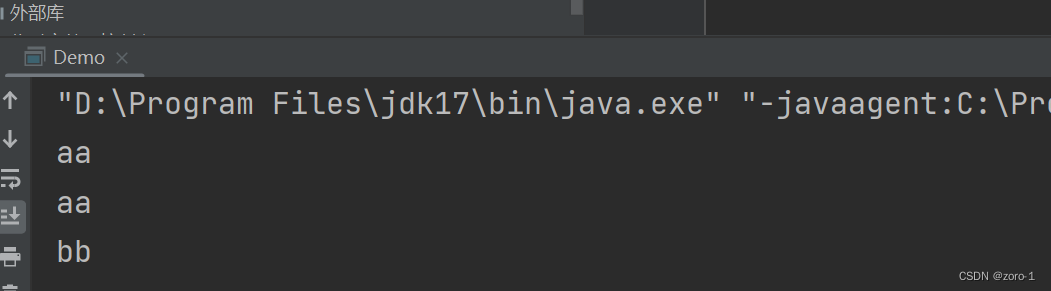
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="aa aa bb";
String[] strs=str.split(" ");
for(int i=0;i<strs.length;i++){
System.out.println(strs[i]);
}
}
}
运行结果:
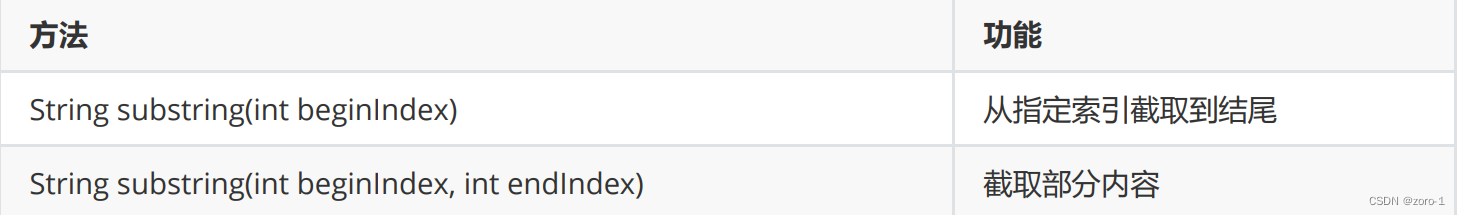
字符串截取
代码演示:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="aaaabb";
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(2,5));
}
}
代码运行结果:
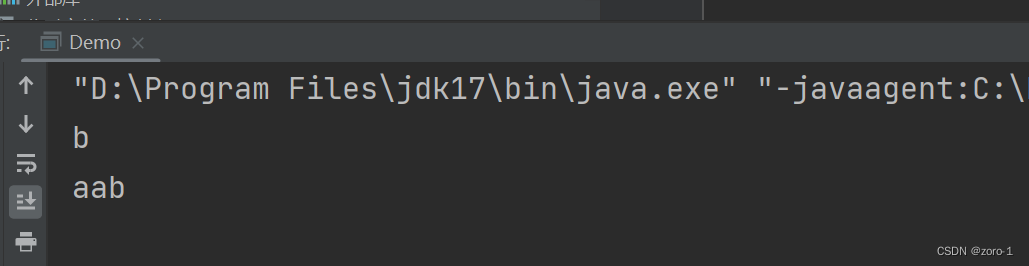
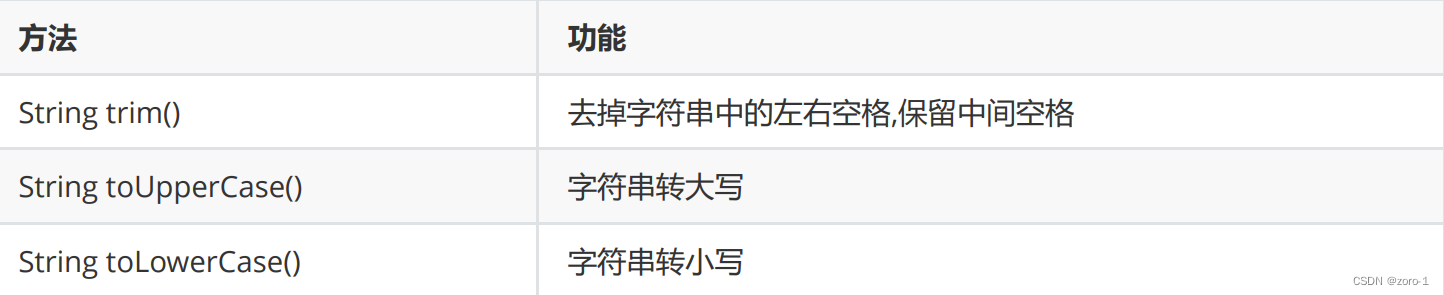
字符串的其他操作方法
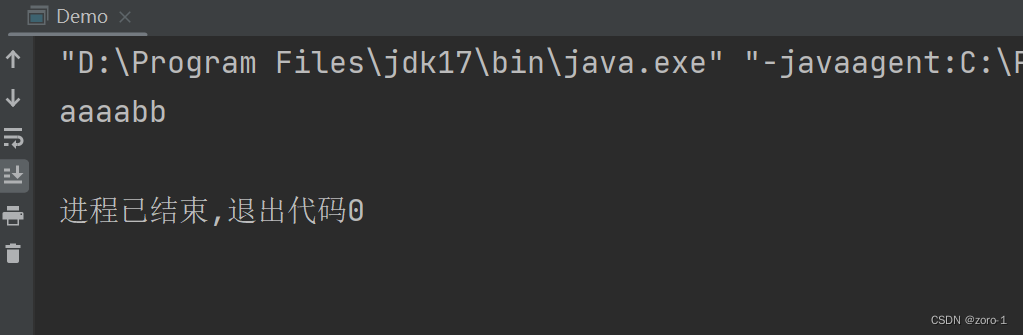
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str=" aaaabb ";
System.out.println(str.trim());
}
}
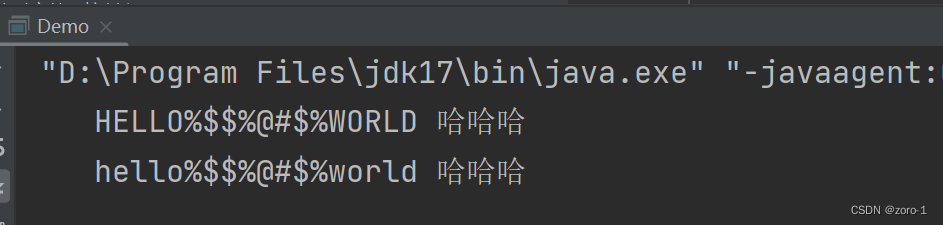
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这两个方法只针对字符串中的字母
String str = "hello%$$%@#$%world 哈哈哈 " ;
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());
}
}
重点:为什么字符串是不可变的

字符串的中的字符实际上存储在value数组中,大多数认为是因为final修饰了value数组,实际上final修饰的数组是说明这个数组不能指向其他引用,但其中的值是可以改变的,fianl修饰的String类说明这个类不能被继承
字符串的修改
注意:尽量避免直接对String类型对象进行修改,因为String类是不能修改的,所有的修改都会创建新对象,效率非常低下。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += " world";
System.out.println(s); // 输出:hello world
}

可以看待在对String类进行修改时,效率是非常慢的,因此:尽量避免对String的直接需要,如果要修改建议尽量使用StringBuffer或StringBuilder。
今天的介绍到这里就结束了下一篇我会介绍StringBuffer和StringBuilder的区别,,希望大家支持一下
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签: