首页 > 基础资料 博客日记
2022-07-21 吉林化工学院 韩嘉宁 第五组 学习笔记(Java面向对象特性 二 —— 继承性)
2023-07-29 18:04:13基础资料围观677次
Java资料网推荐2022-07-21 吉林化工学院 韩嘉宁 第五组 学习笔记(Java面向对象特性 二 —— 继承性)这篇文章给大家,欢迎收藏Java资料网享受知识的乐趣
Java面向对象特性(二) ——— 继承性
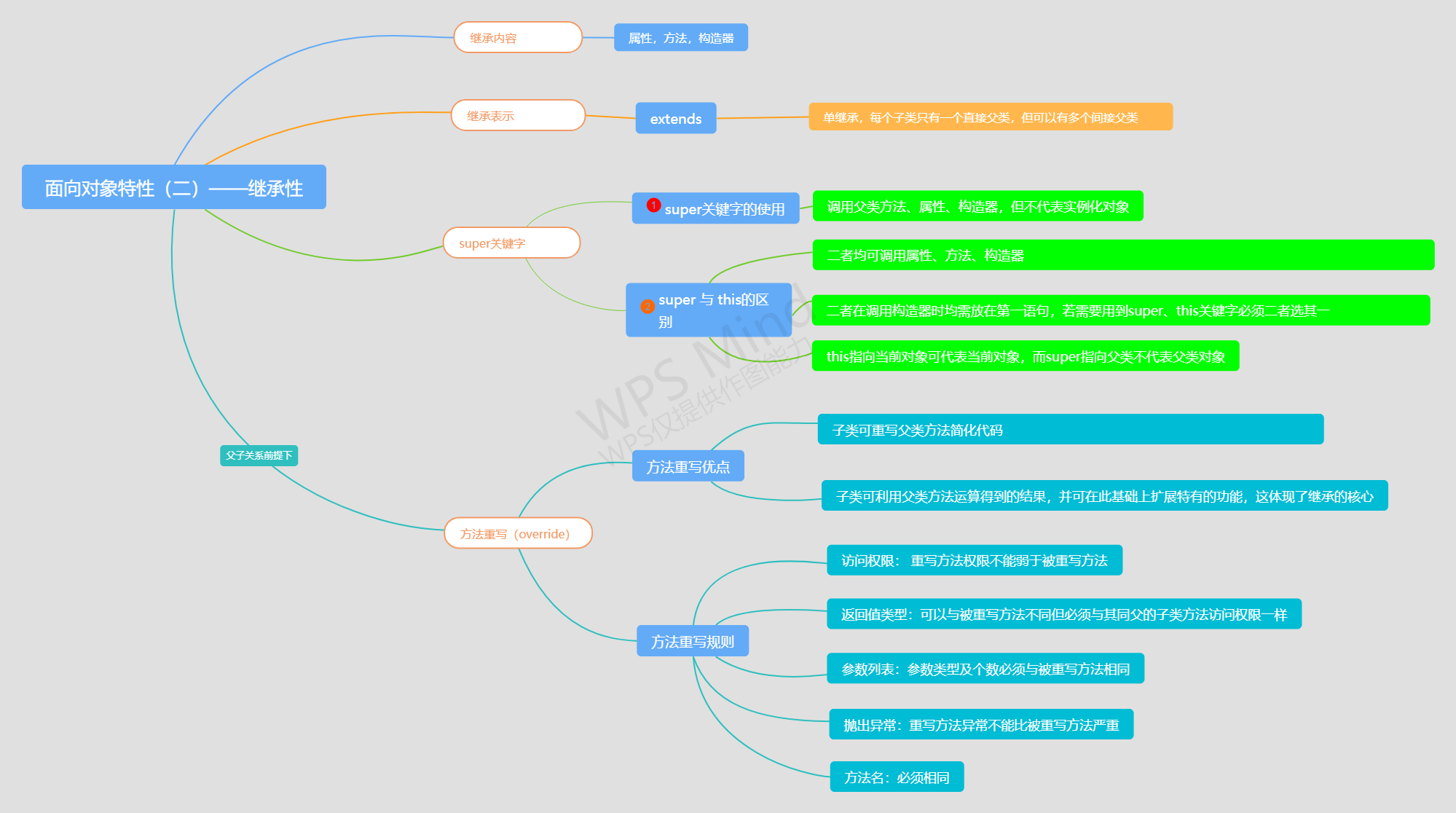
继承性表示形式:(extends关键字)
- 继承表示:类A extends 类B,即类A为B的子类
- 若 类C extends 类A ,即类C为A的直接子类,为类B的间接子类
- 写在关键字 extends 后面的类为 父类(直接父类、间接父类)
- 在Java中,继承是单继承的,一个子类只有一个直接父类,但可以有多个间接父类
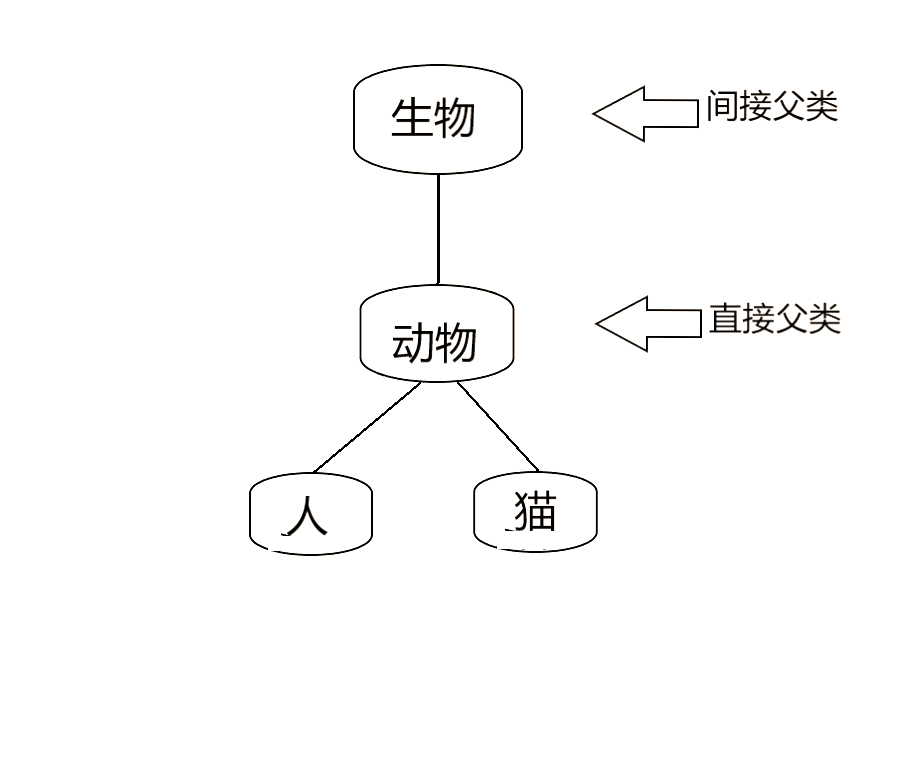
当一个类被实例化,则先实例化其直接父类、间接父类。
调用子类构造器,父类构造器先执行
Super关键字
代表调用父类结构(属性、方法、构造器)
//调用父类属性 super.age=20; //调用父类方法 super.breath(); //调用当前类属性 this.name="han";
super 与 this 的区别:
-
当使用 super 调用父类构造器时,必须位于第一语句
-
在构造器中,如果需要使用super 或 this 调用其他构造器时只能二选一,并必须位于第一位
-
super 指向父类,不代表父类对象
this 指向本类,可以代表当前类对象
方法重写(override)(前提必须是父子关系)
- 子类可以重写父类的方法
- 可以利用父类中方法运算过后的结果,并在此基础上扩展加上自己的方法(只属于自己的),以扩展父类功能(体现了继承核心)
方法重写规则:
- 访问权限:不能弱于被重写方法的访问权限
- 返回值类型 重写方法返回值类型可以与被重写方法返回值类型不同,但必须与被重写方法子类返回值类型相同
- 方法名 必须相同
- 参数列表 必须相同(参数类型、参数个数必须相同)
- 抛出异常 重写方法不能抛出比被重写方法更大的异常
- this代表对象,可对属性进行链式处理,如:person.setAge(20).setName("wow")
案例:银行系统
Card
package com.study.morning.Test;
/*
提示作用
银行卡
*/
public class Card {
private String cardId;
private String password;
private Double banlance;
private Card[] cards=new Card[2];
public Card(){}
public Card(String cardId,String adPassword,Double banlance){
this.cardId=cardId;
this.password=adPassword;
this.banlance=banlance;
}
public void setCarId(String carId) {
this.cardId = carId;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setBanlance(Double banlance) {
this.banlance = banlance;
}
public String getCarId() {
return cardId;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public Double getBanlance() {
return banlance;
}
//登录账户
// public String loginAccount(String cardId,String password){
//
// }
//存款
public Double moneyIn(Double moneyin){
banlance +=moneyin;
System.out.println("存款成功! 余额为:" +banlance);
return banlance;
}
//取款
public Double moneyOut(Double moneyout){
if(banlance>0 &&moneyout<=banlance){
banlance -=moneyout;
System.out.println("取钱成功!! 余额为:" +banlance);
}else{
System.out.println("您的余额不足!! 取钱失败!!");
}
return banlance;
}
}
DebitCard
package com.study.morning.Test;
/**
* 借记卡取款除了考虑余额是否足够
* 转账额度问题:
* 判断:if(getBalance() >= money &&transferAmount >=money)
* 若余额足够,直接调用用父类方法
*/
public class DebitCard extends Card{
private Double banlance;
private Double transferAmount;//转账额度
public DebitCard(){}
public DebitCard(String cardId1,String password1,Double banlance1,Double transferAmount){
super(cardId1,password1,banlance1);
this.transferAmount=transferAmount;
}
//存款
public void in(Double money){
super.moneyIn(money);
}
// public void setBanlance(Double banlance) {
// this.banlance = banlance;
// }
public void setTransferAmount(Double transferAmount) {
this.transferAmount = transferAmount;
}
//取款
public Double out(Double money){
//借记卡在取款时不光要判断余额还要判断转账额度
if(getBanlance()>=money && transferAmount>=money){
super.moneyOut(money);//取出
return Double.valueOf(banlance);
}else if(getBanlance()<money){
