首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
SpringBoot集成 ElasticSearch
2023-08-24 17:48:48基础资料围观595次
Java资料网推荐SpringBoot集成 ElasticSearch这篇文章给大家,欢迎收藏Java资料网享受知识的乐趣
Spring Boot 集成 ElasticSearch
对于ElasticSearch比较陌生的小伙伴可以先看看ElasticSearch的概述ElasticSearch安装、启动、操作及概念简介
好的开始啦~
1、基础操作
1.1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
-
新版本配置方式(推荐使用)
新的配置方式使用的是 High Level REST Client 的方式来替代之前的 Transport Client 方式,使用的是 HTTP 请求,和 Kibana 一样使用的是 Elasticsearch 的 9200 端口。
1.2、自定义配置类
这种配置方案中,你使用的不是配置文件,而是自定义配置类:
/**
* 你也可以不继承 AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration 类,而将 ESConfig 写成一般的配置类的型式。
* 不过继承 AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration 好处在于,它已经帮我们配置好了 elasticsearchTemplate 直接使用。
*/
@Configuration
public class ESConfig extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Override
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration.builder()
.connectedTo("localhost:9200")
.build();
return RestClients.create(clientConfiguration).rest();
}
}
1.3、实体类
Elasticsearch 中的 PO 类:
@Document(indexName = "books",shards = 1,replicas = 0)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ESBook {
@Id
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String language;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String author;
@Field(type = FieldType.Float)
private Float price;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String description;
}
- @Document :注解会对实体中的所有属性建立索引;
- indexName = “books” :表示创建一个名称为 “books” 的索引;
- shards = 1 : 表示只使用一个分片;
- replicas = 0 : 表示不使用复制备份;
- @Field(type = FieldType.Keyword) : 用以指定字段的数据类型。
2、 创建操作的 Repository
@Repository
//看实体类Id索引是什么类型 我这里是String
public interface ESBookRepstitory extends ElasticsearchRepository<ESBook, String> {
}
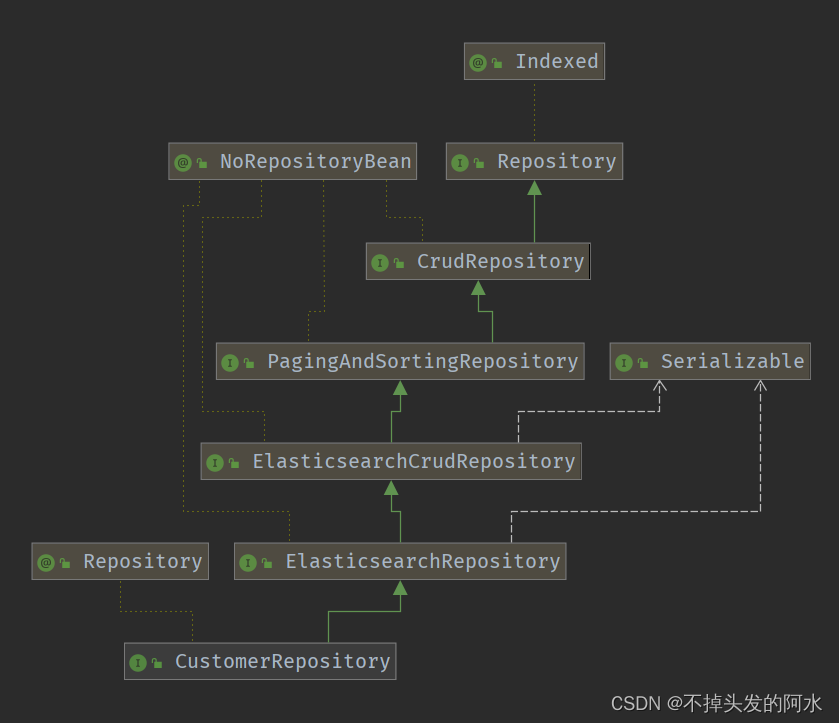
我们自定义的 CustomerRepository 接口,从它的祖先们那里继承了大量的现成的方法,除此之外,它还可以按 spring data 的规则定义特定的方法。
3、 测试 CustomerRepository
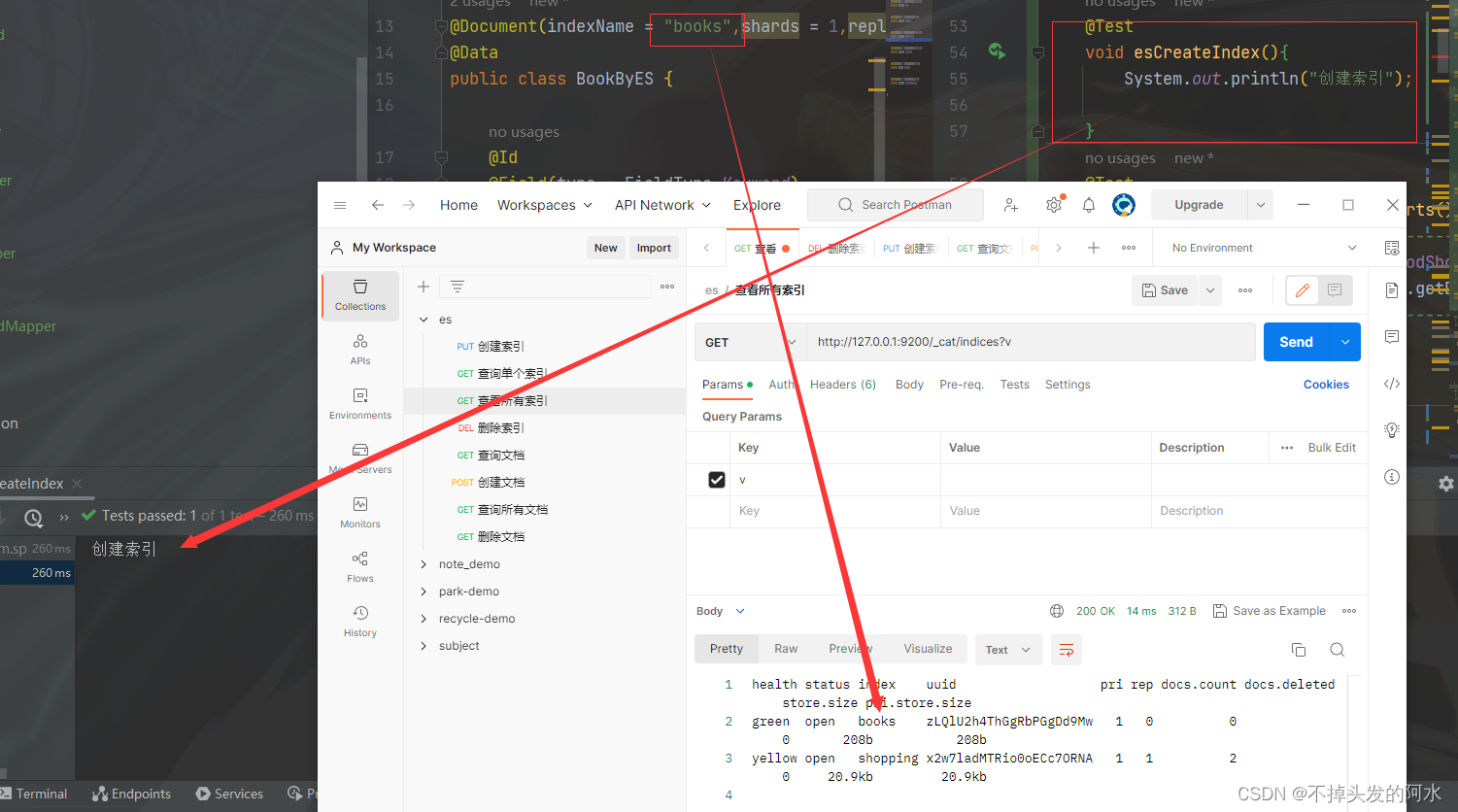
// 创建索引
