首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
Mybatis学习记录
2023-08-29 02:16:40基础资料围观728次
Mybatis学习笔记
今天开始复习一下mybatis的知识,虽然在学校的时候简单用过,但是随着工作中使用的是jpa就逐渐耽搁了。。。现在又要重新复习一下简单用法,顺便再浅浅地看一下源码。
mybatis其实是一种帮助我们转换java对象和数据库表的一种框架,所以我们直接通过一个例子来剖析mybatis是如何帮我们生成实际的sql语句并且返回结果的。
public void SessionTest() {
try (InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")) {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);;
user.setUserName(null);
user.setPassword("America");
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User byCondition = mapper.selectByCondition(user);
System.out.println(byCondition);
User byCondition2 = mapper.selectByCondition(user);
System.out.println(byCondition2);
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//UserMapper
public interface UserMapper {
User selectByCondition(User user);
}
mybatis的用法和一些标签就不在这里介绍了,因为我也不怎么了解(在工作中不怎么使用,在这里主要看一下mybatis的核心功能)。从上面的示例代码可以看出,mybatis的查询逻辑多半就是在我们生成的SqlSession对象中,有同学看到了第一行代码
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")
这里就是使用mybatis中的一个Resources对象读取我们的一些配置,配置也可以贴出来,这个配置是我从官网直接粘贴的,把配置改成自己的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
这些是最基本的配置标签,不过已经足够我们来使用mybatis的查询功能咯。
通过读取配置并且得到了SqlSession后,可以看到
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
这里是通过jdk动态代理生成的我们定义的UserMapper代理类,时序图在下面(画得不是很好)
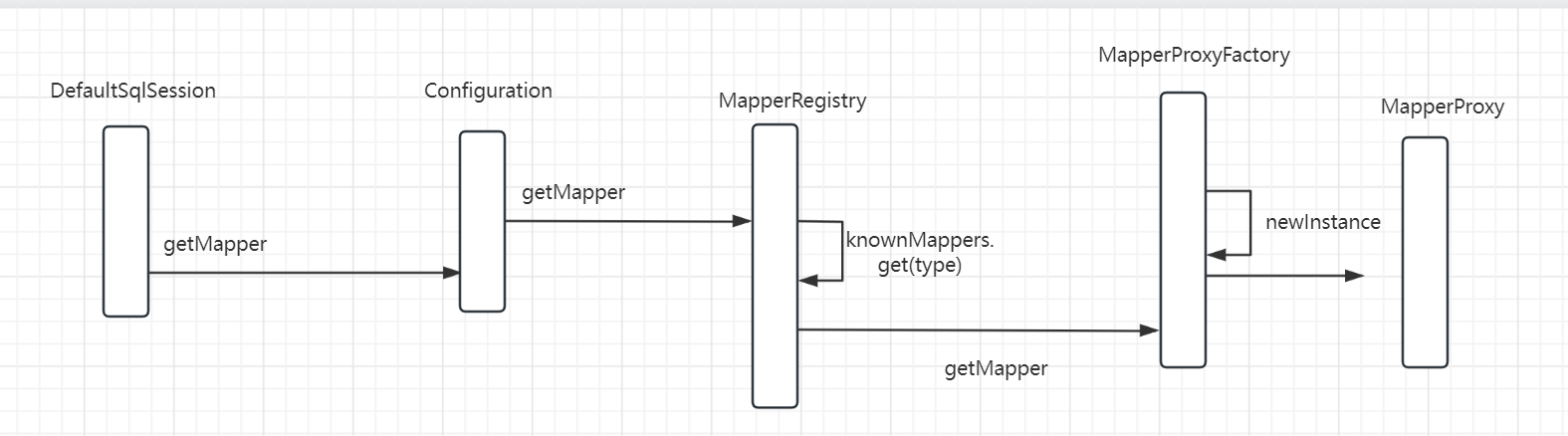
最底层获取到代理对象的一行代码如图所示
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
获取到代理对象之后,接着执行mapper中定义的方法就会执行sql语句了,这里要注意,UserMapper定义的方法始终是要对应到一个mapper文件里面真正想要执行的语句
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUser" resultType="org.example.entity.User">
select * from User where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="org.example.entity.User">
insert into user values(#{id}, #{userName}, #{password})
</insert>
<select id="selectByCondition" parameterType="org.example.entity.User" resultType="org.example.entity.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id!=0">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="userName!=null">
and userName = #{userName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
接下来就是查询方法的执行逻辑咯。
执行语句就是下面这一句
User byCondition = mapper.selectByCondition(user);
上面我们知道了mybatis使用jdk动态代理帮我们生成了一个代理对象,jdk动态代理执行方法实际上就是执行了参数中继承了InvocationHandler的对象的invoke方法,也就是MapperProxy的invoke方法,我们看一下MapperProxy的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
这里又调用了cacheInvoker方法构建了一个内部对象MapperMethodInvoker的invoke方法,该对象有两个实现列,我们选择其中一个看一下。
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
接着往下走,进入MapperMethod的execute方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
这里可以看到基本都是执行sqlSession的对应方法,而sqlSession相关的方法都是其内部的Executor来执行的。好像有点简单了,不过主要是为了给自己看哈哈哈哈,先记录这样吧。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:

