首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
MyBatis源码剖析之Mapper代理方式细节
2023-09-07 17:51:32基础资料围观581次
MyBatis是一个流行的Java持久层框架,它提供了多种方式来执行数据库操作,其中之一就是通过Mapper代理方式。通过Mapper代理方式,开发者可以编写接口,然后MyBatis会动态地生成接口的实现类,从而避免了繁琐的SQL映射配置。
具体代码如下:
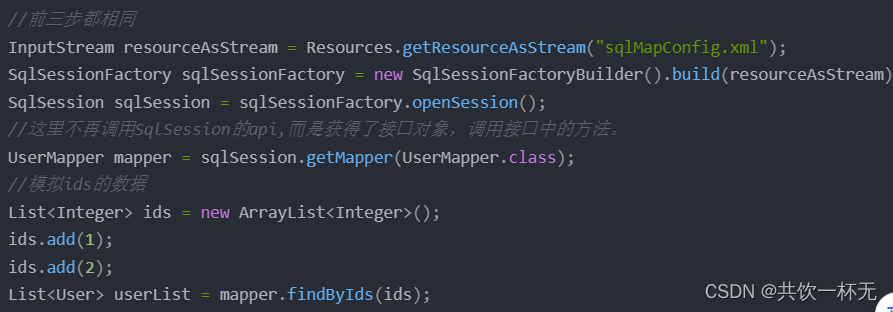
思考⼀个问题,通常的Mapper接⼝我们都没有实现的⽅法却可以使⽤,是为什么呢?
答案很简单:动态代理
public class Configuration {
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
}
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
}
开始之前介绍⼀下MyBatis初始化时对接⼝的处理:MapperRegistry是Configuration中的⼀个属性,它内部维护⼀个HashMap⽤于存放mapper接⼝的⼯⼚类,每个接⼝对应⼀个⼯⼚类。mappers中可以配置接⼝的包路径,或者某个具体的接⼝类。
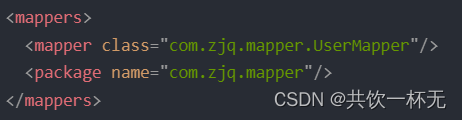
当解析mappers标签时,它会判断解析到的是mapper配置⽂件时,会再将对应配置⽂件中的增删改查标签 封装成MappedStatement对象,存⼊mappedStatements中。当判断解析到接⼝时,会建此接⼝对应的MapperProxyFactory对象,存⼊HashMap中,key =接⼝的字节码对象,value =此接⼝对应MapperProxyFactory对象。
源码剖析-getmapper()
进⼊ sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class )中
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
//调用configuration中的getMapper
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> type);
}
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
//调用configuration 中的getMapper
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
}
public class Configuration {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//调用MapperRegistry 中的getMapper
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
}
public class MapperRegistry {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//从 MapperRegistry 中的 HashMap 中拿 MapperProxyFactory
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//调用MapperProxyFactory的newInstance通过动态代理⼯⼚⽣成实例
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//创建了 JDK动态代理的Handler类
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
//调⽤了重载⽅法
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
}
//MapperProxy 类,实现了 InvocationHandler 接⼝
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
//省略部分源码
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
//构造,传⼊了 SqlSession,说明每个session中的代理对象的不同的!
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//省略部分源码
}
源码剖析-invoke()
在动态代理返回了示例后,我们就可以直接调⽤mapper类中的⽅法了,但代理对象调⽤⽅法,执⾏是在MapperProxy中的invoke⽅法中。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//如果是Object定义的⽅法,直接调⽤
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 获得 MapperMethod 对象
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//重点在这:最终调⽤了MapperMethod执⾏的⽅法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
进⼊execute⽅法:
public class MapperMethod {
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判断mapper中的⽅法类型,最终调⽤的还是SqlSession中的⽅法 switch(command.getType())
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
//转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//执⾏INSERT操作
//转换rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
//转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
//转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 转换 rowCount
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
//⽆返回,并且有ResultHandler⽅法参数,则将查询的结果,提交给 ResultHandler 进⾏处理
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
//执⾏查询,返回列表
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
//执⾏查询,返回Map
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
//执⾏查询,返回Cursor
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
//执⾏查询,返回单个对象
} else {
//转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//查询单条
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
//返回结果为null,并且返回类型为基本类型,则抛出BindingException异常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
//返回结果
return result;
}
}
总的来说,MyBatis的Mapper代理方式通过动态代理机制,将接口方法与SQL语句进行映射,使得开发者能够更加方便地进行数据库操作,同时避免了繁琐的SQL映射配置。这种方式使得代码更加清晰简洁,并且提供了良好的可扩展性和可维护性。
相关文章:
MyBatis插件原理探究和自定义插件实现
MyBatis源码剖析之Configuration、SqlSession、Executor、StatementHandler细节
本文内容到此结束了,
如有收获欢迎点赞👍收藏💖关注✔️,您的鼓励是我最大的动力。
如有错误❌疑问💬欢迎各位指出。
主页:共饮一杯无的博客汇总👨💻保持热爱,奔赴下一场山海。🏃🏃🏃
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:
上一篇:【C++精华铺】9.STL string
下一篇:Postman使用简介