@Test
public void indexList() {
System.out.println("创建索引");
}
// 删除索引
@Test
public void indexList() {
restTemplate.indexOps(IndexCoordinates.of("books")).delete();
System.out.println("删除索引");
}
4.、CRUD操作
4.1、批量新增
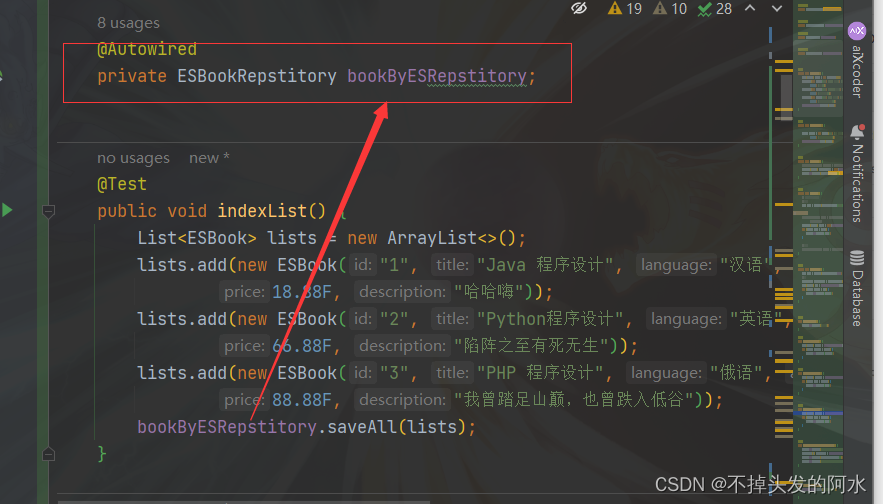
@Autowired
private ESBookRepstitory bookByESRepstitory;
@Test
public void indexList() {
List<ESBook> lists = new ArrayList<>();
lists.add(new ESBook("1", "Java 程序设计", "汉语", "盖伦",
18.88F, "哈哈嗨"));
lists.add(new ESBook("2", "Python程序设计", "英语", "赵信",
66.88F, "陷阵之至有死无生"));
lists.add(new ESBook("3", "PHP 程序设计", "俄语", "宝石",
88.88F, "我曾踏足山巅,也曾跌入低谷"));
bookByESRepstitory.saveAll(lists);
}
id重复的话 会覆盖之前的~~~
4.2、修改
修改和新增是同一个接口,区分的依据就是id,这一点跟我们在页面发起PUT请求是类似的。
ESBook ESBook = new ESBook("3", "宝石 程序设计", "俄语", "宝石",
88.88F, "我曾踏足山巅,也曾跌入低谷");
bookByESRepstitory.save(ESBook);
//由于上面的id = 3 已经存在,故再次save 就是修改
4.3、删除
@Test
public void test2(){
bookByESRepstitory.deleteById("1");
bookByESRepstitory.deleteAll();
}
4.4、基本查询
1、ElasticsearchRepository提供了一些基本的查询方法:
@Test
public void testQuery(){
Optional<BookByES> optionalById = this.bookByESRepstitory.findById("1");
System.out.println(optionalById.get());
}
@Test
public void testFind(){
// 查询全部,并按照价格降序排序
//写法一:
Iterable<BookByES> items = this.bookByESRepstitory.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC,
"price"));
//写法二:
Iterable<BookByES> items1 = this.bookByESRepstitory.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Order.desc("price")));
}
2、分页查询
Spring Data 自带的分页方案:
@Test
public void testByPage(){
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
//分页
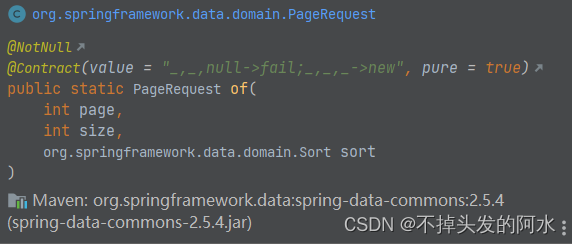
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(0, 2, sort);
Page<BookByES> all = bookByESRepstitory.findAll(pageRequest);
for (BookByES bookByES : all) {
System.out.println(bookByES);
}
}
4.5、自定义方法查询
Spring Data 的另一个强大功能,是根据方法名称自动实现功能。
比如:你的方法名叫做:findByTitle,那么它就知道你是根据title查询,然后自动帮你完成,无需写实现类。
当然,方法名称要符合一定的约定