return Double.valueOf(-1);
}else if(transferAmount <money){
System.out.println("已超出额度,请到前台进行办理!");
return Double.valueOf(-2);
}else{
return Double.valueOf(-3);
}
}
}
CreditCard
package com.study.morning.Test;
public class CreditCard extends Card{
private Double credits;
private Double temp;
public Double getCredits() {
return credits;
}
public void setCredits(Double credits) {
this.credits = credits;
}
public CreditCard(){
}
public CreditCard(String cardId,String password,Double banlance,Double credits){
super(cardId,password,banlance);
this.credits=credits;
this.temp=credits;
}
//存钱
private Double b=0.0;
Double i=getBanlance();
public void in(Double moneyIn) {
if (credits == temp) {
i += moneyIn;
System.out.println("余额:" +i +"信用额度" + credits);
} else if (credits < temp) {
i += (temp - credits);
credits=temp;
System.out.println("余额:" +i +"信用额度" + credits);
}
}
//取钱
public void out (Double moneyout){
b = moneyout - getBanlance();
if (b <= 0) {
i -= moneyout;
System.out.println("您的余额为:" +i +"信用额度:" +credits);
} else {
i = Double.valueOf(0);
credits -= Double.valueOf(b);
System.out.println("余额:" + i +"信用额度:" +credits);
}
}
}
感悟:今日的知识点不多但需要深入理解,必要的时候必须实现在代码上。尤其是在方法重写知识点上,如果只是了解不实践就不会了解它重写实现功能的流程。(这是本人总结出的教训!!望后人忌之!)
文章来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/WorkerHevien/p/16506305.html
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系邮箱:jacktools123@163.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
标签:
上一篇:SMBMS超市管理系统(Javaweb项目)
下一篇:java开发工具推荐