| Keyword | Sample | Elasticsearch Query String |
|---|---|---|
And | findByNameAndPrice | {"bool" : {"must" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"price" : "?"}} ]}} |
Or | findByNameOrPrice | {"bool" : {"should" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"price" : "?"}} ]}} |
Is | findByName | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}} |
Not | findByNameNot | {"bool" : {"must_not" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}} |
Between | findByPriceBetween | {"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
LessThanEqual | findByPriceLessThan | {"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : null,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
GreaterThanEqual | findByPriceGreaterThan | {"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : null,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
Before | findByPriceBefore | {"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : null,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
After | findByPriceAfter | {"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : null,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
Like | findByNameLike | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "?*","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
StartingWith | findByNameStartingWith | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "?*","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
EndingWith | findByNameEndingWith | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "*?","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
Contains/Containing | findByNameContaining | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "**?**","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
In | findByNameIn(Collection<String>names) | {"bool" : {"must" : {"bool" : {"should" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"name" : "?"}} ]}}}} |
NotIn | findByNameNotIn(Collection<String>names) | {"bool" : {"must_not" : {"bool" : {"should" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}}}} |
Near | findByStoreNear | Not Supported Yet ! |
True | findByAvailableTrue | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : true}}}} |
False | findByAvailableFalse | {"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : false}}}} |
OrderBy | findByAvailableTrueOrderByNameDesc | {"sort" : [{ "name" : {"order" : "desc"} }],"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : true}}}} |
如:
import com.springsecurity.domain.ESBook;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 阿水
* @create 2023-04-13 11:05
*/
@Repository
//看实体类Id索引是什么类型 我这里是String
public interface ESBookRepstitory extends ElasticsearchRepository<ESBook, String> {
/**
* 根据描述查询书籍,带分页的
* @param description
* @return
*/
List<ESBook> findESBookByDescription(String description, Pageable variable);
/**
* 根据作者和描述和标题查
*/
List<ESBook> queryESBookByAuthorAndDescriptionOrTitle(String author,String description,String title);
/**
* 根据书的价格范围查询
*/
List<ESBook> queryESBookByPriceBetween(Float price1,Float price2);
}
@Test
void esQueryCondition() {
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Order.desc("id"));
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(0, 2, sort);
List<ESBook> EBooks = bookByESRepstitory.findESBookByDescription("我",pageRequest);
for (ESBook bookByE : EBooks) {
System.out.println(bookByE);
}
}
@Test
void esQueryCondition2() {
List<ESBook> esBooks = bookByESRepstitory.queryESBookByAuthorAndDescriptionOrTitle("盖伦", "哈嗨", "程序");
for (ESBook book : esBooks) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
@Test
void esQueryCondition3() {
List<ESBook> esBooks = bookByESRepstitory.queryESBookByPriceBetween(18.88F,77.88F);
for (ESBook book : esBooks) {
System.out.println(book);
}
}
4.6、使用NativeSearchQuery
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate restTemplate;
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery() #指定字符串作为关键词查询,关键词支持分词
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("华为手机").defaultField("description");
//不指定feild,查询范围为所有feild
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("华为手机");
//指定多个feild
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("华为手机").field("title").field("description");
QueryBuilders.boolQuery #子方法must可多条件联查
QueryBuilders.termQuery #精确查询指定字段不支持分词
QueryBuilders.termQuery("description", "华为手机")
QueryBuilders.matchQuery #按分词器进行模糊查询支持分词
QueryBuilders.matchQuery("description", "华为手机")
QueryBuilders.rangeQuery #按指定字段进行区间范围查询
- `QueryBuilders.boolQuery()`
- `QueryBuilders.boolQuery().must()`:相当于 and
- `QueryBuilders.boolQuery().should()`:相当于 or
- `QueryBuilders.boolQuery().mustNot()`:相当于 not
- ——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
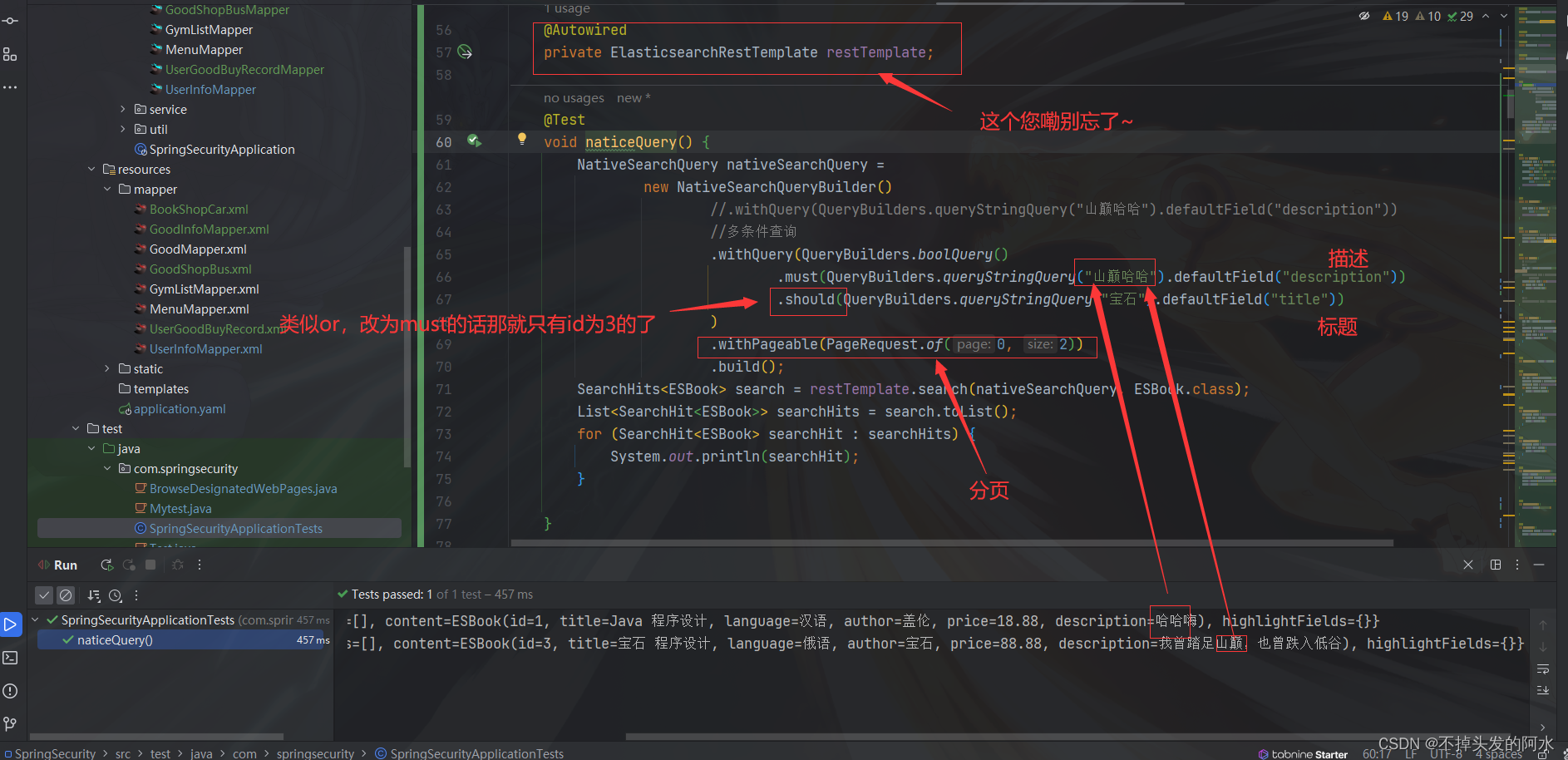
@Test
void naticeQuery() {
NativeSearchQuery nativeSearchQuery =
new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
//.withQuery(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("山巅哈哈").defaultField("description"))
//多条件查询
.withQuery(QueryBuilders.boolQuery()
.must(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("山巅哈哈").defaultField("description"))
.should(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("宝石").defaultField("title"))
)
.withPageable(PageRequest.of(0, 2))
.build();
SearchHits<ESBook> search = restTemplate.search(nativeSearchQuery, ESBook.class);
List<SearchHit<ESBook>> searchHits = search.toList();
for (SearchHit<ESBook> searchHit : searchHits) {
System.out.println(searchHit);
}
}
举个例子:
5、es场景
场景一:对外暴露的数据(数据量大的)的用es,如果不需要对外暴露,不需要全文检索的话,那么直接从数据查,所以做项目分析数据分成2块(哪些数据需要放es,从es查,哪些不需要)
场景二:作为mysql的外置索引,把作为数据库查询条件的列数据放到es里面,这样在查询的时候,先从es查询出符合条件的id,然后根据id去数据库查,数据维护大,一旦es宕机,就麻烦了
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lps12345666/article/details/130134109
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:

